|
Workers' Party Of Ethiopia
The Workers' Party of Ethiopia (, WPE) was a Marxist–Leninist communist party in Ethiopia from 1984 to 1991 led by General Secretary Mengistu Haile Mariam. The Workers' Party of Ethiopia was founded in 1984 by the Derg, the ruling provisional government of Ethiopia, as the vanguard party for a planned future socialist state. In 1987, the WPE became the ruling party after the establishment of the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, and the only legal political party until it was disbanded in 1991. A party was attempted to be formed with the same name in August 2022, but the application was rejected. COPWE In 1974, the Derg, a committee of low-ranking officers and enlisted men in the Ethiopian Army, overthrew Emperor Haile Selassie and the government of the Ethiopian Empire during the mass discontent in the country at the time. Originally a non-ideological representative committee for the military, the Derg became the '' de facto'' government of Ethiopia in the form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mengistu Haile Mariam
Mengistu Haile Mariam (, pronunciation: ; born 21 May 1937) is an Ethiopian former politician, revolutionary, and military officer who served as the head of state of Ethiopia from 1977 to 1991. He was General Secretary of the Workers' Party of Ethiopia from 1984 to 1991, chairman of the Derg—the Marxist–Leninist military junta that ruled Ethiopia—from 1977 to 1987, and president of the People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (PDRE) from 1987 to 1991. The Derg seized power in the Ethiopian Revolution following the overthrow of Emperor Haile Selassie in 1974, marking the end of the Solomonic dynasty which had ruled Ethiopia since the 13th century. Mengistu purged his rivals within the Derg and made himself dictator of Ethiopia, attempting to modernize the feudal economy of Ethiopia through Marxist–Leninist-inspired policies such as nationalization and land redistribution. His bloody consolidation of power in 1977–1978 is known as the Ethiopian Red Terror—a br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
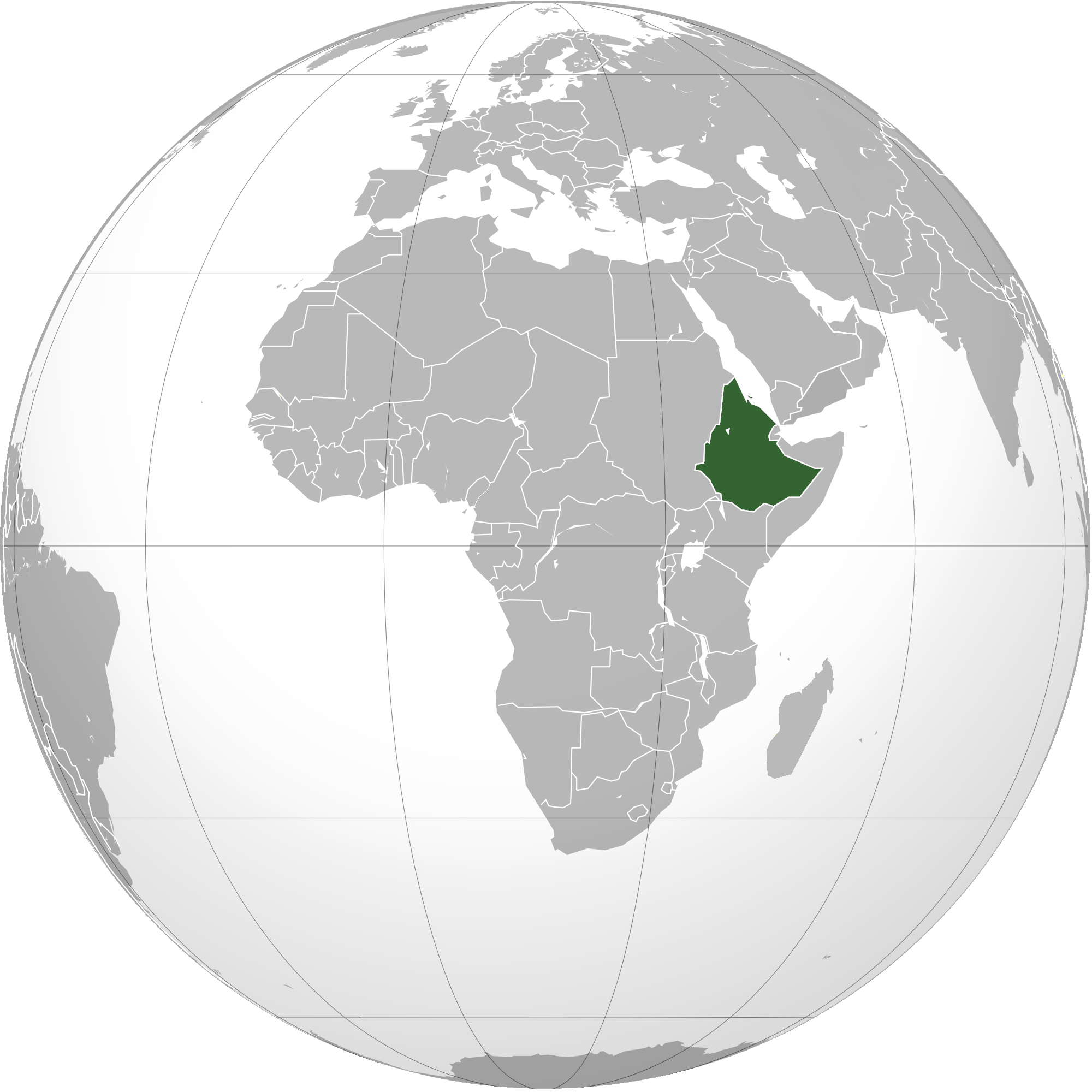
People's Democratic Republic Of Ethiopia
The People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (PDRE; ) was a socialist state that existed in Ethiopia and present-day Eritrea from 1987 to 1991. The PDRE was established in February 1987 as a Marxism-Leninism, Marxist-Leninist one-party state upon the adoption of the 1987 Constitution of Ethiopia, 1987 Constitution, three weeks after its approval in Ethiopian constitutional referendum, 1987, the national referendum. The Derg, the military junta that had ruled Ethiopia as a provisional government since 1974, planned for transition to civilian rule and proclaimed a Socialist state, socialist republic in 1984 after five years of preparation. The Workers' Party of Ethiopia (WPE) was founded that same year as a vanguard party led by Derg chairman Mengistu Haile Mariam. The Derg was dissolved with the proclamation of the PDRE, but continued to rule ''de facto'' until September when the new government took office, three months after the Ethiopian general election, 1987, June general elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sectarianism
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or Religious violence, religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism as a set of social practices where daily life is organized on the basis of communal norms and rules that individuals strategically use and transcend. This definition highlights the co-constitutive aspect of sectarianism and people's agency, as opposed to understanding sectarianism as being fixed and incompatible communal boundaries. While sectarianism is often labelled as religious or political, the reality of a sectarian situation is usually much more complex. In its most basic form, sectarianism has been defined as, 'the existence, within a locality, of two or more divided and actively competing communal identities, resulting in a strong sense of dualism which unremittingly transcends commonality, and is both culturally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary Ethiopia Youth Association
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates for, a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective to describe something producing a major and sudden impact on society. Definition The term—both as a noun and adjective—is usually applied to the field of politics, but is also occasionally used in the context of science, invention or art. In politics, a revolutionary is someone who supports abrupt, rapid, and drastic change, usually replacing the status quo, while a reformist is someone who supports more gradual and incremental change, often working within the system. In that sense, revolutionaries may be considered radical, while reformists are moderate by comparison. Moments which seem revolutionary on the surface may end up reinforcing established institutions. Likewise, evidently small changes may lead to revolutionary consequences in the long term. Thus the clarity of the distinction between revolution and reform is more con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Organisation
Transmission belt is a Marxist–Leninist analogy to describe interactions of the communist party with the people in a communist state via mass organizations, such as trade unions. All these institutions worked under the party's leadership. Examples are the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of the Soviet Union and the All-China Federation of Trade Unions, were and are transmission belt organisations. The term originates from Vladimir Lenin Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov ( 187021 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary, politician and political theorist. He was the first head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 until Death and state funeral of ...'s speech to the 8th All-Russian Congress of Soviets, the All-Russian Central Council of Trade Unions and the Moscow City Council of Trade Unions, on 30 December 1920. References Books * * * Footnotes Communist terminology {{poli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilian
A civilian is a person who is not a member of an armed force. It is war crime, illegal under the law of armed conflict to target civilians with military attacks, along with numerous other considerations for civilians during times of war. If a civilian engages in hostilities, they are an unlawful combatant and temporarily lose their protection from attack. It is slightly different from a non-combatant, because some non-combatants are not civilians (for example, people who are not in a military but support war effort or military operations, military chaplains, or military personnel who are serving with a neutral country). Civilians in the territories of a party to an armed conflict are entitled to certain privileges under the customary international law, customary laws of war and Treaty, international treaties such as the Fourth Geneva Convention. The privileges that they enjoy under international law depends on whether the conflict is an internal one (a civil war) or an internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes the Economic ideology, economic, Political philosophy, political, and Social theory, social theories and Political movement, movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can take various forms, including State ownership, public, Community ownership, community, Collective ownership, collective, cooperative, or Employee stock ownership, employee.: "Just as private ownership defines capitalism, social ownership defines socialism. The essential characteristic of socialism in theory is that it destroys social hierarchies, and therefore leads to a politically and economically egalitarian society. Two closely related consequences follow. First, every individual is entitled to an equal ownership share that earns an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Junta
A military junta () is a system of government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''Junta (governing body), junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the Junta (Peninsular War), national and local junta organized by the Spanish resistance to Peninsular War, Napoleon's invasion of Spain in 1808.Junta ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (last updated 1998). The term is now used to refer to an authoritarian form of government characterized by oligarchic military dictatorship, as distinguished from other categories of authoritarian rule, specifically Strongman (politics), strongman (autocratic military dictatorships); machine (oligarchic party dictatorships); and bossism (autocratic party dictatorships). A junta often comes to power as a result of a coup d'état. The junta may either formally take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire, historically known as Abyssinia or simply Ethiopia, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It existed from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak around 1270 until the 1974 Ethiopian coup d'état, 1974 coup d'état by the Derg, which ended the reign of the final Emperor, Haile Selassie. In the late 19th century, under Emperor Menelik II, the Menelik II's conquests, empire expanded significantly to the south, and in 1952, Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea, Eritrea was federated under Selassie's rule. Despite being surrounded by hostile forces throughout much of its history, the empire maintained a kingdom centered on its Orthodox Tewahedo, ancient Christian heritage. Founded in 1270 by Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Kingdom of Aksum, Aksumite king and ultimately King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, it replaced the Agaw people, Agaw Zagwe Kingdom, kingdom of the Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haile Selassie
Haile Selassie I (born Tafari Makonnen or ''Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles#Lij, Lij'' Tafari; 23 July 189227 August 1975) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as the Ethiopian aristocratic and court titles, Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (') under Empress Zewditu between 1916 and 1930. Widely considered to be a defining figure in modern History of Ethiopia#Modern, Ethiopian history, he is accorded divine importance in Rastafari, an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic religion that emerged in the 1930s. A few years before he began his reign over the Ethiopian Empire, Selassie defeated Ethiopian army commander Gugsa Welle, Ras Gugsa Welle Bitul, nephew of Empress Taytu Betul, at the Battle of Anchem. He belonged to the Solomonic dynasty, founded by Emperor Yekuno Amlak in 1270. Selassie, seeking to modernise Ethiopia, introduced political and social reforms including the 1931 Constitution of Ethiopia, 1931 constitution and the Abolition of slavery i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |