|
Added
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total or '' sum'' of those values combined. For example, the adjacent image shows two columns of apples, one with three apples and the other with two apples, totaling to five apples. This observation is expressed as , which is read as "three plus two equals five". Besides counting items, addition can also be defined and executed without referring to concrete objects, using abstractions called numbers instead, such as integers, real numbers, and complex numbers. Addition belongs to arithmetic, a branch of mathematics. In algebra, another area of mathematics, addition can also be performed on abstract objects such as vectors, matrices, subspaces, and subgroups. Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that the order of the numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition01
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total or '' sum'' of those values combined. For example, the adjacent image shows two columns of apples, one with three apples and the other with two apples, totaling to five apples. This observation is expressed as , which is read as "three plus two equals five". Besides counting items, addition can also be defined and executed without referring to concrete objects, using abstractions called numbers instead, such as integers, real numbers, and complex numbers. Addition belongs to arithmetic, a branch of mathematics. In algebra, another area of mathematics, addition can also be performed on abstract objects such as vectors, matrices, subspaces, and subgroups. Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that the order of the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms. Arithmetic systems can be distinguished based on the type of numbers they operate on. Integer arithmetic is about calculations with positive and negative integers. Rational number arithmetic involves operations on fractions of integers. Real number arithmetic is about calculations with real numbers, which include both rational and irrational numbers. Another distinction is based on the numeral system employed to perform calculations. Decimal arithmetic is the most common. It uses the basic numerals from 0 to 9 and their combinations to express numbers. Binary arithmetic, by contrast, is used by most computers and represents numbers as combinations of the basic numerals 0 and 1. Computer arithmetic deals with the specificities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtraction
Subtraction (which is signified by the minus sign, –) is one of the four Arithmetic#Arithmetic operations, arithmetic operations along with addition, multiplication and Division (mathematics), division. Subtraction is an operation that represents removal of objects from a collection. For example, in the adjacent picture, there are peaches—meaning 5 peaches with 2 taken away, resulting in a total of 3 peaches. Therefore, the ''difference'' of 5 and 2 is 3; that is, . While primarily associated with natural numbers in arithmetic, subtraction can also represent removing or decreasing physical and abstract quantities using different kinds of objects including negative numbers, Fraction (mathematics), fractions, irrational numbers, Euclidean vector, vectors, decimals, functions, and matrices. In a sense, subtraction is the inverse of addition. That is, if and only if . In words: the difference of two numbers is the number that gives the first one when added to the second one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like Number (sports), jersey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic operations other than the standard arithmetic operations, such as addition and multiplication. Elementary algebra is the main form of algebra taught in schools. It examines mathematical statements using variables for unspecified values and seeks to determine for which values the statements are true. To do so, it uses different methods of transforming equations to isolate variables. Linear algebra is a closely related field that investigates linear equations and combinations of them called '' systems of linear equations''. It provides methods to find the values that solve all equations in the system at the same time, and to study the set of these solutions. Abstract algebra studies algebraic structures, which consist of a set of mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation (mathematics)
In mathematics, an operation is a function from a set to itself. For example, an operation on real numbers will take in real numbers and return a real number. An operation can take zero or more input values (also called "'' operands''" or "arguments") to a well-defined output value. The number of operands is the arity of the operation. The most commonly studied operations are binary operations (i.e., operations of arity 2), such as addition and multiplication, and unary operations (i.e., operations of arity 1), such as additive inverse and multiplicative inverse. An operation of arity zero, or nullary operation, is a constant. The mixed product is an example of an operation of arity 3, also called ternary operation. Generally, the arity is taken to be finite. However, infinitary operations are sometimes considered, in which case the "usual" operations of finite arity are called finitary operations. A partial operation is defined similarly to an operatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplication
Multiplication is one of the four elementary mathematical operations of arithmetic, with the other ones being addition, subtraction, and division (mathematics), division. The result of a multiplication operation is called a ''Product (mathematics), product''. Multiplication is often denoted by the cross symbol, , by the mid-line dot operator, , by juxtaposition, or, in programming languages, by an asterisk, . The multiplication of whole numbers may be thought of as repeated addition; that is, the multiplication of two numbers is equivalent to adding as many copies of one of them, the ''multiplicand'', as the quantity of the other one, the ''multiplier''; both numbers can be referred to as ''factors''. This is to be distinguished from term (arithmetic), ''terms'', which are added. :a\times b = \underbrace_ . Whether the first factor is the multiplier or the multiplicand may be ambiguous or depend upon context. For example, the expression 3 \times 4 , can be phrased as "3 ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (mathematics)
Division is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic. The other operations are addition, subtraction, and multiplication. What is being divided is called the ''dividend'', which is divided by the ''divisor'', and the result is called the ''quotient''. At an elementary level the division of two natural numbers is, among other Quotition and partition, possible interpretations, the process of calculating the number of times one number is contained within another. For example, if 20 apples are divided evenly between 4 people, everyone receives 5 apples (see picture). However, this number of times or the number contained (divisor) need not be integers. The division with remainder or Euclidean division of two natural numbers provides an integer ''quotient'', which is the number of times the second number is completely contained in the first number, and a ''remainder'', which is the part of the first number that remains, when in the course of computing the quotient, no further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus And Minus Signs
The plus sign () and the minus sign () are Glossary of mathematical symbols, mathematical symbols used to denote sign (mathematics), positive and sign (mathematics), negative functions, respectively. In addition, the symbol represents the operation of addition, which results in a Sum (mathematics), sum, while the symbol represents subtraction, resulting in a difference (mathematics), difference. Their use has been extended to many other meanings, more or less analogous. and are Latin terms meaning 'more' and 'less', respectively. The forms and are used in many countries around the world. Other designs include for plus and for minus. History Though the signs now seem as familiar as the alphabet or the Arabic numerals, they are not of great antiquity. The Egyptian hieroglyphic sign for addition, for example, resembles a pair of legs walking in the direction in which the text was written (Egyptian language, Egyptian could be written either from right to left or left to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
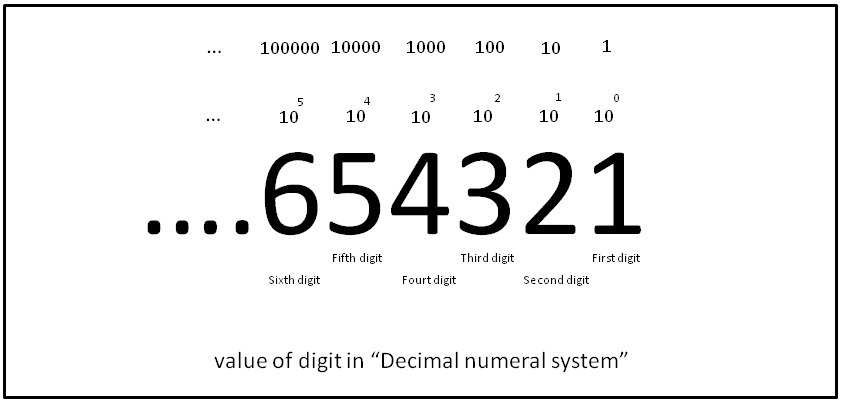
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |