|
Aglycon
An aglycone (aglycon or genin) is the chemical compound remaining after the glycosyl group on a glycoside is replaced by a hydrogen atom. For example, the aglycone of a cardiac glycoside would be a steroid molecule. Detection A way to identify aglycone is proposed to extract it from Agave spp. by using H-NMR and Heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) experiments. The HMBC experiment can be combined with other techniques such as mass spectrometry to further examine the structure and the function of aglycone. Samples of glycones and glycosides from limonoids can be simultaneously quantified through a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method, where a binary solvent system and a diode array detector separate and detect them at a sensitivity of 0.25-0.50 μg. Clinical significance A study on molecular markers in human aortic endothelial cells published that aglycone stopped cell migration but not monocyte adhesion, which is the initial step of atheroscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxin
Digoxin (better known as digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart disease, heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. Digoxin is one of the oldest medications used in the field of cardiology. It works by increasing myocardial contractility, increasing stroke volume and blood pressure, reducing heart rate, and somewhat extending the time frame of the Muscle contraction, contraction. Digoxin is taken by mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein. Digoxin has a half life of approximately 36 hours given at average doses in patients with normal renal function. It is excreted mostly unchanged in the urine. Common side effects include gynecomastia, breast enlargement with other side effects generally due to an excessive dose. These side effects may include loss of appetite, nausea, trouble seeing, confusion, and an Heart arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat. Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxigenin Acsv
Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants ''Digitalis purpurea'', ''Digitalis orientalis'' and ''Digitalis lanata'' (foxgloves), where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides (e.g. digoxin, lanatoside C). Uses in biotechnology Digoxigenin is a hapten, a small molecule with high antigenicity, that is used in many molecular biology applications similarly to other popular haptens such as 2,4-Dinitrophenol, biotin, and fluorescein. Typically, digoxigenin is introduced chemically (conjugation) into biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) to be detected in further assays. Kd of the digoxigenin-antibody interaction has been estimated at ~12 nM (compare to Kd~0.1pM for the biotin-streptavidin interaction). ;DIG-binding proteins Tinberg et al. designed artificial proteins that bind DIG. Their best binder, DIG10.3, was a 141 amino acid protein that bound DIG with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 541 (+/- 193) pM. Anti-digoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxin
Digoxin (better known as digitalis), sold under the brand name Lanoxin among others, is a medication used to treat various heart disease, heart conditions. Most frequently it is used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and heart failure. Digoxin is one of the oldest medications used in the field of cardiology. It works by increasing myocardial contractility, increasing stroke volume and blood pressure, reducing heart rate, and somewhat extending the time frame of the Muscle contraction, contraction. Digoxin is taken by mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein. Digoxin has a half life of approximately 36 hours given at average doses in patients with normal renal function. It is excreted mostly unchanged in the urine. Common side effects include gynecomastia, breast enlargement with other side effects generally due to an excessive dose. These side effects may include loss of appetite, nausea, trouble seeing, confusion, and an Heart arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat. Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants ''Digitalis purpurea'', ''Digitalis orientalis'' and ''Digitalis lanata'' (foxgloves), where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides (e.g. digoxin, lanatoside C). Uses in biotechnology Digoxigenin is a hapten, a small molecule with high antigenicity, that is used in many molecular biology applications similarly to other popular haptens such as 2,4-Dinitrophenol, biotin, and fluorescein. Typically, digoxigenin is introduced chemically (conjugation) into biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) to be detected in further assays. Kd of the digoxigenin-antibody interaction has been estimated at ~12 nM (compare to Kd~0.1pM for the biotin-streptavidin interaction). ;DIG-binding proteins Tinberg et al. designed artificial proteins that bind DIG. Their best binder, DIG10.3, was a 141 amino acid protein that bound DIG with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 541 (+/- 193) pM. Anti-digoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosyl
In organic chemistry, a glycosyl group is a univalent free radical or substituent structure obtained by removing the hydroxyl () group from the hemiacetal () group found in the cyclic form of a monosaccharide and, by extension, of a lower oligosaccharide. Glycosyl groups are exchanged during glycosylation from the glycosyl donor, the electrophile, to the glycosyl acceptor, the nucleophile. The outcome of the glycosylation reaction is largely dependent on the reactivity of each partner. Glycosyl also reacts with inorganic acids, such as phosphoric acid, forming an ester such as glucose 1-phosphate. Examples In cellulose, glycosyl groups link together 1,4-β-D-glucosyl units to form chains of (1,4-β-D-glucosyl)n. Other examples include ribityl in 6,7-Dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine, and glycosylamines. Alternative substituent groups Instead of the hemiacetal hydroxyl group, a ''hydrogen'' atom can be removed to form a substituent, for example the hydrogen from the C3 hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzymatic, enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of ''Heliconius'' butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body. In formal terms, a glycoside is any molecule in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides can be linked by an O- (an ''O-glycoside''), N- (a ''glycosylamine''), S-(a ''thioglycoside''), or C- (a ''C-glycoside'') glycosidic bond. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Glycoside
Cardiac glycosides are a class of organic compounds that increase the output force of the heart and decrease its rate of contractions by inhibiting the cellular sodium-potassium ATPase pump. Their beneficial medical uses include treatments for congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias; however, their relative toxicity prevents them from being widely used. Most commonly found as defensive poisons in several plant genera such as ''Digitalis'' (the foxgloves) and '' Asclepias'' (the milkweeds), these compounds nevertheless have a diverse range of biochemical effects regarding cardiac cell function and have also been suggested for use in cancer treatment. Classification General structure The general structure of a cardiac glycoside consists of a steroid molecule attached to a sugar (glycoside) and an R group. The steroid nucleus consists of four fused rings to which other functional groups such as methyl, hydroxyl, and aldehyde groups can be attached to influence th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
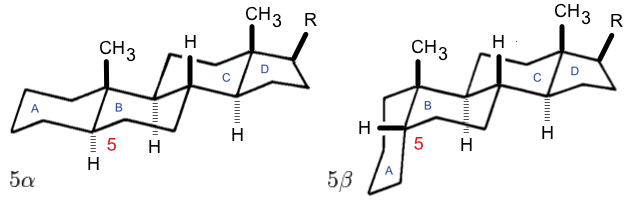
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucoside
A glucoside is a glycoside that is chemically derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes. The name was originally given to plant products of this nature, in which the other part of the molecule was, in the greater number of cases, an aromatic aldehydic or phenolic compound (exceptions are Jinigrin and Jalapin or Scammonin). It has now been extended to include synthetic ethers, such as those obtained by acting on alcoholic glucose solutions with hydrochloric acid, and also the polysaccharoses, e.g. cane sugar, which appear to be ethers also. Although glucose is the most common sugar present in glucosides, many are known which yield rhamnose or iso-dulcite; these may be termed pentosides. Much attention has been given to the non-sugar parts (aglycone) of the molecules; the constitutions of many have been determined, and the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate Chemistry
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |