|
William De Vesci (d.1297)
William de Vesci or Vescy (died 1297) was a prominent 13th-century noble. He was a son of William de Vesci and his second wife Lady Agnes de Ferrers, daughter of William de Ferrers, 5th Earl of Derby, and his first wife Sibyl Marshal. He founded the Grey Abbey in Kildare, Ireland for the Franciscans in 1260. During the Second Barons' War campaign of 1265, William held Gloucester Castle against Prince Edward. He was pardoned afterwards and entered the service of King Henry III of England. He served against the Welsh in 1277 and later in 1282. He was appointed the justice of the forests north of the Trent in 1285. Upon the death of his brother John de Vesci in 1289, William succeeded to the family estates, including as Lord of Sprouston in Scotland. He was also granted the Constable of Scarborough Castle between 1289 and 1292. William was sent with Antony Bek, Bishop of Durham in 1289 to represent King Edward I of England in Scotland. He also founded White Abbey, near Kildar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation. The term itself of 'coat of arms' describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail 'surcoat' garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, and therefore its genealogy across tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
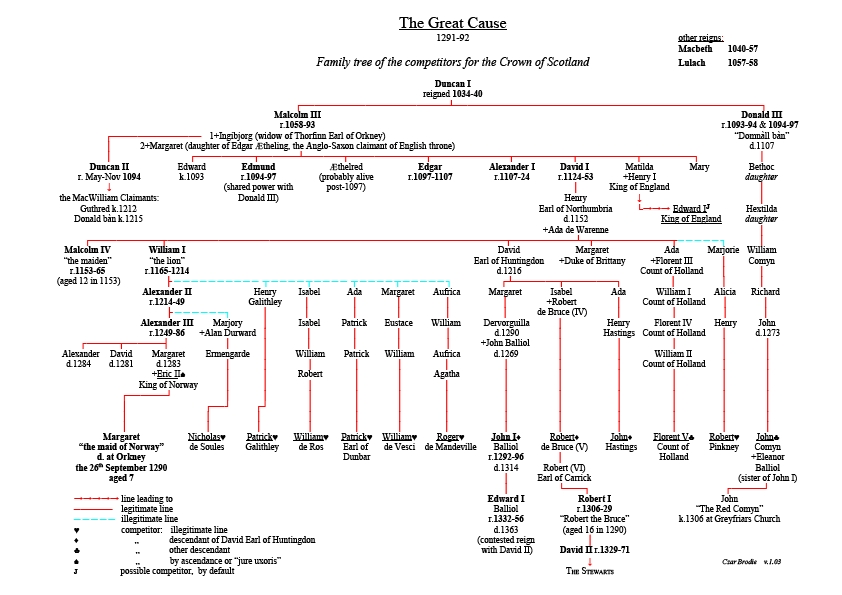
Competitors For The Crown Of Scotland
When the crown of Scotland became vacant in September 1290 on the death of the seven-year-old Queen Margaret, 13 claimants to the throne came forward. Those with the most credible claims were John Balliol, Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale, John Hastings and Floris V, Count of Holland. Fearing civil war, the Guardians of Scotland asked Edward I of England to arbitrate. Before agreeing, he obtained concessions going some way to revive English overlordship over the Scots. A commission of 104 "auditors" was then appointed—24 by Edward himself, acting as president; and the rest by Bruce and Balliol, in equal numbers. In November 1292, the body decided in favour of John Balliol, whose claim was based on the traditional criterion of primogeniture—inheritance through a line of firstborn sons. The decision was accepted by the majority of the powerful in Scotland, and John ruled as King of Scots from then until 1296. Background With the death of King Alexander III in 1286, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defamation
Defamation is the act of communicating to a third party false statements about a person, place or thing that results in damage to its reputation. It can be spoken (slander) or written (libel). It constitutes a tort or a crime. The legal definition of defamation and related acts as well as the ways they are dealt with can vary greatly between countries and jurisdictions (what exactly they must consist of, whether they constitute crimes or not, to what extent proving the alleged facts is a valid defence). Defamation laws can encompass a variety of acts: * Insult against a legal person in general * Defamation against a legal person in general * Acts against public officials * Acts against state institutions (e.g., government, ministries, government agencies, armed forces) * Acts against state symbols * Acts against the state itself * Acts against religions (e.g., blasphemy, discrimination) * Acts against the judiciary or legislature (e.g., contempt of court, censure) Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord High Treasurer Of Ireland
The Lord High Treasurer of Ireland was the head of the Exchequer of Ireland, and chief financial officer of the Kingdom of Ireland. The designation ''High'' was added in 1695. After the Acts of Union 1800 created the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Consolidated Fund Act 1816 merged the Irish Inferior Exchequer into the British Treasury with effect from 1817. The act also mandated that the post of Lord High Treasurer of Ireland could only be held together with the post of Treasurer of the Exchequer, with the person holding both being Lord High Treasurer. If no person is appointed to the combined positions, then the Lord High Treasurer of Ireland is placed in commission and represented by the Lords Commissioners of the Treasury, as has been the case continuously since 1816. The Superior Irish Exchequer, or Court of Exchequer, remained, led by the Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer. Lord Treasurers of Ireland 1217–1695 *1217–1232: John de St John, Bishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William De Essendon
Sir William de Essendon, de Estdene or Eastdean (died after 1314) was an English-born cleric, lawyer and Crown official, much of whose career was spent in Ireland in the reign of Edward I of England. He served twice as Lord High Treasurer of Ireland,Haydn p.449 and had a high reputation for integrity and efficiency. He was a native of East Dean, West Sussex. His name means simply "William of East Dean", and he is referred to frequently in the records as William de Estdene, or occasionally as William of Eastdean.Mackay ''Cambridge Dictionary of Irish Biography'' He was in holy orders, and was presented with the living of Ereford, Winchester in 1282. He enjoyed royal favour from quite early in his career, and in her last years (c.1289-91) Essendon acted as general attorney to the Queen Dowager of England, Eleanor of Provence, and as supervisor of her stewards, with power to investigate their activities on all of her many estates. He was chosen as Lord Treasurer of Ireland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenilworth Castle
Kenilworth Castle is a castle in the town of Kenilworth in Warwickshire, England managed by English Heritage; much of it is still in ruins. The castle was founded during the Norman conquest of England; with development through to the Tudor period. It has been described by the architectural historian Anthony Emery as "the finest surviving example of a semi-royal palace of the later middle ages, significant for its scale, form and quality of workmanship". Kenilworth played an important historical role: it was the subject of the six-month-long siege of Kenilworth in 1266, thought to be the longest siege in Medieval English history, and formed a base for Lancastrian operations in the Wars of the Roses. Kenilworth was the scene of the removal of Edward II from the English throne, the perceived French insult to Henry V in 1414 of a gift of tennis balls (said by John Strecche to have prompted the campaign that led to the Battle of Agincourt), and the Earl of Leicester's lavish re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Connaught
The Kings of Connacht were rulers of the ''cóiced'' (variously translated as portion, fifth, province) of Connacht, which lies west of the River Shannon, Ireland. However, the name only became applied to it in the early medieval era, being named after the Connachta. The old name for the province was Cóiced Ol nEchmacht (the fifth of the Ol nEchmacht). Ptolemy's map of c. 150 AD does in fact list a people called the Nagnatae as living in the west of Ireland. Some are of the opinion that Ptolemy's Map of Ireland may be based on cartography carried out as much as five hundred years before his time. The Connachta were a group of dynasties who claimed descent from the three eldest sons of Eochaid Mugmedon: Brion, Ailill and Fiachrae. They took their collective name from their alleged descent from Conn Cétchathach. Their younger brother, Niall Noigiallach was ancestor to the Uí Néill. The following is a list of kings of Connacht from the fifth to fifteenth centuries. Pre-hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John FitzGerald, 1st Earl Of Kildare
John FitzThomas (c. 1250 – d. 10 September 1316) was an Anglo-Norman in the Peerage of Ireland, as 4th Lord of Offaly from 1287 and subsequently as 1st Earl of Kildare from 1316. Life He was the eldest son of Thomas FitzMaurice (son of Maurice FitzGerald) and Rohesia de St. Michel. He is noticed in 1291 in a serious dispute with William de Vesci, Lord of Kildare, Lord Justice of Ireland, about whom there were many complaints of oppression and neglect of the country's defences. As champion of the complainants John FitzThomas, by then 4th Lord of Offaly (having succeeded to the title in 1287, upon the death of his uncle Maurice FitzGerald, 3rd Lord of Offaly), their paths crossed and instead of addressing the issues, de Vesci charged FitzThomas with minor charges of slander and libel, some touching the King himself. FitzThomas appealed to King Edward I of England, who, to examine and judge the matter impartially, summoned them both to London to hear the cases, where it appears F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Justices (Ireland)
The Lords Justices (more formally the Lords Justices General and General Governors of Ireland) were deputies who acted collectively in the absence of the chief governor of Ireland (latterly the Lord Lieutenant) as head of the executive branch of the Dublin Castle administration. Lords Justices were sworn in at a meeting of the Privy Council of Ireland. History After the Norman Conquest of Ireland, the chief governor of the Lordship of Ireland was appointed by the King of England via letters patent; in medieval times under his privy seal, and later under the Great Seal of England. The patent usually allowed the chief governor to nominate a deputy, though sometimes the King nominated a deputy, and if the chief governor died in office the Privy Council of Ireland would elect a deputy until the King nominated a successor. The title (originally French or Latin) of the chief governor depended on his power, from most to least: King's (or Lord) Lieutenant; (Lord) Deputy; Justiciar ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rathangan Castle
Rathangan Castle was a castle in Rathangan in County Kildare County Kildare ( ga, Contae Chill Dara) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is named after the town of Kildare. Kildare County Council is the local authority for the county, ..., Ireland. Built by the O’ Connors, the castle was demolished in the 18th century. Castles in County Kildare {{Ireland-castle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kildare Castle
Kildare Castle is a ruined castle located at Kildare in County Kildare, Ireland. Built in the 12th century as a motte and bailey castle by Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke (of the first creation), Lord of Leinster, Justiciar of Ireland (113020 April 1176), also known as Richard FitzGilbert, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasio .... The remains of a tower are the only above ground remains of the castle. External links * {{coord, 53.1572, -6.9091, type:landmark_region:IE, display=title Castles in County Kildare Ruined castles in Ireland Ruins in the Republic of Ireland De Vesci family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Kildare
County Kildare ( ga, Contae Chill Dara) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Eastern and Midland Region. It is named after the town of Kildare. Kildare County Council is the local authority for the county, which has a population of 246,977. Geography and subdivisions Kildare is the 24th-largest of Ireland's 32 counties in area and the seventh largest in terms of population. It is the eighth largest of Leinster's twelve counties in size, and the second largest in terms of population. It is bordered by the counties of Carlow, Laois, Meath, Offaly, South Dublin and Wicklow. As an inland county, Kildare is generally a lowland region. The county's highest points are the foothills of the Wicklow Mountains bordering to the east. The highest point in Kildare is Cupidstown Hill on the border with South Dublin, with the better known Hill of Allen in central Kildare. Towns and villages * Allen * Allenwood * Ardclough * Athy * Ballitore * Ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |