|
White Cell (spectroscopy)
Multiple-pass or long path absorption cells are commonly used in spectroscopy to measure low-concentration components or to observe weak spectra in gases or liquids. Several important advances were made in this area beginning in the 1930s, and research into a wide range of applications continues to the present day. Functional Overview Generally the goal of this type of sample cell is to improve detection sensitivity by increasing the total optical path length that travels through a small, constant sample volume. In principle, a longer path length results in greater detection sensitivity. Focusing mirrors must be used to redirect the beam at each reflection point, resulting in the beam being restricted to a predefined space along a controlled path until it exits the optical cavity. The output of the cell is the input of an optical detector (a specialized type of transducer), which senses specific changes in the properties of the beam that occur during interaction with the test sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfund Cell Illustration
Pfund is German for " pound weight" and is also a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *August Herman Pfund (1879–1949), American physicist and spectroscopist *Guillermo Pfund (born 1989), Argentine footballer *Jessica Pfund (born 1998), American skater *Lee Pfund (born 1919), Major League Baseball pitcher *Nicola Pfund (born 1960), Swiss-Italian writer *Randy Pfund Randall C. Pfund''The Sporting News: 1992-93 Official NBA Register'' St. Louis, Missouri: The Sporting News Publishing Co. 1992. (born December 29, 1951) is an American former National Basketball Association (NBA) head coach and executive. He w ..., NBA head coach & executive * Roger Pfund (born 1943), Swiss graphic artist {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald R
Donald is a masculine given name derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers, and partly associated with the spelling of similar-sounding Germanic names, such as ''Ronald''. A short form of ''Donald'' is '' Don''. Pet forms of ''Donald'' include ''Donnie'' and ''Donny''. The feminine given name ''Donella'' is derived from ''Donald''. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Devices
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: *Interferometer for measuring the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
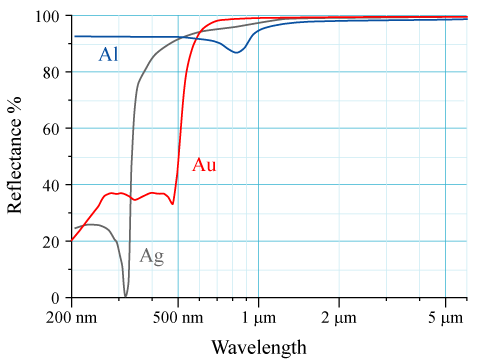
Reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in Reflection (physics), reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Depth
In physics, optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to ''transmitted'' radiant power through a material. Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power through the material. Spectral optical depth or spectral optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. Optical depth is dimensionless, and in particular is not a length, though it is a monotonically increasing function of optical path length, and approaches zero as the path length approaches zero. The use of the term "optical density" for optical depth is discouraged. In chemistry, a closely related quantity called "absorbance" or "decadic absorbance" is used instead of optical depth: the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, that is the optical depth divided by ln 10. Mathematical definitions Optical dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Density
Absorbance is defined as "the logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls)". Alternatively, for samples which scatter light, absorbance may be defined as "the negative logarithm of one minus absorptance, as measured on a uniform sample". The term is used in many technical areas to quantify the results of an experimental measurement. While the term has its origin in quantifying the absorption of light, it is often entangled with quantification of light which is “lost” to a detector system through other mechanisms. What these uses of the term tend to have in common is that they refer to a logarithm of the ratio of a quantity of light incident on a sample or material to that which is detected after the light has interacted with the sample. The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance does not always measure only absorption; it may measure attenuation (of trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption (optics)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is how matter (typically electrons bound in atoms) takes up a photon's energy — and so transforms electromagnetic energy into internal energy of the absorber (for example, thermal energy). A notable effect is attenuation, or the gradual reduction of the intensity of light waves as they propagate through a medium. Although the absorption of waves does not usually depend on their intensity (linear absorption), in certain conditions (optics) the medium's transparency changes by a factor that varies as a function of wave intensity, and saturable absorption (or nonlinear absorption) occurs. Quantifying absorption Many approaches can potentially quantify radiation absorption, with key examples following. * The absorption coefficient along with some closely related derived quantities * The attenuation coefficient (NB used infrequently with meaning synonymous with "absorption coefficient") * The Molar attenuation coefficient ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common arrangement is to direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical System
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS, sometimes referred to as TDLS, TLS or TLAS) is a technique for measuring the concentration of certain species such as methane, water vapor and many more, in a gaseous mixture using tunable diode lasers and laser absorption spectrometry. The advantage of TDLAS over other techniques for concentration measurement is its ability to achieve very low detection limits (of the order of ppb). Apart from concentration, it is also possible to determine the temperature, pressure, velocity and mass flux of the gas under observation. TDLAS is by far the most common laser based absorption technique for quantitative assessments of species in gas phase. Working A basic TDLAS setup consists of a tunable diode laser light source, transmitting (i.e. beam shaping) optics, optically accessible absorbing medium, receiving optics and detector/s. The emission wavelength of the tunable diode laser, viz. VCSEL, DFB, etc., is tuned over the characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Absorption Spectrometry
Laser absorption spectrometry (LAS) refers to techniques that use lasers to assess the concentration or amount of a species in gas phase by absorption spectrometry (AS). Optical spectroscopic techniques in general, and laser-based techniques in particular, have a great potential for detection and monitoring of constituents in gas phase. They combine a number of important properties, e.g. a high sensitivity and a high selectivity with non-intrusive and remote sensing capabilities. Laser absorption spectrometry has become the foremost used technique for quantitative assessments of atoms and molecules in gas phase. It is also a widely used technique for a variety of other applications, e.g. within the field of optical frequency metrology or in studies of light matter interactions. The most common technique is tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) which has become commercialized and is used for a variety of applications. Direct laser absorption spectrometry The mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |