|
X-ray Lithography
X-ray lithography is a process used in semiconductor device fabrication industry to selectively remove parts of a thin film of photoresist. It uses X-rays to transfer a geometric pattern from a mask to a light-sensitive chemical photoresist, or simply "resist," on the substrate to reach extremely small topological size of a feature. A series of chemical treatments then engraves the produced pattern into the material underneath the photoresist. It's less commonly used in commercial production due to prohibitively high costs of materials (such as gold used for X-rays blocking) etc. Mechanisms X-ray lithography originated as a candidate for next-generation lithography for the semiconductor industry, with batches of microprocessors successfully produced. Having short wavelengths (below 1 nm), X-rays overcome the diffraction limits of optical lithography, allowing smaller feature sizes. If the X-ray source isn't collimated, as with a synchrotron radiation, elementary co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XRL Currents )
{{disambiguation ...
XRL may refer to: * Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link, a high-speed railway line connecting Beijing and Hong Kong * Hong Kong West Kowloon railway station, Hong Kong, Immigration Department station code XRL * X-ray laser, a device that uses stimulated emission (The acronym can refer to these in either in the general sense, or as a part of the Strategic Defense Initiative , Project Excalibur Project Excalibur was a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) Cold Warera research program to develop an X-ray laser system as a ballistic missile defense (BMD) for the United States. The concept involved packing large numbers of expendab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
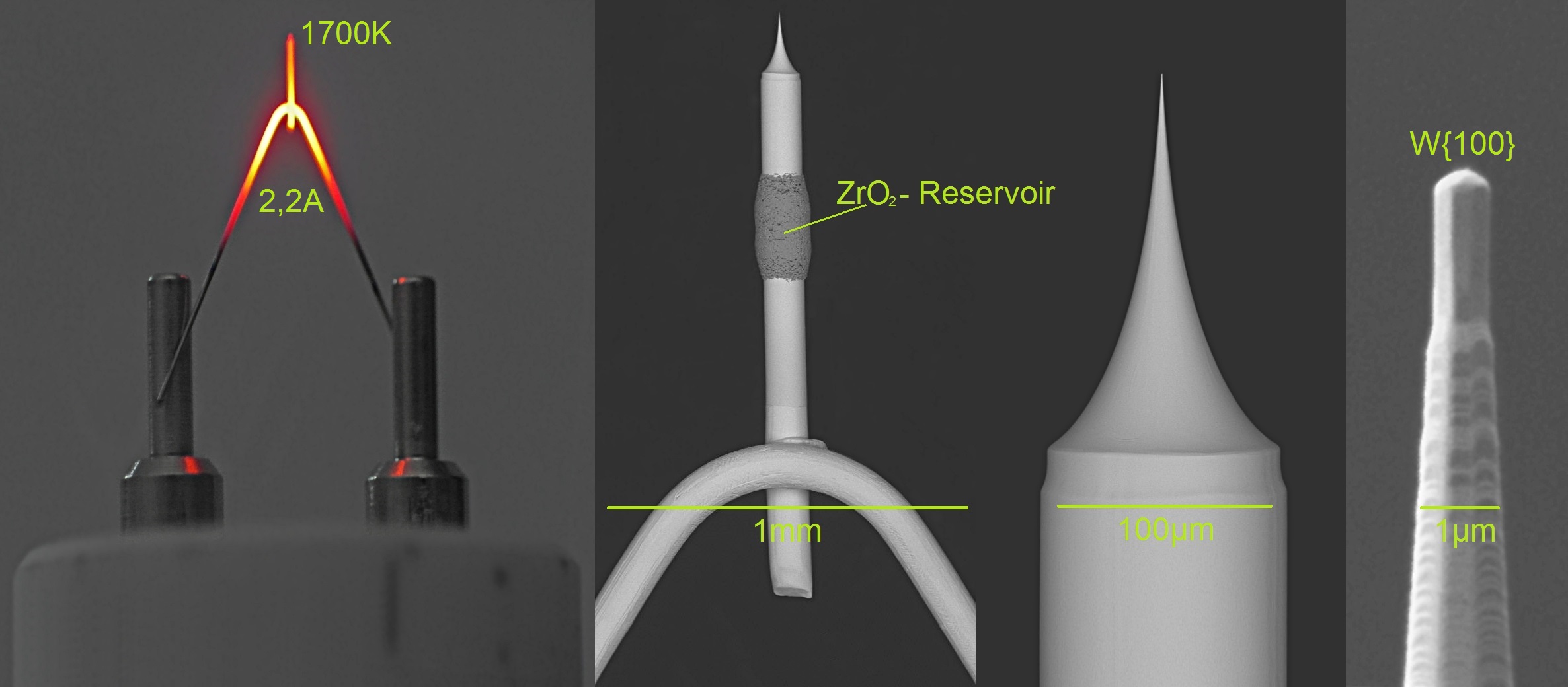
Field Electron Emission
Field electron emission, also known as field emission (FE) and electron field emission, is emission of electrons induced by an electrostatic field. The most common context is field emission from a solid surface into a vacuum. However, field emission can take place from solid or liquid surfaces, into a vacuum, a fluid (e.g. air), or any non-conducting or weakly conducting dielectric. The field-induced promotion of electrons from the valence to conduction band of semiconductors (the Zener effect) can also be regarded as a form of field emission. The terminology is historical because related phenomena of surface photoeffect, thermionic emission (or Richardson–Dushman effect) and "cold electronic emission", i.e. the emission of electrons in strong static (or quasi-static) electric fields, were discovered and studied independently from the 1880s to 1930s. When field emission is used without qualifiers it typically means "cold emission". Field emission in pure metals occurs in high el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. STM senses the surface by using an extremely sharp conducting tip that can distinguish features smaller than 0.1 nm with a 0.01 nm (10 pm) depth resolution. This means that individual atoms can routinely be imaged and manipulated. Most microscopes are built for use in ultra-high vacuum at temperatures approaching zero kelvin, but variants exist for studies in air, water and other environments, and for temperatures over 1000 °C. STM is based on the concept of quantum tunneling. When the tip is brought very near to the surface to be examined, a bias voltage applied between the two allows electrons to tunnel through the vacuum separating them. The resulting ''tunneling current'' is a function of the tip position, app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac Statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac distribution of particles over energy states. It is named after Enrico Fermi and Paul Dirac, each of whom derived the distribution independently in 1926 (although Fermi derived it before Dirac). Fermi–Dirac statistics is a part of the field of statistical mechanics and uses the principles of quantum mechanics. F–D statistics applies to identical and indistinguishable particles with half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, etc.), called fermions, in thermodynamic equilibrium. For the case of negligible interaction between particles, the system can be described in terms of single-particle energy states. A result is the F–D distribution of particles over these states where no two particles can occupy the same state, which has a considerable effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Free Path
In physics, mean free path is the average distance over which a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, or a photon) travels before substantially changing its direction or energy (or, in a specific context, other properties), typically as a result of one or more successive collisions with other particles. Scattering theory Imagine a beam of particles being shot through a target, and consider an infinitesimally thin slab of the target (see the figure). The atoms (or particles) that might stop a beam particle are shown in red. The magnitude of the mean free path depends on the characteristics of the system. Assuming that all the target particles are at rest but only the beam particle is moving, that gives an expression for the mean free path: :\ell = (\sigma n)^, where is the mean free path, is the number of target particles per unit volume, and is the effective cross-sectional area for collision. The area of the slab is , and its volume is . The typical number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auger Electron Spectroscopy
A Hanford scientist uses an Auger electron spectrometer to determine the elemental composition of surfaces. Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. It is a form of electron spectroscopy that relies on the Auger effect, based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal ''Zeitschrift für Physik'' in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in X-ray spectroscopy data. Since 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
Extreme ultraviolet lithography (also known as EUV or EUVL) is an optical Photolithography, lithography technology used in steppers, machines that make integrated circuits (ICs) for computers and other electronic devices. It uses a range of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) wavelengths, roughly spanning a 2% Full width at half maximum, FWHM bandwidth about 13.5Nanometre, nm, to produce a pattern by exposing reflective photomask to UV light which gets reflected onto a substrate covered by photoresist. It is widely applied in semiconductor device fabrication process. As of 2022, ASML Holding is the only company who produces and sells EUV systems for chip production, targeting 5 nm and 3 nm. At the 2019 International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), TSMC reported use of EUV for 5 nm in contact, via, metal line, and cut layers, where the cuts can be applied to fins, gates or metal lines. At IEDM 2020, TSMC reported their 5 nm minimum metal pitch to be reduced 30% from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Beam Lithography
Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography, EBL) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (exposing). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (developing). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by etching. The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution and low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of semiconductor devices, and research and development. Systems Electron-beam lithography systems used in commercial applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |