|
Za'atara
Za'atara ( ar, زعترة) is a Palestinian town located southeast of Bethlehem. The town is in the Bethlehem Governorate central West Bank. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, the town had a population of over 6,289 in 2007.2007 PCBS Census . p.118. History In the wake of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and after the |
Bethlehem Governorate
The Bethlehem Governorate ( ar, محافظة بيت لحم, Muḥāfaẓat Bayt Laḥm) is one of 16 Governorates of Palestine. It covers an area of the West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Its principal city and district capital is Bethlehem. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, its population was estimated to 199,463 in 2012. Geography According to United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the governorate has a total area of around 660 km². Due to the occupation by Israel, Palestinians can only use 13% of the area and much of that is fragmented as of May 2009. Politics Politically, the Bethlehem Governorate is something of a stronghold of the Palestinian left. At the 2006 Palestinian legislative election the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine and The Alternative both had their best votes there. Its current governor is Salah al-Tamari. Localities The governorate consists of 10 municipalities, 3 refugee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used List of writing systems by adoption, writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the third-most by number of users (after the Latin script, Latin and Chinese characters, Chinese scripts). The script was first used to write texts in Arabic, most notably the Quran, the holy book of Islam. With the religion's spread, it came to be used as the primary script for many language families, leading to the addition of new letters and other symbols. Such languages still using it are: Persian language, Persian (Western Persian, Farsi/Dari), Malay language, Malay (Jawi alphabet, Jawi), Uyghur language, Uyghur, Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Punjabi language, Punjabi (Shahmukhi), Sindhi language, Sindhi, Balti language, Balti, Balochi language, Balochi, Pashto, Luri language, Lurish, Urdu, Kashmiri lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
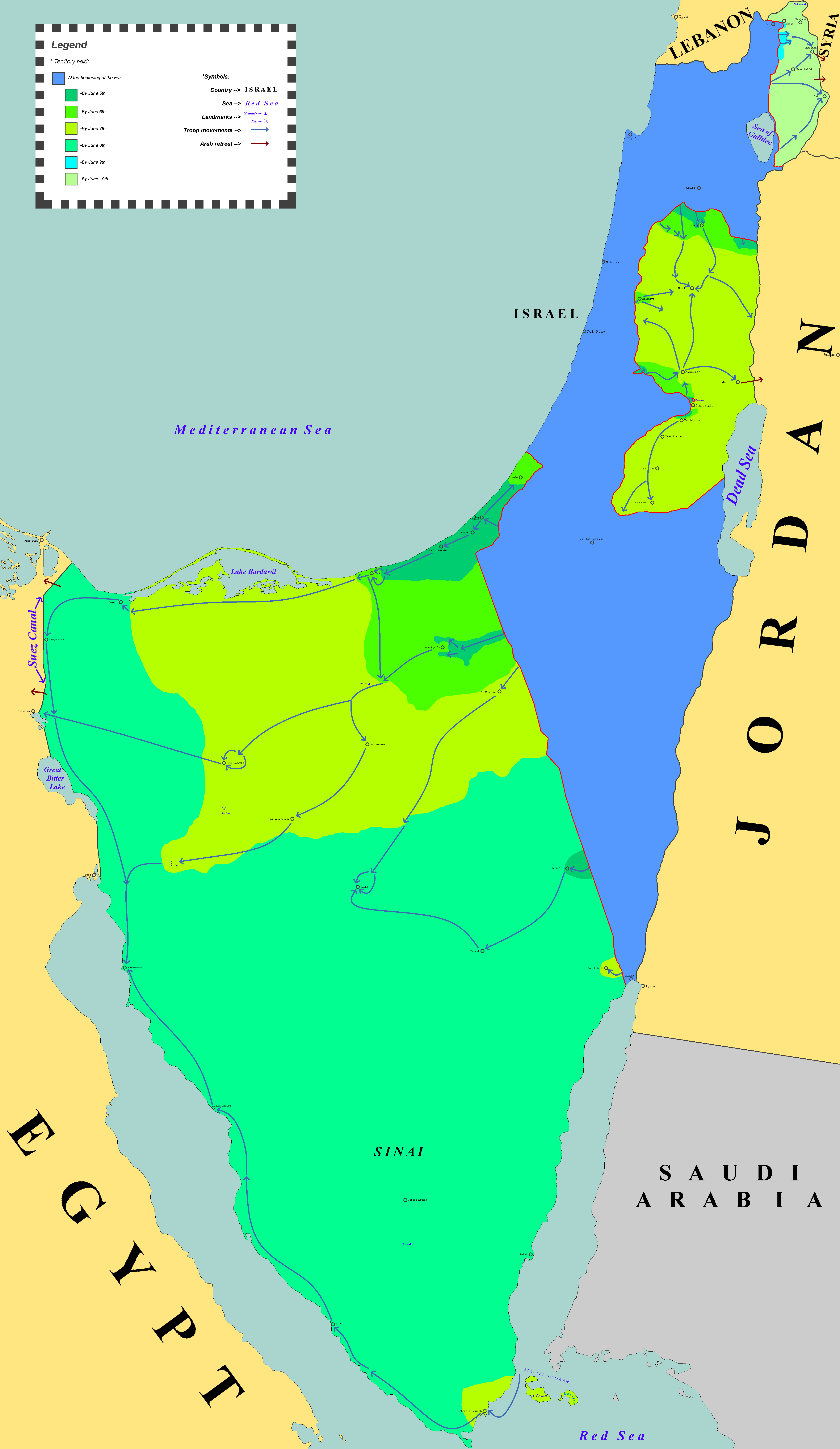
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns In The West Bank
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than city, cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German language, German word , the Dutch language, Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh language, Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Research Institute–Jerusalem
The Applied Research Institute - Jerusalem (ARIJ; ar, معهد الابحاث التطبيقية - القدس) is a Palestinian NGO founded in 1990 with its main office in Bethlehem in the West Bank. ARIJ is actively working on research projects in the fields of management of natural resources, water management, sustainable agriculture and political dynamics of development in the Palestinian Territories. Projects POICA Together with the Land Research Center (LRC), ARIJ runs a joint project named ''POICA, Eye on Palestine–Monitoring Israeli Colonizing activities in the Palestinian Territories''. The project, funded by the European Union, inspects and scrutinizes Israeli colonizing activities in the West Bank and Gaza, and disseminates the related information to policy makers in the European countries and to the general public. Sustainable waste treatment In 2011 ARIJ, along with the TTZ Bremerhaven, the University of Extremadura, and the Institute on Membrane Technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El David
Nokdim ( he, נוֹקְדִים, ''lit.'' Shepherds) is an Israeli settlement organized as a community settlement in the West Bank. Located south of Bethlehem in the northern Judean Mountains, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gush Etzion Regional Council. In it had a population of . The international community considers Israeli settlements in the West Bank illegal under international law, but the Israeli government disputes this. A mixed community of religious and secular Jews, both native Israelis and immigrants, Nokdim is home to the religious pre-army Mechina Magen Shaul, established in 1996. History Nokdim was founded on 5 July 1982 by residents of Tekoa. The settlement was originally named ''El-David'' in memory of two residents of Tekoa - Eli Pressman, a new immigrant from France who was killed in the 1982 Lebanon War, and David Rosenfeld, manager of the tourist site at Herodium who was murdered in July 1982 by two of his Palestinian employees. The name was rejec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Expropriation In The West Bank
Land expropriation in the West Bank refers to the practices employed by the State of Israel to take over Palestinian land in the occupied West Bank. From 1969 to 2019 Israel had issued over 1,150 military seizure orders alone to that purpose. Overview The mechanisms by which Israel seizes or expropriates West Bank land were set forth in a detailed work by B'Tselem in 2002 and many practices outlined there were confirmed in the official Israeli Sasson Report of 2005, which focused on government subsidies and support for the creation of illegal Israeli outposts in knowing contravention of Israel's own laws. This was done after the government had officially frozen new settlements, in both the Oslo Accords and an undertaking by Ariel Sharon. Mechanisms According to the analysis made by B'Tselem in 2002, there have been five mechanisms adopted to take over Palestinian land. Seizure for Military Needs According to Customary international humanitarian law the expropriation of reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area C (West Bank)
Area C ( he, שטח C; ar, منطقة ج) is an Oslo II administrative division of the West Bank, defined as "areas of the West Bank outside Areas A and B". Area C constitutes about 61 percent of the West Bank territory; the area was committed in 1995 under the Oslo II Accord to be "gradually transferred to Palestinian jurisdiction" (with an option for land swaps under a final agreement), but such transfer did not happen. Area C (excluding East Jerusalem), which along with Area B is under Israeli military control since June 1967, is home to roughly 400,000 Israeli settlers, and approximately 300,000 Palestinians; who live in more than 500 residential areas located partially or fully in Area C. The Jewish population in Area C is administered by the Israeli Judea and Samaria Area administration, whereas the Palestinian population is directly administered by the Israeli Coordinator of Government Activities in the Territories (and indirectly by the Palestinian National Authorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area B
The Palestinian enclaves are areas in the West Bank designated for Palestinians under a variety of U.S. and Israeli-led proposals to end the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The enclaves are often compared to the nominally self-governing black homelands created in apartheid-era South Africa, and are therefore referred to as bantustans. They have been referred to figuratively as the Palestinian archipelago, among other terms. The "islands" first took official form as Areas A and B under the 1995 Oslo II Accord. This arrangement was explicitly intended to be temporary with Area C (the rest of the West Bank) to "be gradually transferred to Palestinian jurisdiction" by 1997; however, no such transfers were made. The area of the West Bank currently under partial civil control of the Palestinian National Authority is composed of 165 "islands". The creation of this arrangement has been described by Israeli journalist Amira Hass as "the most outstanding geopolitical occurrence of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area A
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while ''surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve (a one-dimensional concept) or the volume of a solid (a three-dimensional concept). The area of a shape can be measured by comparing the shape to squares of a fixed size. In the International System of Units (SI), the standard unit of area is the square metre (written as m2), which is the area of a square whose sides are one metre long. A shape with an area of three square metres would have the same area as three such squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oslo II Accord
The Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip commonly known as Oslo II or Oslo 2, was a key and complex agreement in the Israeli–Palestinian peace process. Because Oslo II was signed in Taba, it is sometimes called the Taba Agreement. The Oslo Accords envisioned the establishment of a Palestinian interim self-government in the Palestinian territories. Oslo II created the Areas A, B and C in the West Bank. The Palestinian Authority was given some limited powers and responsibilities in the Areas A and B and a prospect of negotiations on a final settlement based on Security Council Resolutions 242 and 338. The Accord was officially signed on 28 September 1995. Historical context The Oslo II Accord was first signed in Taba (in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt) by Israel and the PLO on 24 September 1995 and then four days later on 28 September 1995 by Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat and witnessed by US President Bill Clinton as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levy Economics Institute
Founded in 1986 as the Jerome Levy Economics Institute, the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College is a nonprofit, nonpartisan public policy think tank. The purpose of its research and other activities is to enable scholars and leaders in business, labor, and government to work together on problems of common interest. Its findings are disseminated—via publications, conferences, seminars, congressional testimony, and partnerships with other nonprofits—to a global audience of public officials, private sector executives, academics, and the general public. Through this process of scholarship, analysis, and informed debate, the Levy Institute generates public policy responses to economic problems. The Levy Institute is housed on the campus of Bard College in Annandale-on-Hudson, New York, located 90 miles north of New York City. Blithewood, a Georgian-style manor at the campus's western edge, is the institute's main research and conference facility. Designed as a private reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

