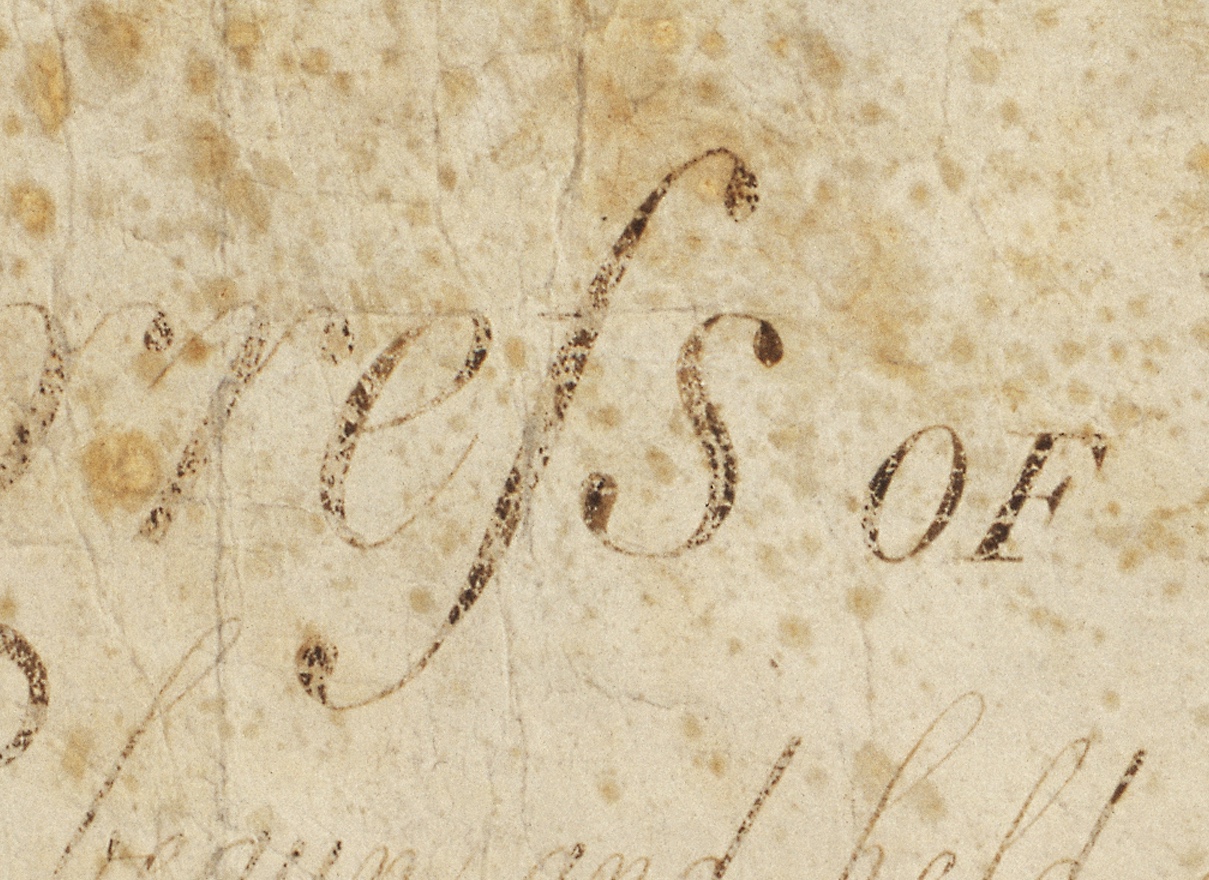|
Waw (letter)
Waw ( "hook") is the sixth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Abjad, Semitic abjads, including Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician ''wāw'' 𐤅, Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic ''waw'' 𐡅, Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew ''vav'' , Syriac alphabet, Syriac ''waw'' ܘ and Arabic alphabet, Arabic ''wāw'' (sixth in abjadi order; 27th in modern Arabic order). It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪅, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and Geʽez script, Ge'ez . It represents the consonant in classical Hebrew, and in modern Hebrew, as well as the vowels and . In text with niqqud, a dot is added to the left or on top of the letter to indicate, respectively, the two vowel pronunciations. It is the origin of Greek Ϝ (digamma) and Υ (upsilon); Latin F, V and later the derived Y, U and W; and the also derived Cyrillic U (Cyrillic), У and Izhitsa, Ѵ. Origin The letter likely originated with an Egyptian hieroglyph which represented List of Egyptian hieroglyphs# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
𝆑
In music, the dynamics of a piece are the variation in loudness between notes or phrases. Dynamics are indicated by specific musical notation, often in some detail. However, dynamics markings require interpretation by the performer depending on the musical context: a specific marking may correspond to a different volume between pieces or even sections of one piece. The execution of dynamics also extends beyond loudness to include changes in timbre and sometimes tempo rubato. Purpose and interpretation Dynamics are one of the expressive elements of music. Used effectively, dynamics help musicians sustain variety and interest in a musical performance, and communicate a particular emotional state or feeling. Dynamic markings are always relative. (''piano'' - "soft") never indicates a precise level of loudness; it merely indicates that music in a passage so marked should be considerably quieter than (''forte'' - "loud"). There are many factors affecting the interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Alphabet
Modern English is written with a Latin-script alphabet consisting of 26 Letter (alphabet), letters, with each having both uppercase and lowercase forms. The word ''alphabet'' is a Compound (linguistics), compound of ''alpha'' and ''beta'', the names of the first two letters in the Greek alphabet. The earliest Old English writing during the 5th century used a runic alphabet known as the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, futhorc. The Old English Latin alphabet was adopted from the 7th century onward—and over the following centuries, various letters entered and fell out of use. By the 16th century, the present set of 26 letters had largely stabilised: There are 5 vowel letters and 19 consonant letters—as well as Y and W, which may function as either type. Written English has a large number of Digraph (orthography), digraphs, such as , , , , and . Diacritics are generally not used to write native English words, which is unusual among orthographies used to write the languages of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s'' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess", but never "poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the "short", "terminal", or "round" ''s''. In typography, the long ''s'' is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash ''s''". The long ''s'' is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , ( or , 'sharp ''s'''). As with other letters, the long ''s'' may have a variant appearance depending on typeface: , , , . Rules English This list of rules for the long ''s'' is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th to early 19th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph () or digram is a pair of character (symbol), characters used in the orthography of a language to write either a single phoneme (distinct sound), or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined. Some digraphs represent phonemes that cannot be represented with a single character in the writing system of a language, like in Spanish ''chico'' and ''ocho''. Other digraphs represent phonemes that can also be represented by single characters. A digraph that shares its pronunciation with a single character may be a relic from an earlier period of the language when the digraph had a different pronunciation, or may represent a distinction that is made only in certain dialects, like the English . Some such digraphs are used for purely etymology, etymological reasons, like in French. In some orthographies, digraphs (and occasionally trigraph (orthography), trigraphs) are considered individual letter (alphabet), letters, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. After adjacent lands had been conquered its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto and western Campania. A large body of literature has flourished on the origins of the Etruscans, but the consensus among modern scholars is that the Etruscans were an indigenous population. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900 BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Alphabet
The Etruscan alphabet was used by the Etruscans, an ancient civilization of central and northern Italy, to write Etruscan language, their language, from about 700 BC to sometime around 100 AD. The Etruscan alphabet derives from the Euboean alphabet used in the Ancient Greece, Greek colonies in southern Italy which belonged to the "western" ("red") type, the so-called Western Greek alphabet. Several Old Italic scripts, including the Latin alphabet, derived from it (or simultaneously with it). Origins The Etruscan alphabet originated as an adaptation of the Euboean alphabet used by the Euboea, Euboean Greeks in their first colonies in Italy, the island of Pithekoussai and the city of Cumae in Campania. In the alphabets of the West, X had the help:IPA, sound value , Ψ stood for ; in Etruscan: X = , Ψ = or (Rix 202–209). The earliest known Etruscan ''abecedarium'' is inscribed on the frame of a wax tablet in ivory, measuring , found at Marsiliana (near Grosseto, Tuscany). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digamma
Digamma or wau (uppercase: Ϝ, lowercase: ϝ, numeral: ϛ) is an Archaic Greek alphabets, archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It originally stood for the sound but it has remained in use principally as a Greek numeral for 6 (number), 6. Whereas it was originally called ''waw'' or ''wau'', its most common appellation in classical Greek is ''digamma''; as a numeral, it was called ''episēmon'' during the Byzantine era and is now known as ''stigma (letter), stigma'' after the Greek ligature, Byzantine ligature combining σ-τ as ϛ. Digamma or wau was part of the original archaic Greek alphabet as initially adopted from Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician. Like its model, Phoenician Waw (letter), waw, it represented the voiced labial-velar approximant and stood in the 6th position in the alphabet between epsilon and zeta. It is the consonantal doublet of the vowel letter upsilon (), which was also derived from waw but was placed near the end of the Greek alphabet. Digamma or wau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon
Upsilon (, ; uppercase Υ, lowercase υ; ''ýpsilon'' ) or ypsilon is the twentieth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, has a value of 400. It is derived from the phoenician alphabet, Phoenician Waw (letter), waw . Etymology The name of the letter was originally just (, also called , hence ''hyoid bone, hyoid'', meaning 'shaped like the letter '), but the name changed to (= , 'u-plain' or 'u-simple') to distinguish it from , which had come to have the same pronunciation. Pronunciation In early Attic Greek (6th century BCE), it was pronounced (a close back rounded vowel like the English "long o͞o"). In Ancient Greek language, Classical Greek, it was pronounced (a close front rounded vowel), at least until 1030. In Modern Greek, it is pronounced ; in the digraph (orthography), digraphs and , as or ; and in the digraph as . In ancient Greek, it occurred in both Ancient Greek phonology#Vowels, long and short versions, but Modern Greek does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an abjad (consonantal alphabet) used across the Mediterranean civilization of Phoenicia for most of the 1st millennium BC. It was one of the first alphabets, attested in Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean basin. In the history of writing systems, the Phoenician script also marked the first to have a fixed writing direction—while previous systems were multi-directional, Phoenician was written horizontally, from right to left. It developed directly from the Proto-Sinaitic script used during the Late Bronze Age, which was derived in turn from Egyptian hieroglyphs. The Phoenician alphabet was used to write Canaanite languages spoken during the Early Iron Age, sub-categorized by historians as Phoenician, Hebrew, Moabite, Ammonite and Edomite, as well as Old Aramaic. It was widely disseminated outside of the Canaanite sphere by Phoenician merchants across the Mediterranean, where it was adopted and adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Hieroglyph
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs ( ) were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined ideographic, logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 1,000 distinct characters.In total, there were about 1,000 graphemes in use during the Old Kingdom period; this number decreased to 750–850 during the Middle Kingdom, but rose instead to around 5,000 signs during the Ptolemaic period. Antonio Loprieno, ''Ancient Egyptian: A Linguistic Introduction'' (Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1995), p. 12. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Egyptian hieroglyphs are the ultimate ancestor of the Phoenician alphabet, the first widely adopted phonetic writing system. Moreover, owing in large part to the Greek and Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |