|
Anarchy
Anarchy is a form of society without rulers. As a type of stateless society, it is commonly contrasted with states, which are centralized polities that claim a monopoly on violence over a permanent territory. Beyond a lack of government, it can more precisely refer to societies that lack any form of authority or hierarchy. While viewed positively by anarchists, the primary advocates of anarchy, it is viewed negatively by advocates of statism, who see it in terms of social disorder. The word "anarchy" was first defined by Ancient Greek philosophy, which understood it to be a corrupted form of direct democracy, where a majority of people exclusively pursue their own interests. This use of the word made its way into Latin during the Middle Ages, before the concepts of anarchy and democracy were disconnected from each other in the wake of the Atlantic Revolutions. During the Age of Enlightenment, philosophers began to look at anarchy in terms of the "state of nature", a thought ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with stateless societies and voluntary free associations. A historically left-wing movement, anarchism is usually described as the libertarian wing of the socialist movement (libertarian socialism). Although traces of anarchist ideas are found all throughout history, modern anarchism emerged from the Enlightenment. During the latter half of the 19th and the first decades of the 20th century, the anarchist movement flourished in most parts of the world and had a significant role in workers' struggles for emancipation. Various anarchist schools of thought formed during this period. Anarchists have taken part in several revolutions, most notably in the Paris Commune, the Russian Civil War and the Spanish Civil War, whose end marked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Nature
In ethics, political philosophy, social contract theory, religion, and international law, the term state of nature describes the hypothetical way of life that existed before humans organised themselves into societies or civilisations. Philosophers of the state of nature theory propose that there was a historical period before societies existed, and seek answers to the questions: "What was life like before civil society?", "How did government emerge from such a primitive start?", and "What are the hypothetical reasons for entering a state of society by establishing a nation-state?". In some versions of social contract theory, there are freedoms, but no rights in the state of nature; and, by way of the social contract, people create societal rights and obligations. In other versions of social contract theory, society imposes restrictions (law, custom, tradition, etc.) that limit the natural rights of a person. Societies existing before the political state are investigated and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a politics, political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. A country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. A state may be a unitary state or some type of federation, federal union; in the latter type, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated state, federated polities that make up the federation, and they may have some of the attributes of a sovereign state, except being under their federation and without the same capacity to act internationally. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include "province", "Region#Administrative regions, region" or other terms.) For most of prehistory, people lived in stateless societies. The earliest forms of states arose about 5,500 years ago. Over time societies became more Social stratification, stratified and developed institutions leading to Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federalism
Federalism is a mode of government that combines a general level of government (a central or federal government) with a regional level of sub-unit governments (e.g., provinces, State (sub-national), states, Canton (administrative division), cantons, territorial, territories, etc.), while dividing the powers of governing between the two levels of governments. Two illustrative examples of federated countries—one of the world's oldest federations, and one recently organized—are Australia #Government and politics, Australia and Federated States of Micronesia, Micronesia. Johannes Althusius (1563–1638), is considered the father of modern federalism, along with Montesquieu. In 1603, Althusius first described the bases of this political philosophy in his ''Politica Methodice Digesta, Atque Exemplis Sacris et Profanis Illustrata''. By 1748, in his treatise ''The Spirit of Law'', Montesquieu (1689-1755) observed various examples of federalist governments: in corporate societies, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered to be one of the founders of modern political philosophy. In his early life, overshadowed by his father's departure following a fight, he was taken under the care of his wealthy uncle. Hobbes's academic journey began in Malmesbury#Westport St Mary, Westport, leading him to the University of Oxford, where he was exposed to classical literature and mathematics. He then graduated from the University of Cambridge in 1608. He became a tutor to the Cavendish family, which connected him to intellectual circles and initiated his extensive travels across Europe. These experiences, including meetings with figures like Galileo, shaped his intellectual development. After returning to England from France in 1637, Hobbes witnessed the destruction and br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statism
In political science, statism or etatism (from French, ''état'' 'state') is the doctrine that the political authority of the state is legitimate to some degree. This may include economic and social policy, especially in regard to taxation and the means of production. While in use since the 1850s, the term ''statism'' gained significant usage in American political discourse throughout the 1930s and 1940s. Opposition to statism is termed anti-statism or anarchism. The latter is usually characterized by a complete rejection of all hierarchical rulership. Overview Statism can take many forms, from small government to big government. Minarchism is a political philosophy that prefers a minimal state such as a night-watchman state to protect people from aggression, theft, breach of contract and fraud with the military, police and courts. This may also include fire departments, prisons and other functions. The welfare state is another form within the spectrum o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errico Malatesta
Errico Malatesta (4 December 1853 – 22 July 1932) was an Italian anarchist propagandist, theorist and revolutionary socialist. He edited several radical newspapers and spent much of his life exiled and imprisoned, having been jailed and expelled from Italy, Britain, France, and Switzerland. Originally a supporter of insurrectionary propaganda by deed, Malatesta later advocated for syndicalism. His exiles included five years in Europe and 12 years in Argentina. Malatesta participated in actions including an 1895 Spanish revolt and a Belgian general strike. He toured the United States, giving lectures and founding the influential anarchist journal ''La Questione Sociale''. After World War I, he returned to Italy where his ''Umanità Nova'' had some popularity before its closure under the rise of Mussolini. Biography Early years Errico Malatesta was born on 4 December 1853 to a family of middle-class landowners in Santa Maria Maggiore, at the time part of the city of Capua (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people. In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought'' Third Edition, Allan Bullock and Stephen Trombley, Eds. p. 115. each of which has authority and is an authority. The term "authority" has multiple nuances and distinctions within various academic fields ranging from sociology to political science. In the exercise of governance, the terms ''authority'' and ''power'' are inaccurate synonyms. The term ''authority'' identifies the political legitimacy, which grants and justifies rulers' right to exercise the power of government; and the term ''power'' identifies the ability to accomplish an authorized goal, either by compliance or by obedience; hence, ''authority'' is the ''power'' to make decisions and the legitimacy to make such legal decisions and order their execution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyranny
A tyrant (), in the modern English language, English usage of the word, is an autocracy, absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurper, usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to political repression, repressive means. The original Greek term meant an absolute sovereign who came to power without constitutional right, yet the word had a neutral connotation during the Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical periods. However, Greek philosopher Plato saw ''tyrannos'' as a negative form of government, and on account of the decisive influence of philosophy on politics, deemed tyranny the "fourth and worst disorder of a state."Plato, ''The Republic'' Book VIII The philosophers Plato and Aristotle defined a tyrant as a person who rules without law, using extreme and cruel methods against both his own people and others. The ''Encyclopédie'' defined the term as a usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
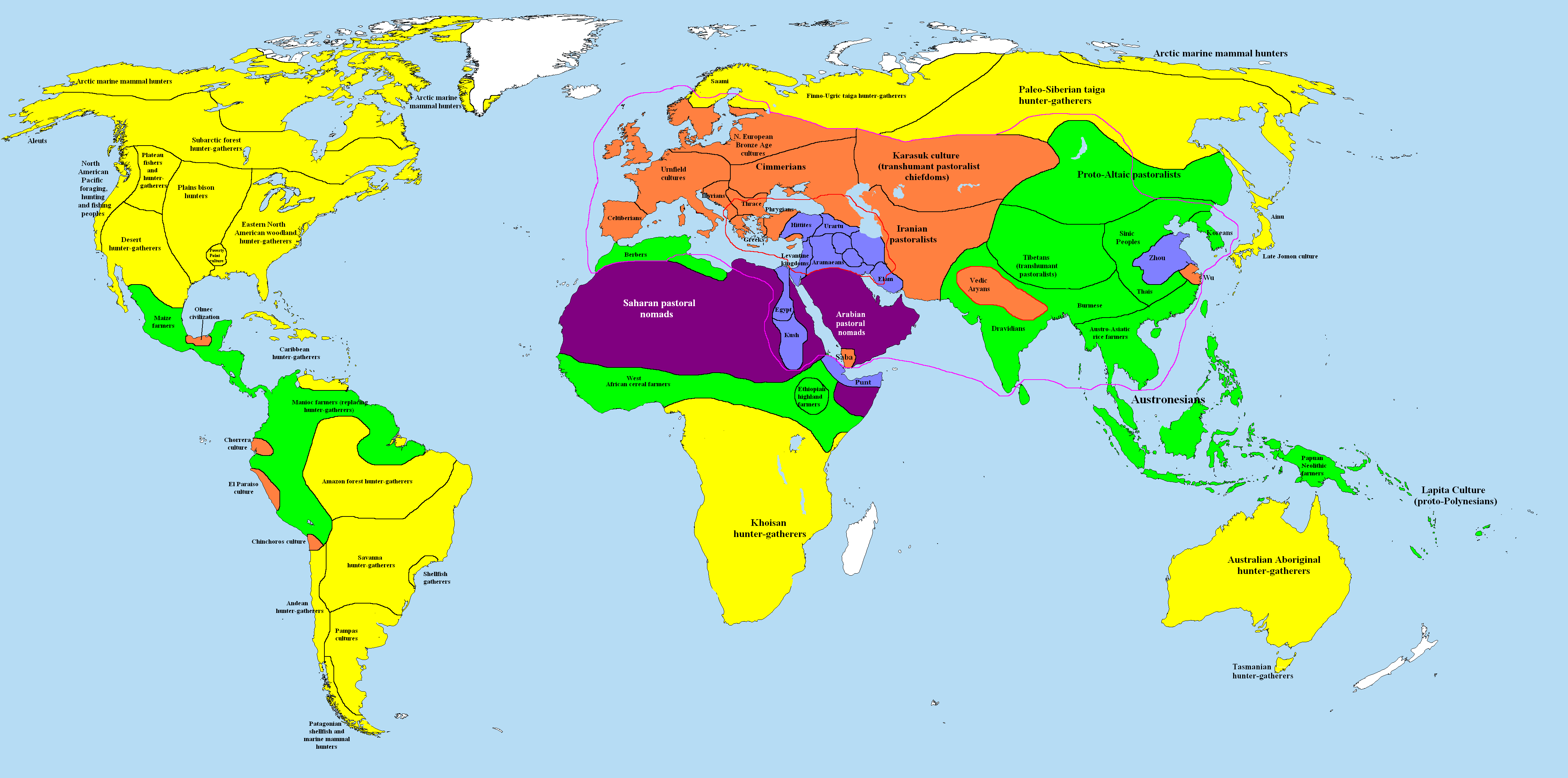
Stateless Society
A stateless society is a society that is not governed by a state. In stateless societies, there is little concentration of authority. Most positions of authority that do exist are very limited in power, and they are generally not permanent positions, and social bodies that resolve disputes through predefined rules tend to be small. Different stateless societies feature highly variable economic systems and cultural practices. While stateless societies were the norm in human prehistory, few stateless societies exist today; almost the entire global population resides within the jurisdiction of a sovereign state, though in some regions nominal state authorities may be very weak and may wield little or no actual power. Over the course of history most stateless peoples have become integrated into external state-based societies. Some political philosophies, particularly anarchism, regard the state as an unwelcome institution and stateless societies as the ideal, while M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |