|
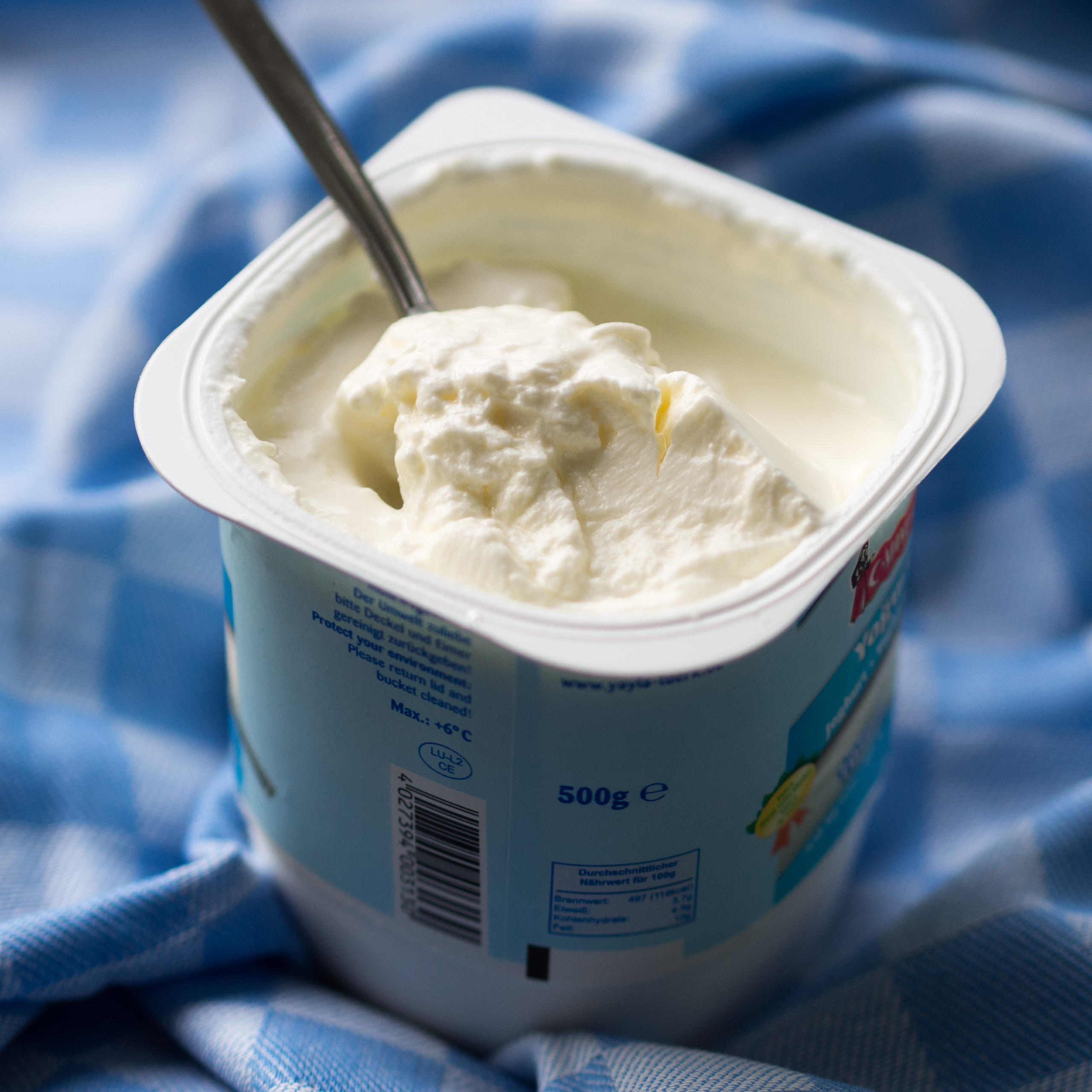
Yogurt
Yogurt (; , from , ; also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bacteria produces lactic acid, which acts on milk protein to give yogurt its texture (food), texture and characteristic tart flavor. Cow's milk is most commonly used to make yogurt. Milk from water buffalo, goats, sheep, ewes, mares, camels, and yaks is also used to produce yogurt. The milk used may be Milk#Creaming and homogenization, homogenized or not. It may be pasteurized or raw milk, raw. Each type of milk produces substantially different results. Yogurt is produced using a culture of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, ''Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' subsp. ''bulgaricus'' and ''Streptococcus thermophilus'' bacteria. Other Lactobacillus, lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium, bifidobacteria are sometimes added during or after culturing yogurt. Some countries require yogurt to contain a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
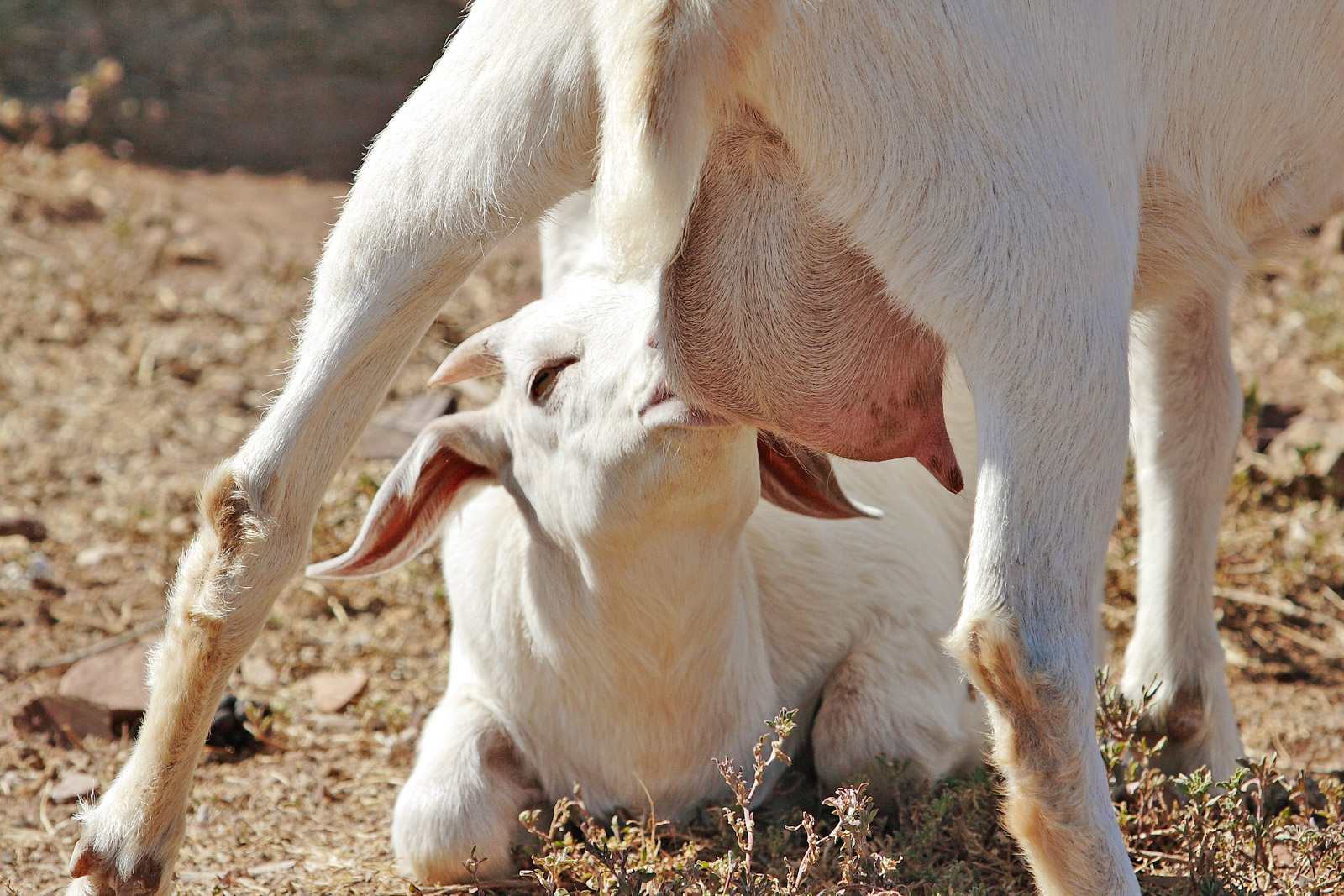
Dairy Product
Dairy products or milk products are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, goat, nanny goat, and Sheep, ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food around the world such as yogurt, cheese, milk and butter. A facility that produces dairy products is a ''dairy''. Dairy products are consumed worldwide to varying degrees. Some people avoid some or all dairy products because of lactose intolerance, veganism, Environmental issues, environmental concerns, other health reasons or beliefs. Types of dairy product Milk Milk is produced after optional Homogenization (chemistry), homogenization or pasteurization, in several grades after standardization of the fat level, and possible addition of the bacteria ''Streptococcus lactis'' and ''Leuconostoc citrovorum''. Milk can be broken down into several different categories based on type of product produced, including cream, butter, cheese, infant formula, and yogurt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Thermophilus
''Streptococcus thermophilus'' formerly known as ''Streptococcus salivarius ''subsp.'' thermophilus'' is a gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive bacterium, and a lactic acid fermentation, fermentative facultative anaerobic organism, facultative anaerobe, of the ''Streptococcus viridans, viridans'' group. It tests negative for cytochrome, oxidase, and catalase, and positive for alpha-hemolytic activity. It is motility, non-motile and does not form endospores. ''S. thermophilus'' is fimbria (bacteriology), fimbriated. It is also classified as a lactic acid bacteria, lactic acid bacterium. ''S. thermophilus'' is found in fermented milk products and is generally used in the production of yogurt, alongside Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, ''Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' subsp. ''bulgaricus''. The two species are synergistic, and ''S. thermophilus'' probably provides ''L. d. bulgaricus'' with folic acid and formic acid, which it uses for purine synthesis. ''S. thermophil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
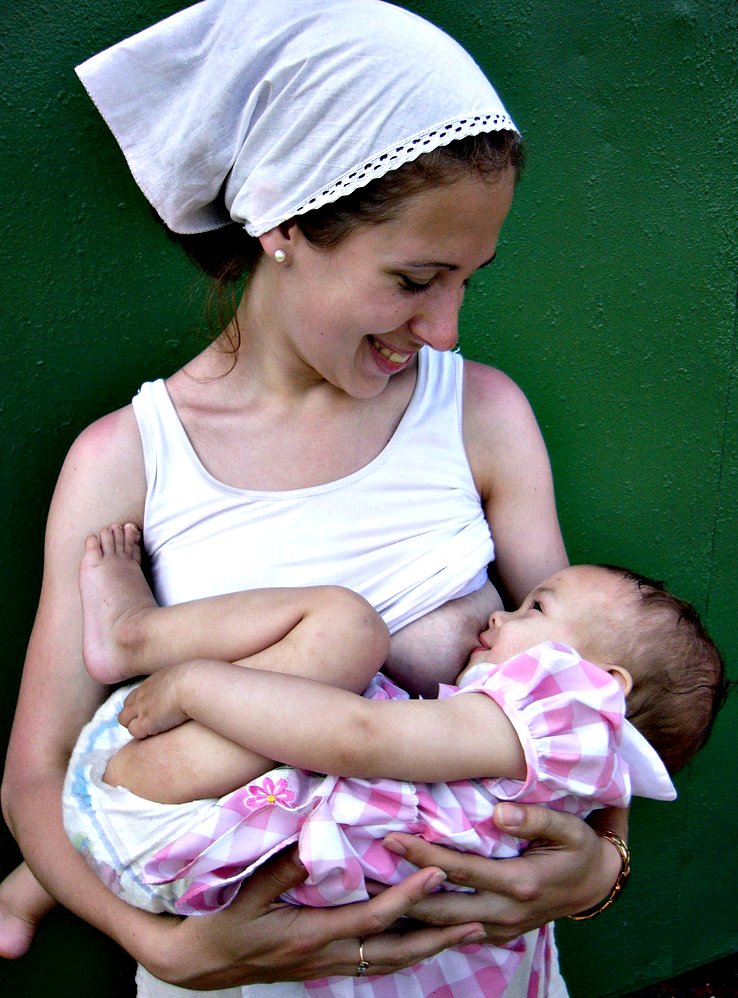
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies and immune-modulating components that milk immunity, strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, Milking, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygala
Oxygala () was a dairy product consumed in the cuisines of ancient Greece and Rome. Oxygala was a form of yogurtDalby, p. 66 and was usually eaten with honey. See also * Greek yogurt * List of dairy products This is a list of dairy products. A dairy product is food produced from the milk of mammals. A production plant for the processing of milk is called a dairy or a dairy factory. Dairy farming is a class of agriculture, agricultural, or an animal hu ... References Bibliography * Ancient Greek cuisine Ancient dishes Condiments Food in ancient Rome {{food-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermented Dairy Product
Fermented milk products or fermented dairy products, also known as cultured dairy foods, cultured dairy products, or cultured milk products, are dairy foods that have been made by fermenting milk with lactic acid bacteria such as ''Lactobacillus'', '' Lactococcus'', and '' Leuconostoc''. The fermentation process increases the shelf life of the product while enhancing its taste and improving the digestibility of its milk. There is evidence that fermented milk products have been produced since around 10,000 BC. A range of different Lactobacilli strains has been grown in laboratories allowing for many cultured milk products with different flavors and characteristics. These bacteria allow the production of many fermented milks such as cheese, yogurt, kefir, butter Most of the bacteria needed to make these product thrive under specific conditions, meaning that the right environment is crucial to the making of the fermented products. Products Many different types of cultured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk Protein
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies and immune-modulating components that strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or formula) should have two servings of milk products a day, and more than six billion people worldwide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
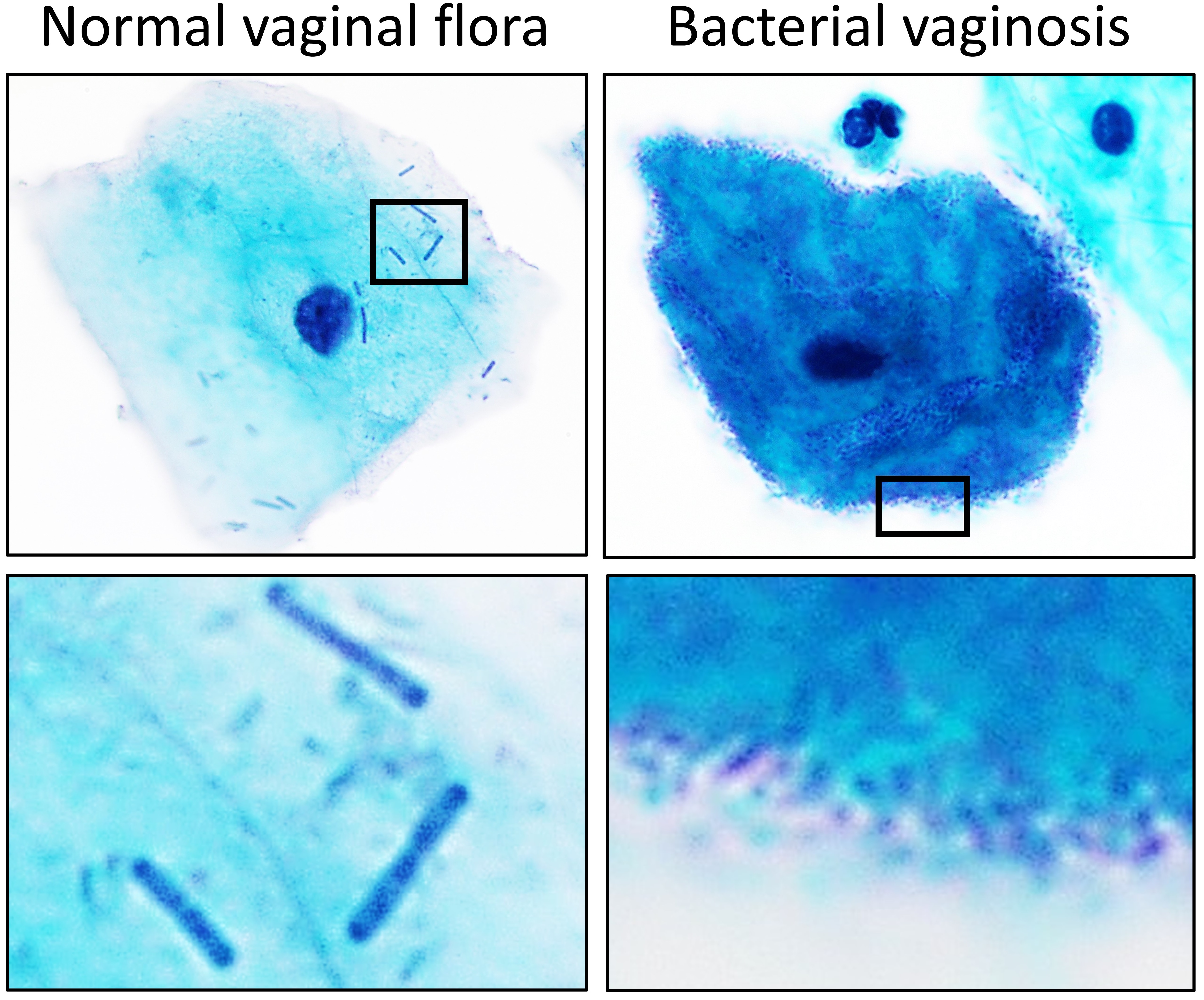
Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Subsp
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist in harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation (food)
In food processing, fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates to alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms—yeasts or bacteria—without an oxidizing agent being used in the reaction. Fermentation usually implies that the action of microorganisms is desired. The science of fermentation is known as zymology or zymurgy. The term "fermentation" sometimes refers specifically to the chemical conversion of sugars into ethanol, producing alcoholic drinks such as wine, beer, and cider. However, similar processes take place in the leavening of bread (CO2 produced by yeast activity), and in the preservation of sour foods with the production of lactic acid, such as in sauerkraut and yogurt. Humans have an enzyme that gives us an enhanced ability to break down ethanol. Other widely consumed fermented foods include vinegar, olives, and cheese. More localized foods prepared by fermentation may also be based on beans, grain, vegetables, fruit, honey, dairy products, and fish. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
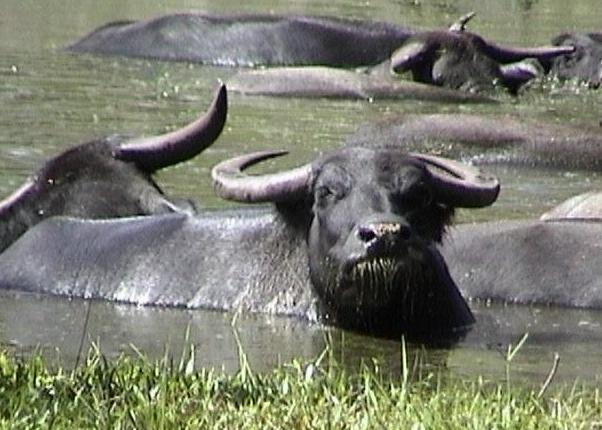
Water Buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called domestic water buffalo, Asian water buffalo and Asiatic water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also kept in Italy, the Balkans, Australia, North America, South America and some African countries. Two extant Type (biology), types of water buffalo are recognized, based on Morphology (biology), morphological and Ethology, behavioural criteria: the river buffalo of the Indian subcontinent and further west to the Balkans, Egypt and Italy; and the swamp buffalo from Assam in the west through Southeast Asia to the Yangtze Valley of China in the east. The wild water buffalo (''Bubalus arnee'') is most probably the ancestor of the domestic water buffalo. Results of a phylogenetic study indicate that the river-type water buffalo probably originated in western India and was domesticated about 6,300 years ago, whereas the swamp-type originated independently from Mainland Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' ( ), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat ( lamb, hogget or mutton), and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate (or the lactate anion). The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl. In solution, it can ionize by a loss of a proton to produce the lactate ion . Compared to acetic acid, its p''K'' is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid is ten times more acidic than acetic acid. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |