|
Adopt
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, from the biological parents to the adoptive parents. Unlike guardianship or other systems designed for the care of the young, adoption is intended to effect a permanent change in status and as such requires societal recognition, either through legal or religious sanction. Historically, some societies have enacted specific laws governing adoption, while others used less formal means (notably contracts that specified inheritance rights and parental responsibility (access and custody), parental responsibilities without an accompanying transfer of filiation). Modern systems of adoption, arising in the 20th century, tend to be governed by comprehensive statutes and regulations. History Antiquity Adoption for the well-born While the modern form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption In Ancient Rome
Adoption in ancient Rome was primarily a Roman law, legal procedure for transferring paternal power ''(patria potestas, potestas)'' to ensure Inheritance law in ancient Rome, succession in the male line within Roman paterfamilias, patriarchal society. The Latin word ''adoptio'' refers broadly to "adoption", which was of two kinds: the transferral of ''potestas'' over a free person from one head of household to another; and ''adrogatio'', when the adoptee had been acting ''sui iuris'' as a legal adult but assumed the status of unemancipated son for purposes of Inheritance law in ancient Rome, inheritance. ''Adoptio'' was a longstanding part of Roman family law pertaining to paternal responsibilities such as perpetuating the value of the family estate and ancestral rites ''(Glossary of ancient Roman religion#sacra gentilicia, sacra)'', which were concerns of the Roman property-owning classes and cultural elite. During the Principate, adoption became a way to ensure List of Roman empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filiation
Filiation is the legal term for the recognized legal status of the relationship between family members, or more specifically the legal relationship between parent and child. As described by the Government of Quebec: Filiation is the relationship which exists between a child and the child’s parents, whether the parents are of the same or the opposite sex. The relationship can be established by blood, by law in certain cases, or by a judgment of adoption. Once filiation has been established, it creates rights and obligations for both the child and the parents, regardless of the circumstances of the child’s birth. Filiation differs from, but impacts, both parental rights and inheritance. An example of law regarding filiation is found in the Civil Code of Quebec, Book 2, Title 2 "Filiation", which details how filiation may be established, claimed, and transferred. Filiation and adoption When an adoption takes place under the laws of the United States, Canada, New Zealand, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traianus Glyptothek Munich 336
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history, during which, by the time of his death, the Roman Empire reached its maximum territorial extent. He was given the title of ('the best') by the Roman Senate. Trajan was born in the of Italica in the present-day Andalusian province of Seville in southern Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his came from the town of Tuder in the Umbria region of central Italy. His namesake father, Marcus Ulpius Traianus, was a general and distinguished senator. Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of Domitian; in AD 89, serving as a in , he supported the emperor against a revolt on the Rhine led by Antonius Saturninus. He then served as gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children At New York Foundling Cph
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor (law), minor, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority (there are exceptions such as, for example, the consume and purchase of alcoholic beverage even after said age of majority), regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adults. Children generally have fewer Children's rights, rights and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, Metaphor, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hānai
''Hānai'' is a term used in the Hawaiian culture that refers to the informal adoption of one person by another. It can be used as an adjective, such as "''hānai'' child," or as a verb, to ''hānai'' someone into the family. Traditionally, ''hānai'' (which translates roughly as "feeding") took place shortly after birth, when a baby's biological parents gave the infant to another couple to raise. In pre-contact Hawaii, paternal grandparents had a claim on the first-born boy, and maternal grandparents on the first-born girl. The practice could serve to expand and strengthen family ties, and was an efficient way for a society to pass knowledge and culture down the generations. However, the adopting couple might be more distant relatives, or not related at all. ''Hānai'' also was used for political alliances to link royal families, and continued among royalty even after Western contact. Lili‘uokalani, Hawai‘i’s last monarch, was the ''hānai'' child of chiefs higher ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Abandonment
A child () is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority (there are exceptions such as, for example, the consume and purchase of alcoholic beverage even after said age of majority), regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adults. Children generally have fewer rights and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being strongly affected by a specific time, place, or circumstance, as in "a child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Officially bequeathing private property and/or debts can be performed by a testator via will, as attested by a notary or by other lawful means. Terminology In law, an "heir" ( heiress) is a person who is entitled to receive a share of property from a decedent (a person who died), subject to the rules of inheritance in the jurisdiction where the decedent was a citizen, or where the decedent died or owned property at the time of death. The inheritance may be either under the terms of a will or by intestate laws if the deceased had no will. However, the will must comply with the laws of the jurisdiction at the time it was created or it will be declared invalid (for example, some states do not recognise handwritten wills as valid, or only in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloodline
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of the organism's genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Culture
Polynesian culture is the culture of the indigenous peoples of Polynesia who share common traits in language, customs and society. The development of Polynesian culture is typically divided into four different historical eras: * Exploration and settlement (c. 1800 BC – c. AD 700) * Development in isolation (c. 700–1595) * European encounter and colonization until World War II (1595–1946) * Post-World War II period History Origins, exploration and settlement (c. 1800 BC – c. 700 AD) Maternal mitochondrial DNA analysis suggests that Polynesians, including Samoans, Tongans, Niueans, Cook Islanders, Tahitians, Hawaiians, Marquesans and Māori, are genetically linked to indigenous peoples of parts of Maritime Southeast Asia including those of Taiwanese aborigines. This DNA evidence is supported by linguistic and archeological evidence. Recent studies into paternal Y chromosome analysis shows that Polynesians are also genetically linked to peoples of Melanesia. Between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
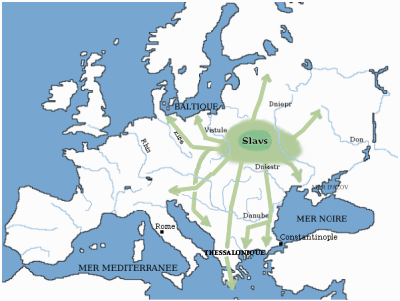
Slavic Peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, and North Asia, Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianization of the Slavs, Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the First Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |