|
Workplace Impact Of Artificial Intelligence
The impact of artificial intelligence on workers includes both applications to improve Occupational safety and health, worker safety and health, and potential Occupational hazard, hazards that must be controlled. One potential application is using AI to Hazard elimination, eliminate hazards by removing humans from hazardous situations that involve risk of Occupational stress, stress, overwork, or Musculoskeletal injury, musculoskeletal injuries. Predictive analytics may also be used to identify conditions that may lead to hazards such as fatigue, Repetitive strain injury, repetitive strain injuries, or Chemical hazard, toxic substance exposure, leading to earlier interventions. Another is to streamline Occupational safety and health, workplace safety and health workflows through automating repetitive tasks, enhancing safety training programs through virtual reality, or detecting and reporting Near miss (safety), near misses. When used in the workplace, AI also presents the possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
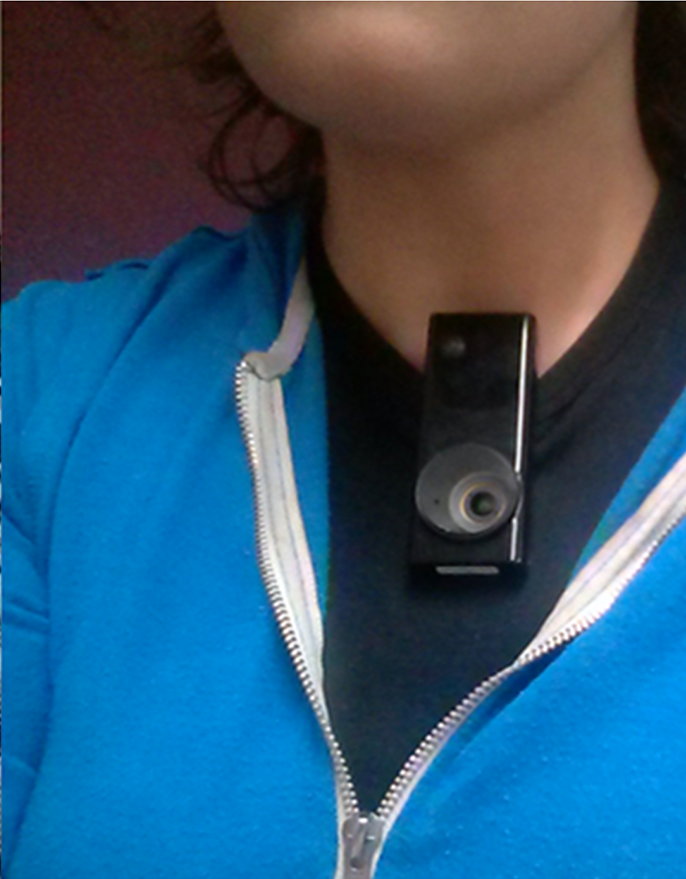
Autographer Lifelogging Device
Autographer is a hands-free, wearable technology, wearable digital camera developed by OMG Life. The camera uses five different sensors to determine when to automatically take photos and can take up to 2,000 pictures a day. It was released in July 2013 and is used primarily for lifelog, lifelogging, entertainment and travel. As of 16 October 2016, OMG Life, the company behind Autographer discontinued operations. History Autographer was developed by British company OMG Life, a wholly owned subsidiary of Oxford Metrics Group (OMG) plc, after licensing technology from Microsoft to create a medical memory aid called the Vicon Revue. The original product was released in October 2009 and was designed to capture the lives of patients with Alzheimer's disease and other memory problems, so that their doctors could assess how many of the events the patients recalled. OMG reinvented the device as a consumer product based on feedback from customers who were using the technology for enterta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Privacy
Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, contextual information norms, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection. Information types Various types of personal information often come under privacy concerns. Cable television This describes the ability to control what information one reveals about oneself over cable television, and who can access that information. For example, third parties can track IP TV programs someone has watched at any given time. "The addition of any information in a broadcasting stream is not required for an audience rating survey, additional devices are not requested to be installed in the houses of viewers or listeners, and without the necessity of their cooperations, audience ratings can be automatically performed in real-time." Educational In the United Kingdom in 2012, the Education Secretary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Hygiene
Occupational hygiene or industrial hygiene (IH) is the Anticipate, recognize, evaluate, control, and confirm, anticipation, recognition, evaluation, control, and confirmation (ARECC) of protection from risks associated with exposures to hazards in, or arising from, the workplace that may result in injury, illness, impairment, or affect the well-being of workers and members of the community. These hazards or stressors are typically divided into the categories biological, chemical, Physical hazard, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial. The risk of a health effect from a given stressor is a function of the hazard multiplied by the exposure to the individual or group. For chemicals, the hazard can be understood by the dose response profile most often based on toxicological studies or models. Occupational hygienists work closely with toxicologists (see Toxicology) for understanding chemical hazards, physicists (see Physics) for physical hazards, and physicians and microbiologists for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existential Risk From Artificial General Intelligence
Existential risk from artificial intelligence refers to the idea that substantial progress in artificial general intelligence (AGI) could lead to human extinction or an irreversible global catastrophe. One argument for the importance of this risk references how human beings dominate other species because the human brain possesses distinctive capabilities other animals lack. If AI were to surpass human intelligence and become superintelligent, it might become uncontrollable. Just as the fate of the mountain gorilla depends on human goodwill, the fate of humanity could depend on the actions of a future machine superintelligence. The plausibility of existential catastrophe due to AI is widely debated. It hinges in part on whether AGI or superintelligence are achievable, the speed at which dangerous capabilities and behaviors emerge, and whether practical scenarios for AI takeovers exist. Concerns about superintelligence have been voiced by computer scientists and tech CEOs such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks. Some researchers argue that state‑of‑the‑art large language models already exhibit early signs of AGI‑level capability, while others maintain that genuine AGI has not yet been achieved. AGI is conceptually distinct from artificial superintelligence (ASI), which would outperform the best human abilities across every domain by a wide margin. AGI is considered one of the definitions of Chinese room#Strong AI vs. AI research, strong AI. Unlike artificial narrow intelligence (ANI), whose competence is confined to well‑defined tasks, an AGI system can generalise knowledge, transfer skills between domains, and solve novel problems without task‑specific reprogramming. The concept does not, in principle, require the system to be an autonomous agent; a static model— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak AI
Weak artificial intelligence (weak AI) is artificial intelligence that implements a limited part of the mind, or, as narrow AI, is focused on one narrow task. Weak AI is contrasted with strong AI, which can be interpreted in various ways: * Artificial general intelligence (AGI): a machine with the ability to apply intelligence to any problem, rather than just one specific problem. * Artificial super intelligence (ASI): a machine with a vastly superior intelligence to the average human being. * Artificial consciousness: a machine that has consciousness, sentience and mind (John Searle uses "strong AI" in this sense). Narrow AI can be classified as being "limited to a single, narrowly defined task. Most modern AI systems would be classified in this category." Artificial general intelligence is conversely the opposite. Applications and risks Some examples of narrow AI are AlphaGo, self-driving cars, robot systems used in the medical field, and diagnostic doctors. Narrow AI syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobot
A cobot, or collaborative robot, also known as a companion robot, is a robot intended for direct human-robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in close proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industrial robot applications in which robots are isolated from human contact or the humans are protected by robotic tech vests. Cobot safety may rely on lightweight construction materials, rounded edges, and inherent limitation of speed and force, or on sensors and software that ensure safe behavior.ISO 10218-1:2011, ISO 10218-2:2011, ISO/TS 15066:2015 Uses The International Federation of Robotics (IFR), a global industry association of robot manufacturers and national robot associations, recognizes two main groups of robots: industrial robots used in automation and service robots for domestic and professional use. Service robots could be considered to be cobots as they are intended to work alongside humans. Industrial robots have traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Factors And Ergonomics
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions (collectively termed institutions), each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious: the desire to understand and influence phenomena has motivated humanity's de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workplace Robotics Safety
Workplace robotics safety is an aspect of occupational safety and health when robots are used in the workplace. This includes traditional industrial robots as well as emerging technologies such as drone aircraft and wearable robotic exoskeletons. Types of accidents include collisions, crushing, and injuries from mechanical parts. Hazard controls include physical barriers, good work practices, and proper maintenance. Background Many workplace robots are industrial robots used in manufacturing. According to the International Federation of Robotics, 1.7 million new robots are expected to be used in factories between 2017 and 2020. Emerging robot technologies include collaborative robots, personal care robots, construction robots, exoskeletons, autonomous vehicles, and drone aircraft (also known as unmanned aerial vehicles or UAVs). Advances in automation technologies (e.g. fixed robots, collaborative and mobile robots, and exoskeletons) have the potential to improve wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Hazard
A physical hazard is an agent, factor or circumstance that can cause harm with contact. They can be classified as type of occupational hazard or environmental hazard. Physical hazards include ergonomic hazards, radiation, heat and cold stress, vibration hazards, and noise hazards. Engineering controls are often used to mitigate physical hazards. Physical hazards are a common source of injuries in many industries. They are perhaps unavoidable in certain industries, such as construction and mining, but over time people have developed safety methods and procedures to manage the risks of physical danger in the workplace. Employment of children may pose special problems. A physical hazard is also a naturally occurring process that has the potential to create loss or damage. Physical hazards include earthquakes, floods, fires, and tornadoes. Physical hazards often have both human and natural elements. For example, flood problems can be affected by the natural elements of climate flu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blame In Organizations
Blame in organizations may flow between management and staff, or laterally between professionals or partner organizations. In a blame culture, problem-solving is replaced by blame-avoidance. Blame shifting may exist between rival factions. Maintaining one's reputation may be a key factor explaining the relationship between accountability and blame avoidance. The blame culture is a serious issue in certain sectors such as safety-critical domains. Blame culture The flow of blame in an organization may be a primary indicator of that organization's robustness and integrity. Blame flowing downwards, from management to staff, or laterally between professionals or partner organizations, indicates organizational failure. In a blame culture, problem-solving is replaced by blame-avoidance. Blame coming from the top generates "fear, malaise, errors, accidents, and passive-aggressive sometimes actual aggressive responses from the bottom", with those at the bottom feeling powerless and lacking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Bias
Algorithmic bias describes systematic and repeatable harmful tendency in a computerized sociotechnical system to create " unfair" outcomes, such as "privileging" one category over another in ways different from the intended function of the algorithm. Bias can emerge from many factors, including but not limited to the design of the algorithm or the unintended or unanticipated use or decisions relating to the way data is coded, collected, selected or used to train the algorithm. For example, algorithmic bias has been observed in search engine results and social media platforms. This bias can have impacts ranging from inadvertent privacy violations to reinforcing social biases of race, gender, sexuality, and ethnicity. The study of algorithmic bias is most concerned with algorithms that reflect "systematic and unfair" discrimination. This bias has only recently been addressed in legal frameworks, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (proposed 2018) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |