|
Zgoda Labour Camp
Zgoda () was a labour camp (sometimes also described as a concentration camp), set up in February 1945 in Zgoda district of Świętochłowice, Silesia. It was controlled by the communist secret police until its closure in November of the same year.The Polish Institute of National Remembrance Bulletin"Salomon Morel and the camp at Świętochłowice-Zgoda" including Index of articles, copies of IPN documents and notes. Publication date: 21 July 2005. Between 1943 and January 1945 during World War II, the camp in Świętochłowice operated by Nazi Germany as Arbeitslager. It was a labour subcamp (''Arbeitslager Eintrachtshütte'') or the Eintrachthütte concentration camp of the Nazi concentration camp Auschwitz. After the NKVD transfer of the facility to MBP, Colonel Salomon Morel became the commander of the renamed Zgoda camp on 15 March 1945.Dr. Adam Dziurok Obóz Pracy Świętochłowice-Zgoda. Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, 2010 Zgoda Labour Camp operation The Nazi German camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaworzno Concentration Camp
The Jaworzno concentration camp was a concentration camp in WW2 German-occupied Poland and later in Communist Poland. It was first established by the Nazis in 1943 during the Second World War and was later used from 1945 to 1956 by the Soviet NKVD and then by the Ministry of Public Security and other agencies of the Polish communist regime. Today the site is an apartment complex and also houses a memorial to the camp's victims. Originally, it was established as a Nazi concentration camp called ''SS-Lager Dachsgrube'' ("SS Camp Dachsgrube) also known as ''Arbeitslager Neu-Dachs'' ("Work Camp Neu-Dachs") established during World War II by the Third Reich on the territory of German-occupied Poland in Jaworzno, Lesser Poland. The camp operated under the Nazi German administration from June 1943 until its evacuation in January 1945. After the communist takeover of Poland, the camp was reinstated and run first by the Soviet Union and then the People's Republic of Poland till 1956, main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Głubczyce
Głubczyce ( cs, Hlubčice or sparsely ''Glubčice'', german: Leobschütz, Silesian German: ''Lischwitz'') is a town in Opole Voivodeship in southern Poland, near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Głubczyce County and Gmina Głubczyce. Geography Głubczyce is situated on the Głubczyce Plateau ( pl, Płaskowyż Głubczycki; a part of the Silesian Lowlands) on the Psina (Cina) river, a left tributary of the Oder. The town centre is located approximately south of Opole and just northwest of Ostrava. History Middle Ages The settlement named ''Glubcici'' was first mentioned in an 1107 deed. At the time, it was a small village, dominated by a large wooden castle. It stood on the right bank of the Psina River, which according to an 1137 peace treaty between the dukes Soběslav I of Bohemia and Bolesław III of Poland formed the border between the Moravian lands (then ruled by the Bohemian dukes) and the Polish province of Silesia. The exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prudnik
Prudnik (, szl, Prudnik, Prōmnik, german: Neustadt in Oberschlesien, Neustadt an der Prudnik, la, Prudnicium) is a town in southern Poland, located in the southern part of Opole Voivodeship near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Prudnik County and Gmina Prudnik. Its population numbers 21,368 inhabitants (2016). Since 2015, Prudnik is a member of the Cittaslow, Cittaslow International. The town was founded in the 1250s, and was historically part of the Polish-ruled Duchy of Opole, and afterwards was located within the Habsburg monarchy, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland, Habsburg Monarchy again, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Germany, and eventually Poland again. It was once an important industrial hub known for its shoe-making traditions and more recently towel making by the Zakłady Przemysłu Bawełnianego "Frotex", ZPB "Frotex" Company, one of the largest towel manufacturers in Europe. The town also possesses numerous architectural m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks And Insignia Of The Nazi Party
Ranks and insignia of the Nazi Party were paramilitary titles used by the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP) between approximately 1928 and the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945. Such ranks were held within the political leadership corps of the Nazi Party, charged with the overseeing of the regular Nazi Party members. The first purpose of the Nazi Party's political ranks was to provide election district leadership positions during the years where the Nazis were attempting to come to power in Germany. After 1933, when the Third Reich had been established, Nazi Party ranks played a much more important role existing as a political chain of command operating side by side with the German government. Contrary to modern-day cinema and layman perceptions regarding the Nazi Party, which often portrays all Nazis as wearing brown shirts with swastika armbands, Nazi ranks and titles were only used by a small minority within the Party, this being the political leadership corps. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers' Party (; DAP), existed from 1919 to 1920. The Nazi Party emerged from the extremist German nationalist, racist and populist paramilitary culture, which fought against the communist uprisings in post– World War I Germany. The party was created to draw workers away from communism and into nationalism. Initially, Nazi political strategy focused on anti– big business, anti- bourgeois, and anti-capitalist rhetoric. This was later downplayed to gain the support of business leaders, and in the 1930s, the party's main focus shifted to antisemitic and anti-Marxist themes. The party had little popular support until the Great Depression. Pseudoscientific racist theories were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksliste
The Deutsche Volksliste (German People's List), a Nazi Party institution, aimed to classify inhabitants of Nazi-occupied territories (1939-1945) into categories of desirability according to criteria systematised by ''Reichsführer-SS'' Heinrich Himmler. The institution originated in occupied western Poland (occupied 1939-1945). Similar schemes were subsequently developed in Occupied France (1940-1944) and in the Reichskommissariat Ukraine (1941-1944). ''Volksdeutsche'' (ethnic Germans) topped the list as a category. They comprised people without German citizenship but of German ancestry living outside Germany (unlike German expatriates). Though ''Volksdeutsche'' did not hold German citizenship, the strengthening and development of ethnic German communities throughout east-central Europe formed an integral part of the Nazi vision for the creation of Greater Germany (''Großdeutschland''). In some areas, such as Romania, Croatia, and Yugoslavia/Serbia, ethnic Germans were legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union. Established in 1917 as NKVD of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, the agency was originally tasked with conducting regular police work and overseeing the country's prisons and labor camps. It was disbanded in 1930, with its functions being dispersed among other agencies, only to be reinstated as an all-union commissariat in 1934. The functions of the OGPU (the secret police organization) were transferred to the NKVD around the year 1930, giving it a monopoly over law enforcement activities that lasted until the end of World War II. During this period, the NKVD included both ordinary public order activities, and secret police activities. The NKVD is known for its role in political repression and for carrying out the Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For instanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Occupation Of Poland
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups that emerged afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
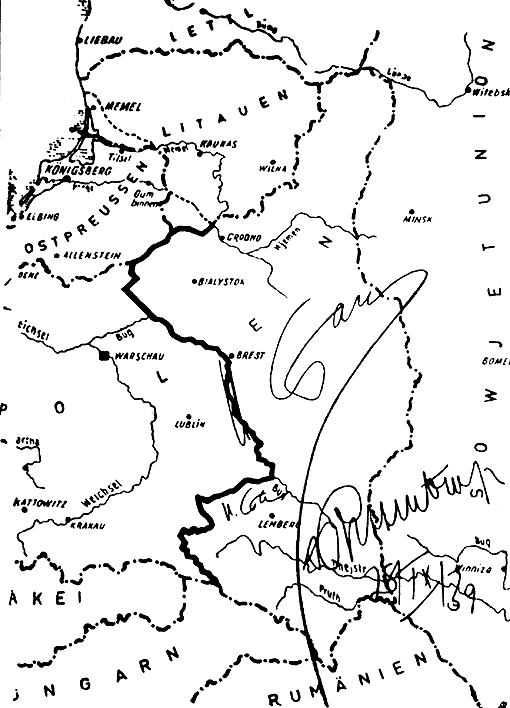
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |