|
Wort Plants
This is an alphabetical listing of wort plants, meaning plants that employ the syllable ''wort'' in their English-language common names. According to the Oxford English Dictionary's Ask Oxford site, "A word with the suffix ''-wort'' is often very old. The Old English word was ''wyrt''. The modern variation, ''root'', comes from Old Norse. It was often used in the names of herbs and plants that had medicinal uses, the first part of the word denoting the complaint against which it might be specially efficacious. By the middle of the 17th-century ''-wort'' was beginning to fade from everyday use. The ''Naturalist Newsletter'' states, "''Wort'' derives from the Old English ''wyrt'', which simply meant ''plant''. The word goes back even further, to the common ancestor of English and German, to the Germanic ''wurtiz''. ''Wurtiz'' also evolved into the modern German word ''Wurzel'', meaning ''root''." ''Wort'' plants :Adderwort, adder's wort - '' Persicaria bistorta''. :American lungwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysimachia Nummularia In Minsk
''Lysimachia'' () is a genus consisting of 193 accepted species of flowering plants traditionally classified in the family Primulaceae. Based on a molecular phylogenetic study it was transferred to the family Myrsinaceae, before this family was later merged into the Primulaceae. Characteristics ''Lysimachia'' species often have yellow flowers, and grow vigorously. They tend to grow in damp conditions. Several species within ''Lysimachia'' are commonly called loosestrife, although this name is also used for plants within the genus ''Lythrum''. The genus is named in honor of Lysimachus, a king of ancient Sicily, who is said to have calmed a mad ox by feeding it a member of the genus. ''Lysimachia'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some butterflies and moths, including the dot moth, grey pug, lime-speck pug, small angle shades, and v-pug. Specialized pollinators Bees of the genus ''Macropis'' are specialized to pollinate oil-producing ''Lysimachia'' plants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanulaceae
The family Campanulaceae (also bellflower family), of the order Asterales, contains nearly 2400 species in 84 genera of herbaceous plants, shrubs, and rarely small trees, often with milky sap. Among them are several familiar garden plants belonging to the genera ''Campanula'' (bellflower), '' Lobelia'', and ''Platycodon'' (balloonflower). '' Campanula rapunculus'' (rampion or r. bellflower) and ''Codonopsis lanceolata'' are eaten as vegetables. '' Lobelia inflata'' (indian tobacco), '' L. siphilitica'' and '' L. tupa'' (devil's tobacco) and others have been used as medicinal plants. '' Campanula rapunculoides'' (creeping bellflower) may be a troublesome weed, particularly in gardens, while '' Legousia'' spp. may occur in arable fields. Most current classifications include the segregate family Lobeliaceae in Campanulaceae as subfamily Lobelioideae. A third subfamily, Cyphioideae, includes the genus '' Cyphia'', and sometimes also the genera '' Cyphocarpus'', '' Nemacladus'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
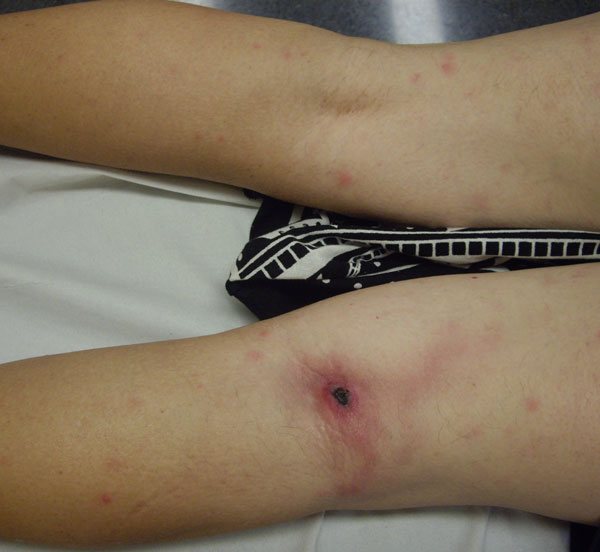
Escharotic
An eschar (; Greek: ''ἐσχάρᾱ'', ''eskhara''; Latin: ''eschara'') is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term ‘eschar’ is not interchangeable with ‘scab’. An eschar contains necrotic tissue whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate. Black eschars are most frequently attributed in medicine to cutaneous anthrax (infection by ''Bacillus anthracis''), which may be contracted through herd animal exposure and also from ''Pasteurella multocida'' exposure in cats and rabbits. A newly identified human rickettsial infection, ''R. parkeri'' rickettsiosis, can be differentiated from Rocky Mountain spotted fever by the presence of an eschar at the site of inoculation. Eschar is sometimes called a ''black wound'' because t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanguinaria Canadensis
''Sanguinaria canadensis'', bloodroot, is a perennial, herbaceous flowering plant native to eastern North America. It is the only species in the genus ''Sanguinaria'', included in the poppy family Papaveraceae, and is most closely related to '' Eomecon'' of eastern Asia. ''Sanguinaria canadensis'' is sometimes known as Canada puccoon, bloodwort, redroot, red puccoon, and black paste. Plants are variable in leaf and flower shape, and have been separated as a different subspecies due to these variable shapes, indicating a highly variable species. In bloodroot, the juice is red and poisonous. Products made from sanguinaria extracts, such as black salve, are escharotic and can cause permanent disfiguring scarring. Although preliminary studies have suggested that sanguinaria may have potential applications in cancer therapy, clinical studies are lacking, and its use is not recommended. Description Bloodroot grows from tall. It has one large basal leaf, up to across, with f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments ( saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that grows in or near water and is either emergent, submergent, or floating. In lakes and rivers macrophytes provide cover for fish, substrate for aquatic invertebrates, produce oxygen, and act as food for some fish and wildlife. Macrophytes are primary producers and are the basis of the food web for many organisms. They have a significant effect on soil chemistry and light levels as they slow down the flow of water and capture pollutants and trap sediments. Excess sediment will settle into the benthos aided by the reduction of flow rates caused by the presence of plant stems, leaves and roots. Some plants have the capability of absorbing pollutants into their tissue. Seaweeds are multicellular marine algae and, although their ecolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utricularia
''Utricularia'', commonly and collectively called the bladderworts, is a genus of carnivorous plants consisting of approximately 233 species (precise counts differ based on classification opinions; a 2001 publication lists 215 species).Salmon, Bruce (2001). ''Carnivorous Plants of New Zealand''. Ecosphere Publications. They occur in fresh water and wet soil as terrestrial or aquatic species across every continent except Antarctica. ''Utricularia'' are cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and orchids, especially amongst carnivorous plant enthusiasts. All ''Utricularia'' are carnivorous and capture small organisms by means of bladder-like traps. Terrestrial species tend to have tiny traps that feed on minute prey such as protozoa and rotifers swimming in water-saturated soil. The traps can range in size from .Taylor, Peter. (1989). '' The genus Utricularia - a taxonomic monograph''. Kew Bulletin Additional Series XIV: London. Aquatic sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladderwort
''Utricularia'', commonly and collectively called the bladderworts, is a genus of carnivorous plants consisting of approximately 233 species (precise counts differ based on classification opinions; a 2001 publication lists 215 species).Salmon, Bruce (2001). ''Carnivorous Plants of New Zealand''. Ecosphere Publications. They occur in fresh water and wet soil as terrestrial or aquatic species across every continent except Antarctica. ''Utricularia'' are cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and orchids, especially amongst carnivorous plant enthusiasts. All ''Utricularia'' are carnivorous and capture small organisms by means of bladder-like traps. Terrestrial species tend to have tiny traps that feed on minute prey such as protozoa and rotifers swimming in water-saturated soil. The traps can range in size from .Taylor, Peter. (1989). ''The genus Utricularia - a taxonomic monograph''. Kew Bulletin Additional Series XIV: London. Aquatic spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentiana Lutea
''Gentiana lutea'', the great yellow gentian, is a species of gentian native to the mountains of central and southern Europe. Growth ''Gentiana lutea'' is an herbaceous perennial plant, growing to tall, with broad lanceolate to elliptic leaves long and broad. The flowers are yellow, with the corolla separated nearly to the base into 5–7 narrow petals. It grows in grassy alpine and sub-alpine pastures, usually on calcareous soils. Uses ''Gentiana lutea'' is remarkable for the intense bitterness of the root and every part of the herbage. Before the introduction of hops, gentian was used occasionally in brewing. Gentian root has a long history of use as an herbal bitter and is an ingredient of many proprietary medicines. The parts used include the dried, underground parts of the plant and the fresh, above-ground parts. The root, which can be over thick and has few branches, is harvested in the autumn and dried for later use. Caution should be exercised as to its use beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitterwort
''Gentiana lutea'', the great yellow gentian, is a species of gentian native to the mountains of central and southern Europe. Growth ''Gentiana lutea'' is an herbaceous perennial plant, growing to tall, with broad lanceolate to elliptic leaves long and broad. The flowers are yellow, with the corolla separated nearly to the base into 5–7 narrow petals. It grows in grassy alpine and sub-alpine pastures, usually on calcareous soils. Uses ''Gentiana lutea'' is remarkable for the intense bitterness of the root and every part of the herbage. Before the introduction of hops, gentian was used occasionally in brewing. Gentian root has a long history of use as an herbal bitter and is an ingredient of many proprietary medicines. The parts used include the dried, underground parts of the plant and the fresh, above-ground parts. The root, which can be over thick and has few branches, is harvested in the autumn and dried for later use. Caution should be exercised as to its use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stachys Officinalis
''Betonica officinalis'' (syn. ''Stachys officinalis''), commonly known as common hedgenettle, betony, purple betony, wood betony, bishopwort, or bishop's wort, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae, native to Europe, western Asia, and northern Africa. Pliny (25, 8, 46, § 84) calls the plant both ''betonica'' and ''vettonica'', claiming that the Vettones used it as a herbal medicine. It is commonly known as ''Stachys officinalis'', the word ''stachys'' coming from the Greek, meaning "an ear of grain," and refers to the fact that the inflorescence is often a spike. The Latin specific epithet ''officinalis'' refers to plants which had a culinary or medicinal use. Description ''Betonica officinalis'' is a rhizotomous, patch-forming, grassland herbaceous perennial growing to tall. Its leaves are stalked on upright stems, narrowly oval, with a heart-shaped base, with a somewhat wrinkled texture and toothed margins. The calyx is 5–7 mm long, with 5 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristolochiaceae
The Aristolochiaceae () are a family, the birthwort family, of flowering plants with seven genera and about 400 known species belonging to the order Piperales. The type genus is ''Aristolochia'' L. Description They are mostly perennial, herbaceous plants, shrubs, or lianas. The membranous, cordate simple leaves are spread out, growing alternately along the stem on leaf stalks. The margins are commonly entire. No stipules are present. The bizarre flowers are large to medium-sized, growing in the leaf axils. They are bilaterally or radially symmetrical. Classification Aristolochiaceae are magnoliids, a basal group of angiosperms which are not part of the large categories of monocots or eudicots. As of APG IV (2016), the former families Hydnoraceae and Lactoridaceae are included, because exclusion would make Aristolochiaceae in the traditional sense paraphyletic. Some newer classification schemes, such as the update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, place the fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |