|
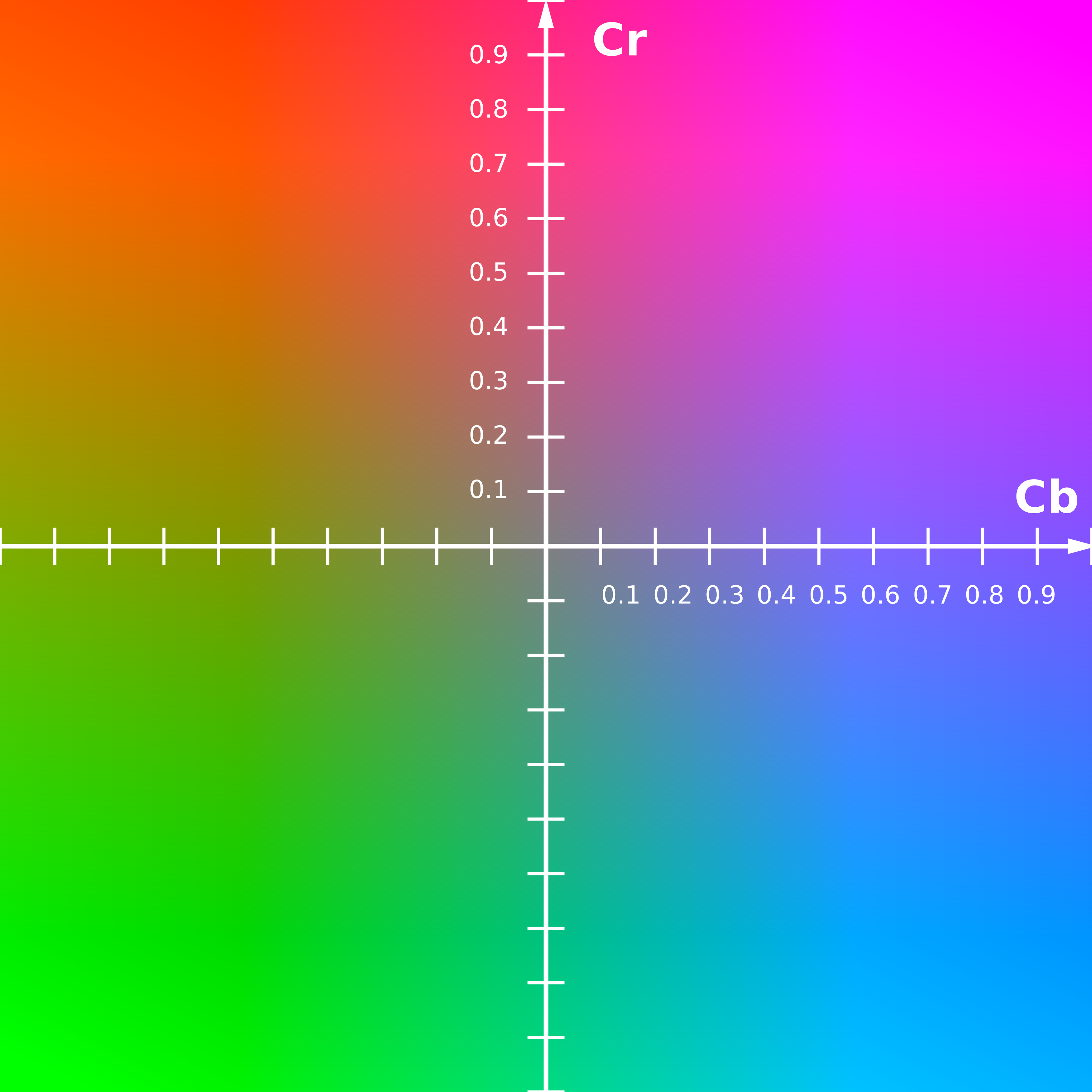
Y'CbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in digital video and photography systems. Like YPBPR, it is based on RGB primaries; the two are generally equivalent, but YCBCR is intended for digital video, while YPBPR is designed for use in analog systems. Y′ is the luma component, and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components. Luma Y′ (with prime) is distinguished from luminance Y, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries. Y′CbCr color spaces are defined by a mathematical coordinate transformation from an associated RGB primaries and white point. If the underlying RGB color space is absolute, the Y′CbCr color space is an absolute color space as well; conversely, if the RGB space is ill-defined, so is Y′CbCr. The transformation is defined in equations 32, 33 in ITU-T H.273. Rationale Black and white t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chroma Subsampling
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for Chrominance, chroma information than for luma (video), luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance. It is used in many video and still image encoding schemesboth analog and digitalincluding in JPEG encoding. Rationale Digital signals are often compressed to reduce file size and save transmission time. Since the human visual system is much more sensitive to variations in brightness than color, a video system can be optimized by devoting more bandwidth to the luma (video), luma component (usually denoted Y'), than to the color difference components Cb and Cr. In compressed images, for example, the 4:2:2 Y'CbCr scheme requires two-thirds the bandwidth of non-subsampled "4:4:4" R'G'B'. This reduction results in almost no visual difference as perceived by the viewer. How subsampling works The Visual perception, human vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in digital video and digital photography, photography systems. Like YPbPr, YPBPR, it is based on RGB primaries; the two are generally equivalent, but YCBCR is intended for digital video, while YPBPR is designed for use in Analogue electronics, analog systems. Y′ is the Luma (video), luma component, and CB and CR are the B-Y, blue-difference and R-Y, red-difference chrominance, chroma components. Luma Y′ (with Prime (symbol), prime) is distinguished from relative luminance, luminance Y, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries. Y′CbCr color spaces are defined by a mathematical coordinate transformation from an associated RGB primaries and white point. If the underlying RGB color spaces, RGB color space is absolute, the Y′CbCr color space is an absolute color space as well; conversely, if the RGB spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Image Pipeline
An image pipeline or video pipeline is the set of components commonly used between an image source (such as a camera, a scanner, or the rendering engine in a computer game), and an image renderer (such as a television set, a computer screen, a computer printer or cinema screen), or for performing any intermediate digital image processing consisting of two or more separate processing blocks. An image/video pipeline may be implemented as computer software, in a digital signal processor, on an FPGA, or as fixed-function ASIC. In addition, analog circuits can be used to do many of the same functions. Typical components include image sensor corrections (including debayering or applying a Bayer filter), noise reduction, image scaling, gamma correction, image enhancement, colorspace conversion (between formats such as RGB, YUV or YCbCr), chroma subsampling, framerate conversion, image compression/video compression (such as JPEG), and computer data storage/data transmission. Typical g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog signal, analog or a Digital data, digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical Palette (computing), color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the Natural Color System, NCS System, Adobe RGB color space, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
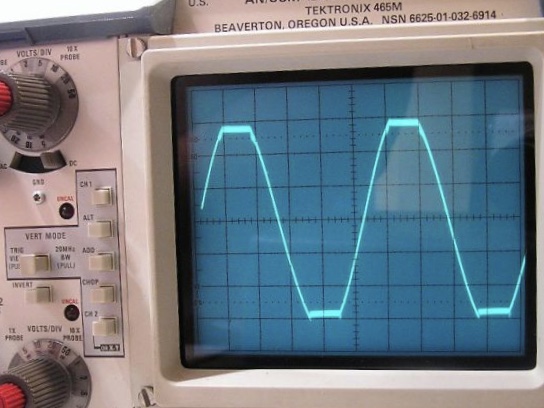
Clipping (signal Processing)
Clipping is a form of distortion that limits a signal once it exceeds a threshold. Clipping may occur when a signal is recorded by a sensor that has constraints on the range of data it can measure, it can occur when a signal is digitized, or it can occur any other time an analog or digital signal is transformed, particularly in the presence of gain or overshoot and undershoot. Clipping may be described as hard, in cases where the signal is strictly limited at the threshold, producing a flat cutoff; or it may be described as soft, in cases where the clipped signal continues to follow the original at a reduced gain. Hard clipping results in many high-frequency harmonics; soft clipping results in fewer higher-order harmonics and intermodulation distortion components. Audio In the frequency domain, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high-frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a square wave). The extra high-frequency weighting of the signal could ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods, which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission bandwidth. While MPEG-2 is not as efficient as newer standards such as H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC, backwards compatibility with existing hardware and software means it is still widely used, for example in over-the-air digital television broadcasting and in the DVD-Video standard. Main characteristics MPEG-2 is widely used as the format of digital television signals that are broadcast by terrestrial (over-the-air), cable, and direct broadcast satellite TV systems. It also specifies the format of movies and other programs that are distributed on DVD and similar discs. TV stations, TV receivers, DVD players, and other equipment are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France as well as the flag of monarchist France from 1815 to 1830, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek temples and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''Psychologie de la couleur – effets et symboliques'', pp. 105–26. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus the Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a Nonlinearity, nonlinear operation used to encode and decode Relative luminance, luminance or CIE 1931 color space#Tristimulus values, tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following Power law, power-law expression: : V_\text = A V_\text^\gamma, where the non-negative real input value V_\text is raised to the power \gamma and multiplied by the constant ''A'' to get the output value V_\text. In the common case of , inputs and outputs are typically in the range 0–1. A gamma value \gamma 1 is called a ''decoding gamma'', and the application of the expansive power-law nonlinearity is called gamma expansion. Explanation Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. The human perception of brightness (lightness), un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Video
Video is an Electronics, electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving picture, moving image, visual Media (communication), media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, Display aspect ratio, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities, and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcasts, magnetic tape, optical discs, Video file format, computer files, and Streaming media, network streaming. Etymology The word ''video'' comes from the Latin verb ''video,'' meaning to see or ''videre''. And as a noun, "that which is displayed on a (television) screen," History Analog video Video developed from facsimile systems developed in the mid-19th century. Early mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model (e.g., additive, subtractive) that uses the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina to be able to accurately display the intended colors. The most common color mixing models are the additive primary colors (red, green, blue) and the subtractive primary colors (cyan, magenta, yellow). Red, yellow and blue are also commonly taught as primary colors (usually in the context of subtractive color mixing as opposed to additive color mixing), despite some criticism due to its lack of scientific basis. Primary colors can also be conceptual (not necessarily real), either as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |