|
Al-Murtafi'a
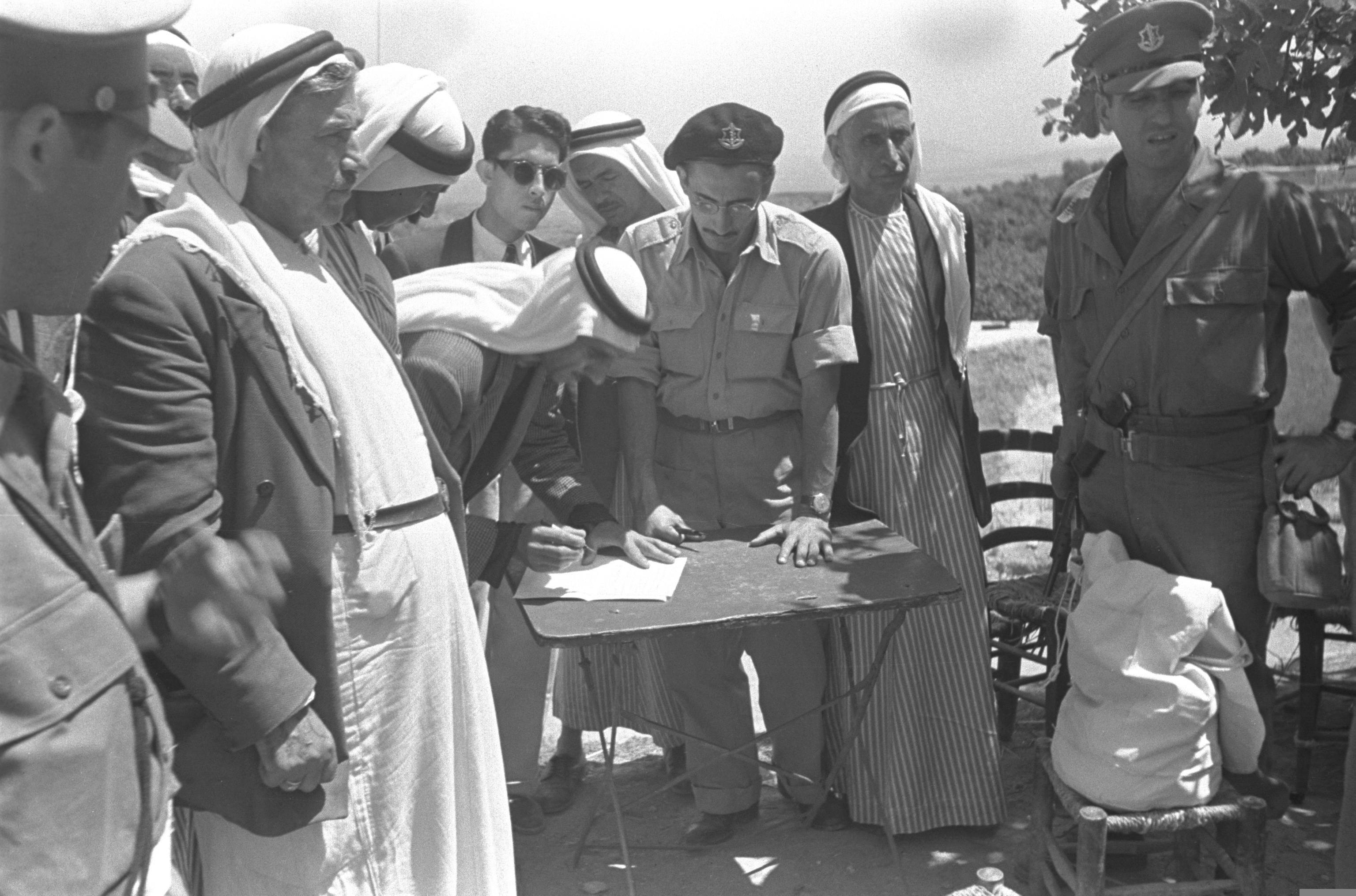
Zalafa (, ) is an Arab village in Israel's Haifa District. The village is in the Wadi Ara area of the northern Triangle, northeast of Umm al-Fahm. Since 1996, it has been under the jurisdiction of the Ma'ale Iron local council whose headquarters is in the village. The village is divided into three neighborhoods: East, West and al-Murtafi'a. In mid-2016, Zalafa's population was 4,639, all of whom are Muslim. History According to archeological evidence, Zalafa location has been settled continuously since the Iron Age, but with a decline in the Ottoman era. Building foundations, burial tombs, potsherds from the Byzantine era and an ancient well can be found under the village. Ottoman and British Mandate periods In 1870, French explorer Victor Guérin found Zalafa "almost completely deserted", and in the 1870s it was described as "a small ruined village with a well" by the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' (SWP). In 1870/1871 (1288 AH), an Ottoman census listed the village i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umm Al-Fahm
Umm al-Fahm ( , ''Umm al-Faḥm''; ''Um el-Faḥem'') is a city located northwest of Jenin in the Haifa District of Israel. In its population was , nearly all of whom are Palestinian citizens of Israel. The city is situated on the Umm al-Fahm mountain ridge, the highest point of which is Mount Iskander ( above sea level), overlooking Wadi Ara. Umm al-Fahm is the social, cultural and economic center for residents of the Wadi Ara and Triangle regions. Etymology Umm al-Fahm literally means "Mother of Charcoal" in Arabic. According to local lore, the village was surrounded by forests which were used to produce charcoal. History Several archaeological sites around the city date to the Iron Age II, as well as the Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, early Muslim and the Middle Ages.Zertal, 2016, p119/ref> Mamluk era In 1265 C.E. (663 H.), after Baybars won the territory from the Crusaders, the revenues from Umm al-Fahm were given to the Mamluk ''na'ib al-saltana'' (viceroy) of Syria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
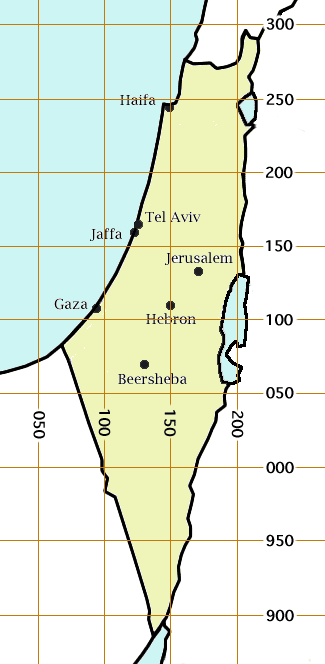
Palestine Grid
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini projection, Cassini-Soldner projection. The central Meridian (geography), meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza City, Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative Easting and northing, northing coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine Exploration Fund
The Palestine Exploration Fund is a British society based in London. It was founded in 1865, shortly after the completion of the Ordnance Survey of Jerusalem by Royal Engineers of the War Department. The Fund is the oldest known organization in the world created specifically for the study of the Levant region, also known as Palestine (region), Palestine. Often simply known as the PEF, its initial objective was to carry out surveys of the topography and ethnography of History of Palestine#Ottoman period, Ottoman Palestine – producing the PEF Survey of Palestine. Its remit was considered to fall between an expeditionary survey and military intelligence gathering. There was also strong religious interest from Christians; William Thomson (Archbishop of York), William Thomson, Archbishop of York, was the first president of the PEF. As a result, the PEF had a complex relationship with Corps of Royal Engineers of the War Department. The PEF members sent back reports to the UK on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunam
A dunam ( Ottoman Turkish, Arabic: ; ; ; ), also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area analogous in role (but not equal) to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount of land that could be ploughed by a team of oxen in a day. The legal definition was(when?) "forty standard paces in length and breadth", but its actual area varied considerably from place to place, from a little more than in Ottoman Palestine to around in Iraq.Λεξικό της κοινής Νεοελληνικής (Dictionary of Modern Greek), Ινστιτούτο Νεοελληνικών Σπουδών, Θεσσαλονίκη, 1998. The unit is still in use in many areas previously ruled by the Ottomans, although the new or metric dunam has been redefined(as of when, by who?) as exactly one decare (), which is 1/10 hectare (1/10 × ), like the modern Greek royal stremma. History The name dönüm, from the Ottoman Turkish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Statistics, 1945
Village Statistics, 1945 was a joint survey work prepared by the Government Office of Statistics and the Department of Lands of the British Mandate Government for the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry on Palestine which acted in early 1946. Hadawi, S., Village statistics, 1945, A Classification of Land and Area Ownership in Palestine, pp11 The data were calculated as of April 1, 1945, and was later published and also served the UNSCOP committee that operated in 1947. The survey encompasses data on land ownership, its uses, population statistics, and tax payment records. The land data was derived from the work conducted for the Peel Commission and subsequently updated by the Mandate Government's Lands Department. The population data was based on the 1931 census of Palestine, updated with information from various partial censuses primarily conducted in the Jewish sector, along with immigration and natural reproduction data. The data for the entire Land of Israel is deemed more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Census Of Palestine
The 1931 census of Palestine was the second census carried out by the authorities of Mandatory Palestine. It was carried out on 18 November 1931 under the direction of Major E. Mills after the 1922 census of Palestine. * Census of Palestine 1931, Volume I. Palestine Part I, Report. Alexandria, 1933 (349 pages). * Census of Palestine 1931, Volume II. Palestine, Part II, Tables. Alexandria, 1933 (595 pages). References Further reading * Miscellaneous short extracts from the census reports at Emory University * J. McCarthy, The Population of Palestine, Columbia University Press (1988). This contains many pages of tables extracted from the census reports. {{Authority control Censuses in Mandatory Palestine Census Of Palestine, 1931 Documents of Mandatory Palestine Palestine Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 Census Of Palestine
The 1922 census of Palestine was the first census carried out by the authorities of the British Mandate of Palestine, on 23 October 1922. The reported population was 757,182, including the military and persons of foreign nationality. The division into religious groups was 590,890 Muslims, 83,794 Jews, 73,024 Christians, 7,028 Druze, 408 Sikhs, 265 Baháʼís, 156 Metawalis, and 163 Samaritans. Operation Censuses carried out by the Ottoman Empire, most recently in 1914, had been for the purpose of imposing taxation or locating men for military service. For this reason, the announcement of a census was unpopular and effort was made in advance to reassure the population.Barron, pp. 1–4. This was believed to be successful except in the case of the Bedouins of the Beersheva Subdistrict, who refused to cooperate. Many census gatherers, supervised by 296 Revising Operators and Enumerators, visited each dwelling, with special arrangements made for persons having no fixed address ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine (region)
The region of Palestine, also known as historic Palestine, is a geographical area in West Asia. It includes the modern states of Israel and Palestine, as well as parts of northwestern Jordan in some definitions. Other names for the region include Canaan, the Promised Land, the Land of Israel, or the Holy Land. The earliest written record Timeline of the name Palestine, referring to Palestine as a geographical region is in the ''Histories (Herodotus), Histories'' of Herodotus in the 5th century BCE, which calls the area ''Palaistine'', referring to the territory previously held by Philistia, a state that existed in that area from the 12th to the 7th century BCE. The Roman Empire conquered the region and in 6 CE established the province known as Judaea (Roman province), Judaea. In the aftermath of the Bar Kokhba revolt (132–136 CE), the province was renamed Syria Palaestina. In 390, during the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
''Aliyah'' (, ; ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine (region), Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jerusalem in Judaism, Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action – emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel – is referred to in the Hebrew language as ''yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Knesset, Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of Jewish history, their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to Jewish militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the ), or Marj Ibn Amir (), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. It is bordered to the north by the highlands of the Lower Galilee region, to the south by the Samarian highlands, to the west and northwest by the Mount Carmel range, and to the east by the Jordan Valley (Middle East), Jordan Valley, with Mount Gilboa marking its southern extent. The largest settlement in the valley is the city of Afula, which lies near its center. Name The Jezreel Valley takes its name from the ancient city of Jezreel (city), Jezreel (known in Hebrew as Yizre'el; ; known in Arabic as Zir'in, Zir'ēn, ) which was located on a low hill overlooking the southern edge of the valley. The word ''Jezreel'' comes from the Hebrew, and means "God sows" or "El (god), El sows".Cheyne and Black, ''Encyclopedia Biblica'' The Arabic name of the valley is Marj Bani Amir (), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilad Al-Ruha
The Manasseh Hills or hill country of Manasseh, directly derived from Hebrew: Menashe Heights (), called Bilad ar-Ruha in Arabic, meaning "Land of Winds", is a geographical region in northern Israel, located on the Carmel Range, between Mount Carmel and Mount Amir/Umm al-Fahm. Etymology The hill country of Manasseh or Manasseh hill country, sometimes fully capitalised, is named for its location within the allotment of the biblical Tribe of Manasseh, itself named after its biblical forefather, Manasseh or Manasses. History During the Ottoman Period, the Menashe Hills formed part of Turabay Emirate (1517-1683), which encompassed also the Jezreel Valley, Haifa, Jenin, Beit She'an Valley, Mount Carmel, northern Jabal Nablus, and the northern part of the Sharon plain. During the late Ottoman period, the largest dispersal in the Mannaseh Hills was of people from Egypt, with another significant group being those from Hebron (Khalilia). These migrants likely settled in the area f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that the study of kinship is the study of what Human, humans do with these basic facts of lifemating, gestation, Parenting, parenthood, socialization, siblingship etc. Human society is unique, he argues, in that we are "working with the same raw material as exists in the animal world, but [we] can conceptualize and categorize it to serve social ends." These social ends include the socialization of children and the formation of basic economic, political and religious groups. Kinship can refer both to the patterns of social relationships themselves, or it can refer to the study of the patterns of social relationships in one or more human cultures (i.e. kinship studies). Over its history, anthropology has developed a number of related concepts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |