|
XX Male
XX male syndrome, also known as de la Chapelle syndrome or 46,XX testicular disorder of sex development (or 46,XX DSD) is a rare intersex condition in which an individual with a 46,XX karyotype develops a male phenotype.updated 2015 In 90 percent of these individuals, the syndrome is caused by the Y chromosome's '' SRY'' gene, which triggers male reproductive development, being atypically included in the crossing over of genetic information that takes place between the pseudoautosomal regions of the X and Y chromosomes during meiosis in the father. When the X with the ''SRY'' gene combines with a normal X from the mother during fertilization, the result is an XX genetic male. Less common are ''SRY''-negative individuals, who appear to be XX genetic females, which is caused by a mutation in an autosomal or X chromosomal gene. Masculinization in those with the condition is variable, and those with the condition are sterile. This syndrome is diagnosed and occurs in appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert De La Chapelle
Albert Fredrik de la Chapelle, MD, Ph.D (11 February 1933 – 10 December 2020) was a Finnish human geneticist, long-time head of Finland's first Department of Medical Genetics at the University of Helsinki, and subsequently professor of Human Cancer Genetics at Ohio State University. He was best known for his role in the elucidation of the genetics of hereditary colorectal cancer and Lynch syndrome. Biography Personal life and education Albert de la Chapelle was born in 1933, Helsinki, one of three sons (along with Claës-Henrik and Gustaf) of Claës Carl Fredrik René de la Chapelle (1900–1974) and Stina Serlachius (1902–1984). He spent his early childhood on his parents' apple growing estate. He attended school locally, transferring later to high school in Helsinki. Graduating from high school in 1950 he enrolled directly into medical school at the University of Helsinki, obtaining his MD in 1957 after a hiatus to complete 11 months of military service resulting in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
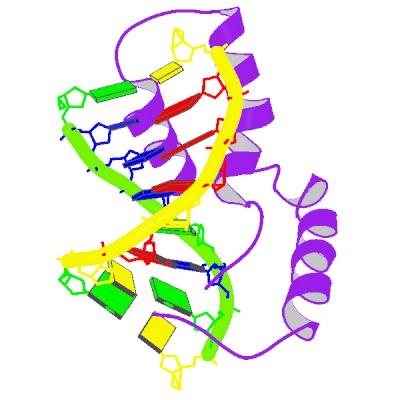
Testis-determining Factor
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein (also known as gene-regulatory protein/transcription factor) encoded by the ''SRY'' gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals ( placentals and marsupials). ''SRY'' is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype. SRY is a member of the SOX (SRY-like box) gene family of DNA-binding proteins. When complexed with the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein, SRY acts as a transcription factor that causes upregulation of other transcription factors, most importantly SOX9. Its expression causes the development of primary sex cords, which later develop into seminiferous tubules. These cords form in the central part of the yet-undifferentiated gonad, turning it into a testis. The now-induced Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets (mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA) in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues. Probes – RNA and DNA In biology, a probe is a single strand of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a nucleotide sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include Karyotype, karyotyping, analysis of G banding, G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as Fluorescence in situ hybridization, fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramesonephric Duct
The paramesonephric ducts (or Müllerian ducts) are paired ducts of the embryo in the reproductive system of humans and other mammals that run down the lateral sides of the genital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. They form in both sexes during 6th week of fetal development. In the female, go on to form the fallopian tubes/oviducts, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina. In males fetuses, they are normally made to regress by anti-Müllerian hormone which begins to be secreted by the testes during 8th week of fetal development. Each maramesonephric duct is situated just lateral to the mesonephric ducts, mesonephric ducts (Wolffian duct) of the same side. Development The female reproductive system is composed of two embryological segments: the urogenital sinus and the paramesonephric ducts. The two are conjoined at the sinus tubercle. Paramesonephric ducts are present on the embryo of both sexes. Only in females do they d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Canal
The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body (one on each side of the midline), which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. The canals are approximately 4 to 6 cm long, angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually called the "anterior wall", "inferior wall ("floor")", "superior wall ("roof")", and "po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WNT4
WNT4 is a secreted protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''WNT4'' gene, found on chromosome 1. It promotes female sex development and represses male sex development. Loss of function may have consequences, such as female to male sex reversal. Function The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and embryogenesis. Pregnancy WNT4 is involved in many features of pregnancy as a downstream target of BMP2. For example, it regulates endometrial stromal cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. These processes are all necessary for the development of an embryo. Ablation in female mice results in subfertility, with defects in implantation and decidualization. For instance, there is a decrease in responsiveness to progesterone signaling. Furthermore, postnatal uterine differentiatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SF1 (gene)
Splicing factor 1 also known as zinc finger protein 162 (ZFM162) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SF1'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Splicing factor SF1 is involved in the ATP-dependent formation of the spliceosome complex. SF1 gene is necessary to make the bipotential gonad; but while SF1 levels decline in the genital ridge of XX mouse embryos, the SF1 gene stays on the developing testes. SF 1 (transcription factor) appears to be active in masculining both the Leydig cells and Sertoli cells. In Sertoli cells with the SOX9 protein it elevates the level of AMH transcription. In Leydig cells it activates the gene encoding the enzyme that make testosterone hormone. Interactions SF1 (gene) has been shown to interact with Ewing sarcoma break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Allele
A null allele is a nonfunctional allele (a variant of a gene) caused by a genetic mutation. Such mutations can cause a complete lack of production of the associated gene product or a product that does not function properly; in either case, the allele may be considered nonfunctional. A null allele cannot be distinguished from deletion of the entire locus solely from phenotypic observation. A mutant allele that produces no RNA transcript is called an RNA null (shown by Northern blotting or by DNA sequencing of a deletion allele), and one that produces no protein is called a protein null (shown by Western blotting). A genetic null or amorphic allele has the same phenotype when homozygous as when heterozygous with a deficiency that disrupts the locus in question. A genetic null allele may be both a protein null and an RNA null, but may also express normal levels of a gene product that is nonfunctional due to mutation. Null alleles can have lethal effects depending on the importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOX9
Transcription factor SOX-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOX9'' gene. Function SOX-9 recognizes the sequence CCTTGAG along with other members of the HMG-box class DNA-binding domain, DNA-binding proteins. It is expressed by proliferating but not hypertrophic chondrocytes that is essential for differentiation of precursor cells into chondrocytes and, with steroidogenic factor 1, regulates transcription of the anti-Müllerian hormone (Anti-Müllerian hormone, AMH) gene. SOX-9 also plays a pivotal role in male sexual development; by working with Sf1, SOX-9 can produce AMH in Sertoli cells to inhibit the creation of a female reproductive system. It also interacts with a few other genes to promote the development of male sexual organs. The process starts when the transcription factor testis determining factor (encoded by the sex-determining region SRY of the Y chromosome) activates SOX-9 activity by binding to an enhancer (genetics), enhancer sequence Upstream and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRY Gene
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein (also known as gene-regulatory protein/transcription factor) encoded by the ''SRY'' gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals ( placentals and marsupials). ''SRY'' is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype. SRY is a member of the SOX (SRY-like box) gene family of DNA-binding proteins. When complexed with the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein, SRY acts as a transcription factor that causes upregulation of other transcription factors, most importantly SOX9. Its expression causes the development of primary sex cords, which later develop into seminiferous tubules. These cords form in the central part of the yet-undifferentiated gonad, turning it into a testis. The now-induced L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |