|
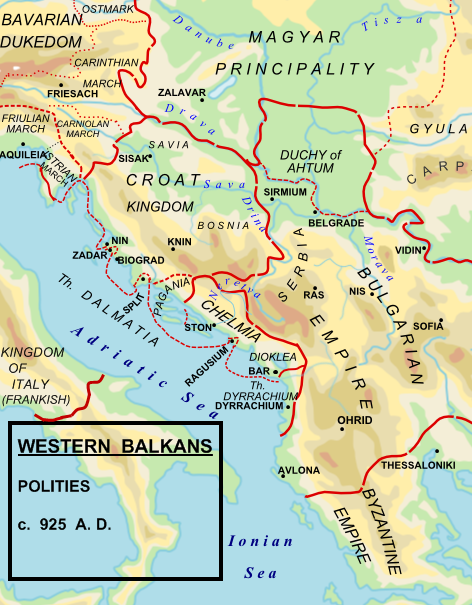
Zahumlje
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a medieval principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina and southern Dalmatia (today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia, respectively). In some periods it was a fully independent or semi-independent South Slavic principality. It maintained relations with various foreign and neighbouring powers (Byzantine Empire, First Bulgarian Empire, Kingdom of Croatia, Principality of Serbia) and later was subjected (temporarily or for a longer period) to Kingdom of Hungary, Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom of Bosnia, and at the end to the Ottoman Empire. Etymology Zachlumia is a derivative of ''Hum'', from Proto-Slavic '' *xŭlmŭ'', borrowed from a Germanic language (cf. Proto-Germanic '' *hulma-''), meaning ''"Hill"''. South Slavic ''Zahumlje'' is named after the mountain of Hum (za + Hum "behind the Hum"), above Bona, at the mouth of the Buna. The principality is named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Of Zahumlje
Michael of Zahumlje (reign usually dated c. 910–935), also known as Michael Višević (Serbo-Croatian: ''Mihailo Višević'', Serbian Cyrillic: Михаило Вишевић) or rarely as Michael Vuševukčić,Mihanovich, ''The Croatian nation in its struggle for freedom and independence: a symposium'', p. 112 was a semi-independent, or independent Slavic ruler of Zahumlje, in present-day central Herzegovina and southern Croatia, who flourished in the early part of the 10th century. Prince Michael of Zahumlje had a common boundary with the Serbia and probably with the Kingdom of Croatia, but was an ally of Bulgaria. He was nevertheless able to maintain independent rule throughout at least a majority of his reign. Michael came into territorial conflict with Petar of Serbia, who expand his power to the province of Narenta or Pagania, west from the Neretva River. To eliminate the threat, Michael warned his ally, the Bulgarian Tsar Simeon I, about the alliance between Petar and Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljutovid
Ljutovid ( sr-cyr, Љутовид) was an independent local Slavic chieftain and ruler of Zahumlje with a title of '' knez''. The region of Zahumlje included parts of present-day western Herzegovina in Bosnia and Herzegovina and southern Croatia along the coast. Ljutovid flourished in the middle of the 11th century as a vassal of the Byzantine Empire. As the local Slavic ruler of Zahumlje, and recipient of Byzantine ranks and titles, he was styled as "''protospatharios epi tou Chrysotriklinou, hypatos, strategos'' of Serbia and Zahumlje" in July 1039, and claimed supremacy in military ranks not only in his local domain but also to the entirety of Serbia.Stephenson 2003, pp. 42-43: "if the idea of developing a ''thema'' of Serbia existed briefly, it was swiftly abandoned and the title ''strategos'' passed to the local aristocracy. In a charter issued July 1039 the Slavic ruler of Zahumlje styled himself "Ljutovit, ''protospatharios epi tou Chrysotriklinou, hypatos, strategos'' of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duklja
Duklja ( sr-Cyrl, Дукља; ; ) was a medieval South Slavs, South Slavic state which roughly encompassed the territories of modern-day southeastern Montenegro, from the Bay of Kotor in the west to the Bojana river in the east, and to the sources of the Zeta (river), Zeta and Morača rivers in the north. First mentioned in 10th– and 11th-century Byzantine chronicles, it was a vassal of the First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarian Empire between 997 and 1018, and then of the Byzantine Empire until it became independent in 1040 under Stefan Vojislav ( 1034–43) who rose up and managed to take over territories of the earlier Principality of Serbia (early medieval), Serbian Principality, founding the Vojislavljević dynasty. Between 1043 and 1080, under Mihailo Vojislavljević ( 1050–81), and his son, Constantine Bodin ( 1081–1101), Duklja saw its apogee. Mihailo was given the nominal title ''King of Slavs'' by the Pope after having left the Byzantine camp and supported an Uprising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Serbia (early Medieval)
Principality of Serbia (Modern sr-Cyrl-Latn, Кнежевина Србија, Kneževina Srbija, separator=" / "; also known as Principality of Serbs, (Modern sr-Cyrl-Latn, Кнежевина Срба, Kneževina Srba, separator=" / "; ; ) was one of the early medieval states of the Serbs, located in the western regions of Southeastern Europe. It existed from the 8th century up to c. 969–971 and was ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty. Its first ruler known by name was Višeslav who started ruling around 780. While by that time, starting from the year 680–681, the Bulgarian state had taken the lands to the east. Vlastimir resisted and defeated the Bulgarian army in a three-year-war (839–842), and the two powers lived in peace for some decades. Vlastimir's three sons succeeded in ruling Serbia together, although not for long; Serbia became a key part in the power struggle between the Byzantines and Bulgarians, predominantly allied with the Byzantines, which also resulte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical Regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia (region), Bosnia. It presently does not have strictly defined administrative borders; however, in the past it was organized as Sanjak of Herzegovina (1470–1833; 1851–1912) and Herzegovina Eyalet (1833–1851). Bosnia, the larger of the two regions, lies to the north of Herzegovina; the Regions of Croatia, Croatian region of Dalmatia lies to the southwest; the Regions of Montenegro, Montenegrin region of Old Herzegovina lies to the southeast. The land area of Herzegovina is around , or around 23–24% of the country. The largest city is Mostar, in the center of the region. Other large settlements include Trebinje, Široki Brijeg, Ljubuški, Čapljina, Konjic and Posušje. Etymology The Ottomans were the first to officially use the name (E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle Of The Priest Of Duklja
The ''Chronicle of the Priest of Dioclea or Duklja'' ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ljetopis popa Dukljanina, Љетопис попа Дукљанина; ) is the usual name given to a medieval chronicle written in two versions between 1295 and 1301 by an ecclesiastic from Duklja, recently identified as Rudger, Archbishop of Bar. Its oldest preserved copy is in Latin from the 17th century, and modern historians have debated the text's date of composition (mid-12th to late 16th century) and authenticity. It contains some semi-mythical material on the early history of the Western South Slavs. Historians have yet to discount the work as based on inaccuracies and fiction. The postulates are there that Slavs lived in the Balkans from the 5th- to the 12th-century. It recounts the history of Dalmatia and nearby regions from the 5th to the mid-12th century. The section "Life of St. Jovan Vladimir", is believed to be one of the local traditions integrated into the narrative. Authorship and date The wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bosnia
The Kingdom of Bosnia ( / Краљевина Босна), or Bosnian Kingdom (''Bosansko kraljevstvo'' / Босанско краљевство), was a medieval kingdom that lasted for nearly a century, from 1377 to 1463, and evolved out of the Banate of Bosnia, which itself lasted since at least 1154. King Tvrtko I of Bosnia, Tvrtko I (r. 1353–91) acquired portions of western Serbia and most of the Adriatic coast south of the Neretva River. During the late part of his reign, Bosnia became one of the strongest states in the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. However, feudal fragmentation remained important in Bosnia and the Bosnian nobility held significant power, exercising it at the Stanak meetings where members deliberated on matters such as Royal elections, election of the new king or queen and coronations, foreign policy, sale or cession of territory, contracting and signing treaties with neighboring countries, and military issues. The Ottoman Empire Ottoman conquest of Bosnia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosnia And Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest, with a coast on the Adriatic Sea in the south. Bosnia (region), Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Its geography is largely mountainous, particularly in the central and eastern regions, which are dominated by the Dinaric Alps. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city. The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, with permanent human settlement traced to the Neolithic cultures of Butmir culture, Butmir, Kakanj culture, Kakanj, and Vučedol culture, Vučedol. After the arrival of the first Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-Europeans, the area was populated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buna (Neretva)
The Buna ( sr-Cyrl, Буна) is a short river in Bosnia and Herzegovina; it is a left-bank tributary of the Neretva. Its source, Vrelo Bune (''Buna Spring''), is a strong karstic spring located near the village of Blagaj, southeast of Mostar. Vrelo Bune is one of the strongest springs in Europe and has extremely cold water. The Buna flows west for approximately 9 km, starts at Blagaj and, meandering through the villages of Blagaj, Kosor, Malo Polje and Hodbina, joins the Neretva near the settlement Buna. The site of confluence is called Buna Canals. The Bunica river is the main left-bank tributary of the Buna. The Buna is major habitat for an endemic trout species known under its vernacular name as Softmouth trout. See also * Vrelo Bunice * Mostarska Bijela * Hutovo Blato * Daorson Daorson was the capital of the Illyrian tribe of the Daorsi (Ancient Greek Δαόριζοι, Δαούρσιοι; Latin ''Daorsei''). The Daorsi lived in the valley of the Neretva Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bona (Hum)
Blagaj is a historic village and protected heritage site in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the south-eastern region of the Mostar basin, in the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton. It stands at the edge of Bišće plain and is one of the most valuable mixed urban and rural built environments in Bosnia and Herzegovina, distinguished from other similar built environments in its urban layout. Blagaj was most likely named for its mild weather patterns since ''blaga'' in Bosnian means "mild". Blagaj is situated at the spring of the Buna river and a historical '' tekija'' (Dervish monastery). The Blagaj Tekija was built around 1520, with elements of Ottoman architecture and Mediterranean style and is considered a national monument. Blagaj Tekke is a monastery built for the Dervish. Sources Vrelo Bune, the source of the Buna river, is a strong karstic spring. The river flows west for approximately and joins the Neretva near the village Buna. The historic site of the Blagaj Fort (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas. Heraclius's reign was marked by several military campaigns. The year Heraclius came to power, the empire was threatened on multiple frontiers. Heraclius immediately took charge of the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628. The first battles of the campaign ended in defeat for the Byzantines; the Persian army fought their way to the Bosphorus but Constantinople was protected by Walls of Constantinople, impenetrable walls and a strong navy, and Heraclius was able to avoid total defeat. Soon after, he initiated reforms to rebuild and strengthen the military. Heraclius drove the Persians out of Asia Minor and pushed deep into their territory, defeating them decisively in 627 at the Battle of Nineveh (627), Battle of Nineveh. The Persian Shah Khosrow II was overthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byzantine encyclopaedism. Author and background The emperor Constantine VII "Porphyrogenitus" (905–959) was only surviving son of the emperor Leo VI the Wise (886–912). Leo VI gave the crown to young Constantine VII in 908 and he became the co-emperor. Leo VI died in May 912, and his brother and co-emperor Alexander became the ruler of Constantinople, but Alexander died in 913. Constantine VII was too young to rule on his own, and the governorship was created. Later in May 919 Constantine VII married Helena Lekapene, daughter of Romanos Lekapenos. In December 920, Romanos I Lekapenos (920–944) was crowned a co-emperor, but he really took over the imperial reign in Constantinople. From 920, Constantine VII become increasingly distant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |