|
Anovulation
Anovulation is when the ovaries do not release an oocyte during a menstrual cycle. Therefore, ovulation does not take place. However, a woman who does not ovulate at each menstrual cycle is not necessarily going through menopause. Chronic anovulation is a common cause of infertility. In addition to the alteration of menstrual periods and infertility, chronic anovulation can cause or exacerbate other long-term problems, such as hyperandrogenism or osteopenia. It plays a central role in the multiple imbalances and dysfunctions of polycystic ovary syndrome. During the first two years after menarche 50% of the menstrual cycles could be anovulatory cycles. It is in fact possible to restore ovulation using appropriate medication, and ovulation is successfully restored in approximately 90% of cases. The first step is the diagnosis of anovulation. The identification of anovulation is not easy; contrary to what is commonly believed, women undergoing anovulation still have (more or less) r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name originated from the observation of cysts which form on the ovaries of some women with this condition. However, this is not a universal symptom and is not the underlying cause of the disorder. The primary characteristics of PCOS include hyperandrogenism, anovulation, insulin resistance, and neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine disruption. Women may also experience Abnormal uterine bleeding, irregular menstrual periods, Menorrhagia, heavy periods, hirsutism, excess hair, acne, pelvic pain, infertility, difficulty getting pregnant, and patches of acanthosis nigricans, darker skin. Beyond its reproductive implications, PCOS is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial metabolic condition with significant long-term health consequences, including an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name originated from the observation of cysts which form on the ovaries of some women with this condition. However, this is not a universal symptom and is not the underlying cause of the disorder. The primary characteristics of PCOS include hyperandrogenism, anovulation, insulin resistance, and neuroendocrine disruption. Women may also experience irregular menstrual periods, heavy periods, excess hair, acne, pelvic pain, difficulty getting pregnant, and patches of darker skin. Beyond its reproductive implications, PCOS is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial metabolic condition with significant long-term health consequences, including an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. A review of international evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to Sexual reproduction, reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of fertility, reproductive capacity, are excluded. It is also a normal state in women after menopause. In humans, ''infertility'' is defined as the inability to become pregnant after at least one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner. There are many causes of infertility, including some that Assisted reproductive technology, medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year, with estimates ranging from 12% to 28%. Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days. Menarche (the onset of the first period) usually occurs around the age of 12 years; menstrual cycles continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligoovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase. Ovulation is stimulated by an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. If it is not, it will break down in less than a day. Meanwhile, the uterine lining (endometrium) continues to thicken to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation. Some people choose to track ovulation in order to improve or aid becoming pregnant by timing intercourse with their ovulation. The signs of ovulation may include cervical mucus changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase. Ovulation is stimulated by an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. If it is not, it will break down in less than a day. Meanwhile, the uterine lining ( endometrium) continues to thicken to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation. Some people choose to track ovulation in order to improve or aid becoming pregnant by timing intercourse with their ovulation. The signs of ovulation may include cervical muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hormones. Menstruation is triggered by falling progesterone levels, and is a sign that pregnancy has not occurred. Women use feminine hygiene products to maintain hygiene during menses. The first period, a point in time known as menarche, usually begins during puberty, between the ages of 11 and 13. However, menstruation starting as young as 8 years would still be considered normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world, and earlier in the developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women; in adults, the range is between 21 and 35 days with the average often cited as 28 days. In the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a tachycardia, fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, goitre, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a hyperthermia, high temperature; this often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
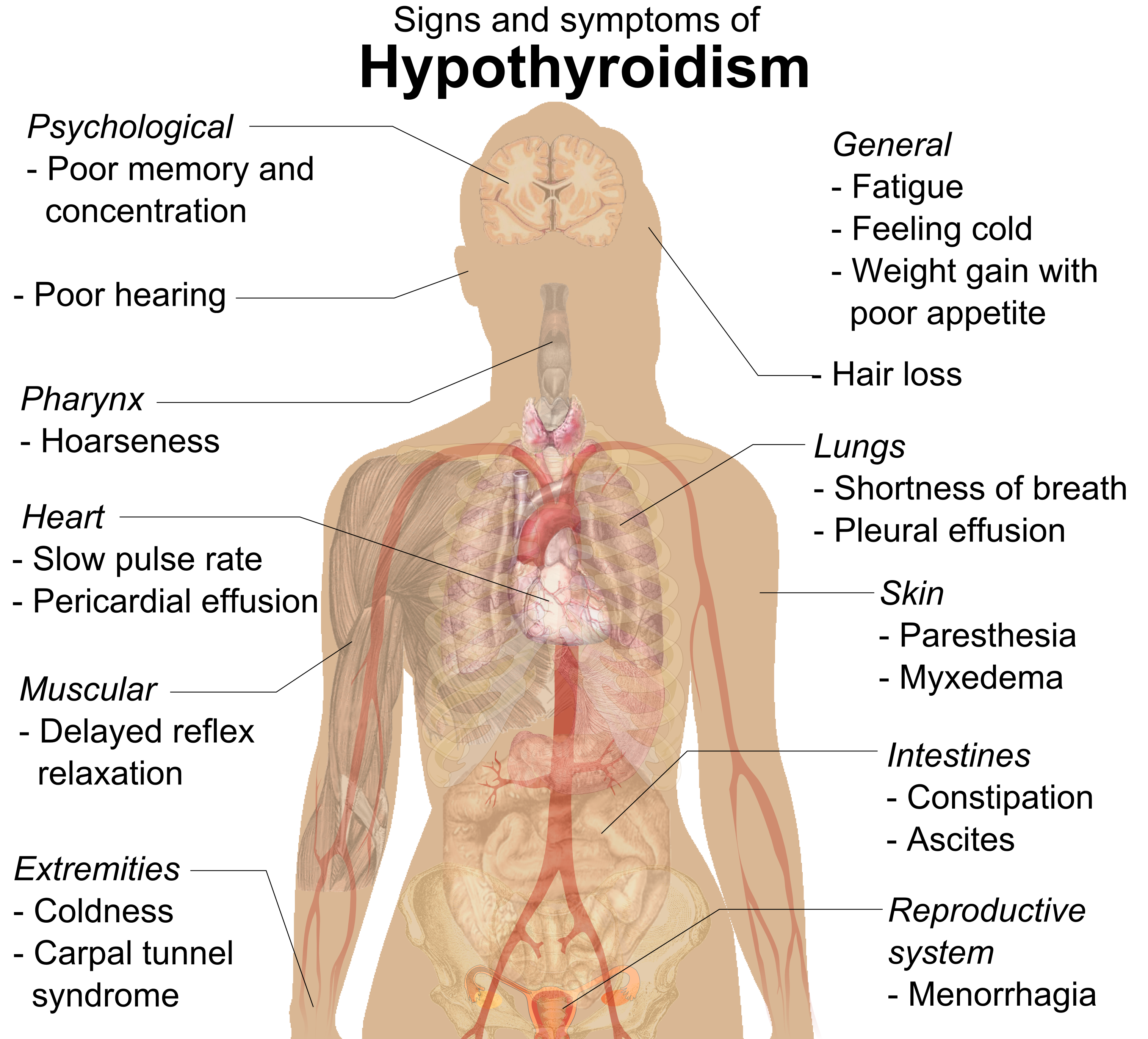
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), is due to problems with either the hypothalamus or pituitary gland affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (HPG axis). Hypothalamic disorders result from a deficiency in the release of gonadotropic releasing hormone ( GnRH), while pituitary gland disorders are due to a deficiency in the release of gonadotropins from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is the central regulator in reproductive function and sexual development via the HPG axis. GnRH is released by GnRH neurons, which are hypothalamic neuroendocrine cells, into the hypophyseal portal system acting on gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary. The release of gonadotropins, LH and FSH, act on the gonads for the development and maintenance of proper adult reproductive physiology. LH acts on Leydig cells in the male testes and theca cells in the female. FSH acts on Sertoli cells in the male and follicular cells in the female. Combined this causes the secretion of gonadal sex st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences) is the area of medicine concerned with conditions affecting the Female reproductive system, female reproductive system. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy and childbirth, thereby forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN). Gynaecology encompasses both Primary care, primary and Preventive healthcare, preventative care of issues related to female reproduction and sexual health, such as the uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and breasts; subspecialties include family planning; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric and adolescent gynecology; and pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. While gynaecology has traditionally centered on Cisgender, cisgender women, it increasingly encompasses anyone with female organs, including transgender, intersex, and Non-binary gender, nonbinary individuals; however, many non-cis women face acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |