|
Ancient Greek Phonology
Ancient Greek phonology is the reconstructed phonology or pronunciation of Ancient Greek. This article mostly deals with the pronunciation of the standard Attic dialect of the fifth century BC, used by Plato and other Classical Greek writers, and touches on other dialects spoken at the same time or earlier. The pronunciation of Ancient Greek is not known from direct observation, but determined from other types of evidence. Some details regarding the pronunciation of Attic Greek and other Ancient Greek dialects are unknown, but it is generally agreed that Attic Greek had certain features not present in English or Modern Greek, such as a three-way distinction between voiced, voiceless, and aspirated stops (such as , as in English "bot, spot, pot"); a distinction between single and double consonants and short and long vowels in most positions in a word; and a word accent that involved pitch. Koine Greek, the variety of Greek used after the conquests of Alexander the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accent (phonetics)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or Sentence (linguistics), sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in Tone (linguistics), tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''Pitch-accent language, pitch accent'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; English uses what is called ''variable stress accent''. Since stress can be realised through a wide range of Phonetics, phonetic properties, such as loudness, vowel length, and pitch (which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and was written in dactylic hexameter. It contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of Western literature, European literature and is a central part of the Epic Cycle. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the war's final weeks. In particular, it traces the anger () of Achilles, a celebrated warrior, from a fierce quarrel between him and King Agamemnon, to the death of the Trojan prince Hector.Homer, ''Iliad, Volume I, Books 1–12'', translated by A. T. Murray, revised by William F. Wyatt, Loeb Classical Library 170, Cambridge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Greek
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Central Ionic), and from BC onward in Asiatic Ionia (East Ionic), where Ionian colonists from Athens founded their cities. Ionic was the base of several literary language forms of the Archaic and Classical periods, both in poetry and prose. The works of Homer and Hesiod are among the most popular poetic works that were written in a literary form of the Ionic dialect, known as Epic or Homeric Greek. The oldest Greek prose, including that of Heraclitus, Herodotus, Democritus, and Hippocrates, was also written in Ionic. By the end of the 5th century BC, Ionic was supplanted by Attic, which had become the dominant dialect of the Greek world. History The Ionic dialect appears to have originally spread from the Greek mainland across the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete is located about south of the Peloponnese, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete covers 260 km from west to east but is narrow from north to south, spanning three longitudes but only half a latitude. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete (), which is the southernmost of the 13 Modern regions of Greece, top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
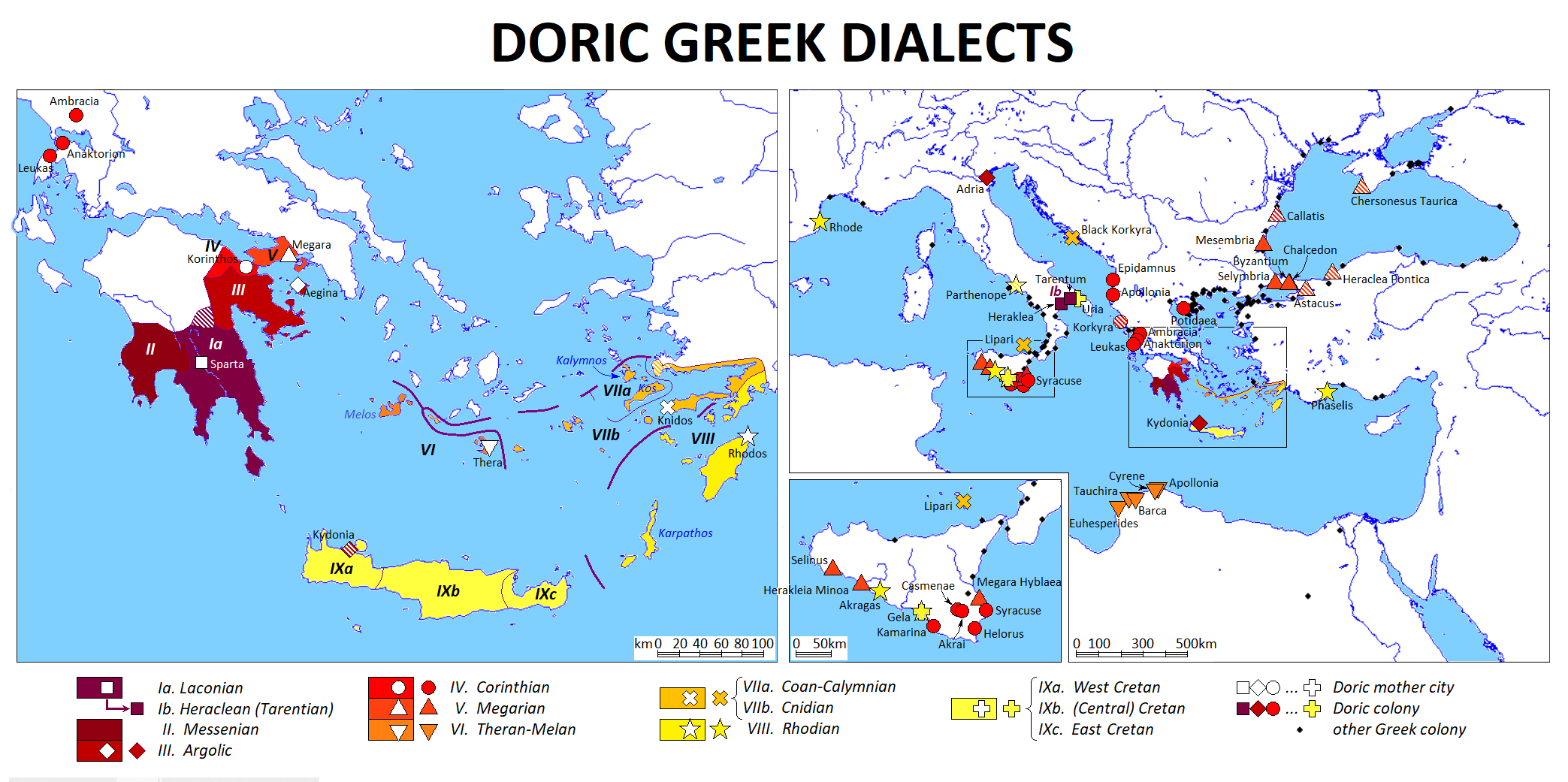
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Greek Language
The Proto-Greek language (also known as Proto-Hellenic) is the Indo-European language which was the last common ancestor of all varieties of Greek, including Mycenaean Greek, the subsequent ancient Greek dialects (i.e., Attic, Ionic, Aeolic, Doric, Arcadocypriot, and ancient Macedonian—either a dialect or a closely related Hellenic language) and, ultimately, Koine, Byzantine and Modern Greek (along with its variants). Proto-Greek speakers entered Greece sometime between 2200 and 1900BC, with the diversification into a southern and a northern group beginning by approximately 1700BC. Origins Proto-Greek emerged from the diversification of the late Proto-Indo-European language (PIE); a process whose last phase gave rise to the later language families and occurred .. Pre-Proto-Greek, the Indo-European dialect from which Proto-Greek originated, emerged , in an area which bordered pre- Proto-Indo-Iranian to the east and pre- Proto-Armenian and pre-Proto- Phrygian to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Dialects
Ancient Greek in classical antiquity, before the development of the common Koine Greek of the Hellenistic period, was divided into several varieties. Most of these varieties are known only from inscriptions, but a few of them, principally Aeolic, Doric, and Ionic, are also represented in the literary canon alongside the dominant Attic form of literary Greek. Likewise, Modern Greek is divided into several dialects, most derived from Koine Greek. Provenance * The earliest known Greek dialect is Mycenaean Greek, the South/Eastern Greek variety attested from the Linear B tablets produced by the Mycenaean civilization of the Late Bronze Age in the late 2nd millennium BC. The classical distribution of dialects was brought about by the migrations of the early Iron Age after the collapse of the Mycenaean civilization. Some speakers of Mycenaean were displaced to Cyprus while others remained inland in Arcadia, giving rise to the Arcadocypriot dialect. This is the only dialect wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluricentric Language
A pluricentric language or polycentric language is a language with several codified standard forms, often corresponding to different countries. Many examples of such languages can be found worldwide among the most-spoken languages, including but not limited to Chinese in the People's Republic of China, Taiwan and Singapore; English in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, South Africa, India, Singapore, and elsewhere; and French in France, Canada, and elsewhere. The converse case is a monocentric language, which has only one formally standardized version. Examples include Japanese and Russian. In some cases, the different standards of a pluricentric language may be elaborated to appear as separate languages, e.g. Malaysian and Indonesian, Hindi and Urdu, while Serbo-Croatian is in an earlier stage of that process. Examples of varying degrees of pluricentrism Arabic Pre-Islamic Arabic can be considered a polycentric language. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Recent Developments
More may refer to: Computing * MORE (application), outline software for Mac OS * more (command), a shell command * MORE protocol, a routing protocol * Missouri Research and Education Network Music Albums * ''More!'' (album), by Booka Shade, 2010 * ''More'' (soundtrack), by Pink Floyd with music from the 1969 film * ''More...'' (Trace Adkins album), or the title song, 1999 * ''More'' (Mary Alessi album), 2005 * ''More'' (Beyoncé EP), 2014 * ''More'' (Michael Bublé EP), 2005 * ''More'' (Clarke-Boland Big Band album), 1968 * ''More'' (Double Dagger album), 2009 * ''More...'' (Montell Jordan album), 1996 * ''More'' (Crystal Lewis album), 2001 * ''More'' (Giuseppi Logan album), 1966 * ''More'' (No Mercy album), 1998 * ''More'' (No Trend album), 2001 * ''More'' (Jeremy Riddle album), or the title song, 2017 * ''More'' (Pulp album), 2025 * ''More'' (Symphony Number One album), 2016 * ''More'' (Tamia album), or the title song, 2004 * ''More'' (Vitamin C album), 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koine Greek Phonology
The Greek language underwent pronunciation changes during the Koine Greek period, from about 300 BC to 400 AD. At the beginning of the period, the pronunciation was close to Classical Greek, while at the end it was almost identical to Modern Greek. Vowel length distinctions are important for classical poetry and drama, but become less important for prose into the patristic age. Overview The most significant changes during the Koine Greek period concerned vowels: these were the loss of vowel length distinction, the shift of the Ancient Greek system of pitch accent to a stress accent system, and the monophthongization of diphthongs (except and ). These changes seem widely attested from the 2nd century BC in Egyptian Greek, and in the early 2nd century AD in learned Attic inscriptions; it is therefore likely that they were already common in the 2nd century BC and generalized no later than the 2nd century AD. Another change was the frication of the second element of diphthongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |