|
Women's Royal Naval Service
The Women's Royal Naval Service (WRNS; popularly and officially known as the Wrens) was the women's branch of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. First formed in 1917 for the World War I, First World War, it was disbanded in 1919, then revived in 1939 at the beginning of the World War II, Second World War, remaining active until integrated into the Royal Navy in 1993. WRNS included Cooking, cooks, clerks, Morse code, wireless telegraphists, Plot (radar), radar plotters, weapons analysts, Rangefinding telemeter, range assessors, electricians, air mechanics, ground transport vehicle drivers and despatch_rider, motorcycle dispatch riders. History First World War The WRNS was formed in 1917 during the World War I, First World War. On 10 October 1918, nineteen-year-old Josephine Carr from Cork (city), Cork became the first Wren to die on active service, when her ship, the RMS Leinster, RMS ''Leinster'' was torpedoed. By the end of the war the service had 5,500 members, 500 of them offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Correct Angle At Which The New Wrns Hat Is To Be Worn
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps to form the Royal Air Force (RAF), the world's first independent air force. It was replaced by the Fleet Air Arm, initially consisting of those RAF units that normally operated from ships, but emerging as a separate unit similar to the original RNAS by the time of the Second World War. History Background On 21 July 1908 Captain Reginald Bacon, who was a member of the Aerial Navigation Sub-Committee, submitted to the First Sea Lord John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, Sir John Fisher that a rigid airship based on the Imperial Germany, German Zeppelin be designed and constructed by the firm of Vickers. After much discussion on the Committee of Imperial Defence the suggestion was approved on 7 May 1909. Though Bacon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THE ROYAL NAVY 1945 - 1975 TR23169-2
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colossus Computer
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British cryptanalysis, codebreakers in the years 1943–1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used vacuum tube, thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean algebra (logic), Boolean and counting operations. Colossus is thus regarded as the world's first computer programming, programmable, electronics, electronic, digital electronics, digital computer, although it was programmed by switches and plugs and not by a stored-program computer, stored program. Colossus was designed by General Post Office (GPO) research telephone engineer Tommy Flowers based on plans developed by mathematician Max Newman at the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park. Alan Turing's use of probability in cryptanalysis (see Banburismus) contributed to its design. It has sometimes been erroneously stated that Turing designed Colossus to aid the cryptanalysis of the Enigma. (Turing's machine that helped decode Enigma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
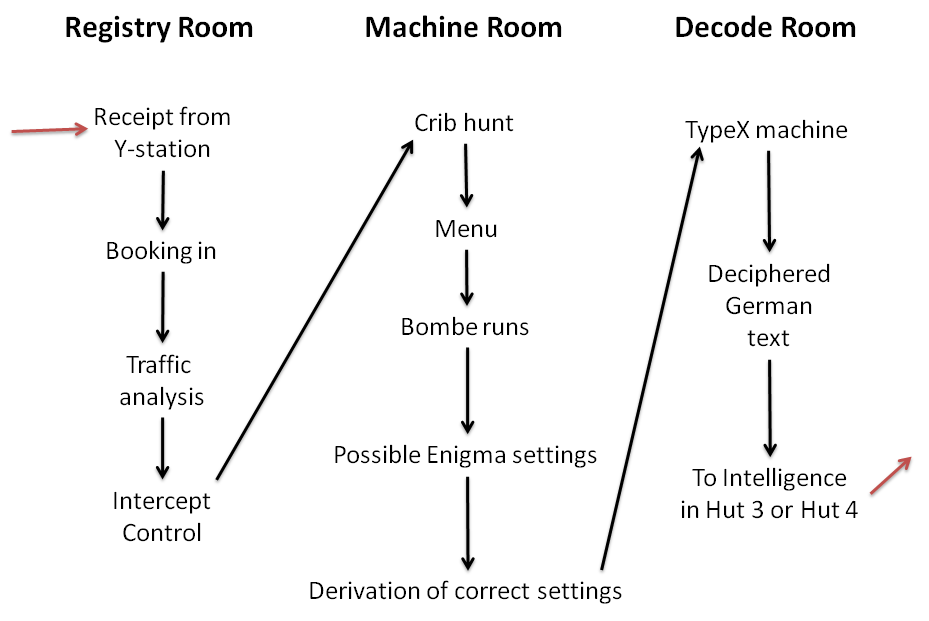
Bombe
The bombe () was an Electromechanics, electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma machine, Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The United States Navy, US Navy and United States Army, US Army later produced their own machines to the same functional specification, albeit engineered differently both from each other and from Polish and British bombes. The British bombe was developed from a device known as the "Bomba (cryptography), bomba" (), which had been designed in Poland at the Biuro Szyfrów (Cipher Bureau) by cryptologist Marian Rejewski, who had been breaking German Enigma machine, Enigma messages for the previous seven years, using it and earlier machines. The initial design of the British bombe was produced in 1939 at the UK Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park by Alan Turing, with an important refinement devised in 1940 by Gordon Welchman. The engineering design and construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and Bletchley Park estate, estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes (Buckinghamshire), that became the principal centre of Allies of World War II, Allied World War II cryptography, code-breaking during the Second World War. During World War II, the estate housed the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS), which regularly penetrated the secret communications of the Axis Powers most importantly the German Enigma machine, Enigma and Lorenz cipher, Lorenz ciphers. The GC&CS team of codebreakers included John Tiltman, Dilwyn Knox, Alan Turing, Harry Golombek, Gordon Welchman, Conel Hugh O'Donel Alexander, Hugh Alexander, Donald Michie, W. T. Tutte, Bill Tutte and Stuart Milner-Barry. The team at Bletchley Park devised automatic machinery to help with decryption, culminating in the development of Colossus computer, Colossus, the world's first programmable digital electronic computer. Codebreaking operations at Bletchley Park ended in 1946 and al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Code And Cypher School
The Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) was a British signals intelligence agency set up in 1919. During the First World War, the British Army and Royal Navy had separate signals intelligence agencies, MI1b and NID25 (initially known as Room 40) respectively. It was particularly known for its work on codebreaking at Bletchley Park and after the war became the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ). Interwar period In 1919, the Cabinet's Secret Service Committee, chaired by Lord Curzon, recommended that a peacetime codebreaking agency should be created, a task which was given to the Director of Naval Intelligence, Hugh Sinclair.Johnson, 1997, p. 44 Sinclair merged staff from NID25 and MI1b into the new organisation, which initially consisted of around 25–30 officers and a similar number of clerical staff. It was titled the "Government Code and Cypher School" (GC&CS), a cover-name which was chosen by Victor Forbes of the Foreign Office. Alastair Denniston, who h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colossus
Colossus, Colossos, or the plural Colossi or Colossuses, may refer to: Statues * Any exceptionally large statue; colossal statues, are generally taken to mean a statue at least twice life-size ** List of tallest statues ** :Colossal statues * '' Apennine Colossus'', a stone statue created as a personification of the Apennine mountains * '' Colossus of Barletta'', a bronze statue of an unidentified Roman emperor * ''Colossus of Constantine'', a bronze and marble statue of the Roman emperor Constantine the Great * ''Colossi of Memnon'', two stone statues of Pharaoh Amenhotep III * '' Colossus of Nero'', a bronze statue of the Roman emperor Nero * '' Colossus of Ramesses II'' * ''Colossus of Rhodes'', a bronze statue of the Greek god Helios Amusement rides * Colossus (Ferris wheel), Ferris wheel at Six Flags St. Louis, Missouri, US * ''Colossus'', a pirate ship at Robin Hill theme park, Isle of Wight, UK Roller coasters * Colossos (Heide Park), in Lower Saxony, Germany * Colos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slogan
A slogan is a memorable motto or phrase used in a clan or a political, commercial, religious, or other context as a repetitive expression of an idea or purpose, with the goal of persuading members of the public or a more defined target group. The '' Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines a slogan as "a short and striking or memorable phrase used in advertising". A slogan usually has the attributes of being memorable, very concise and appealing to the audience. Etymology The word ''slogan'' is derived from ''slogorn'', which was an Anglicisation of the Scottish Gaelic and Irish ( 'army', 'host' and 'cry').Merriam-Webster (2003), p. 1174. Irish George E. Shankel's (1941, as cited in Denton 1980) research states that "English-speaking people began using the term by 1704". The term at that time meant "the distinctive note, phrase or cry of any person or body of persons". Slogans were common throughout the European continent during the Middle Ages; they were used primarily as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wounded In Action
Wounded in action (WIA) describes combatants who have been wounded while fighting in a combat zone during wartime, but have not been killed. Typically, it implies that they are temporarily or permanently incapable of bearing arms or continuing to fight. Generally, the Wounded in Action are far more numerous than those killed. Common combat injuries include second and third-degree burns, broken bones, shrapnel wounds, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, nerve damage, paralysis, loss of sight and hearing, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and limb loss. For the U.S. military, becoming WIA in combat generally results in subsequent conferral of the Purple Heart, because the purpose of the medal itself (one of the highest awards, military or civilian, officially given by the American government) is to recognize those killed, incapacitated, or wounded in battle. NATO's definitions Wounded in action A battle casualty other than ''killed in action'' who has incurred an inju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killed In Action
Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces at the moment of action. The United States Department of Defense, for example, says that those declared KIA did not need to have fired their weapons, but only to have been killed due to hostile attack. KIAs include those killed by friendly fire during combat, but not from incidents such as accidental vehicle crashes, murder, or other non-hostile events or terrorism. KIA can be applied both to front-line combat troops and naval, air, and support forces. Furthermore, the term died of wounds (DOW) is used to denote personnel who reached a medical treatment facility before dying. The category ''died of wounds received in action'' (''DWRIA'') is also used for combat related casualties which occur after medical evacuation. PKIA means presumed killed in action. This term is used when personnel are lost in battle, initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethel Goodenough
Superintendent Ethel Mary Goodenough (12January 190010February 1946), usually known as Angela Goodenough, was a British naval officer who was the deputy director of the Women's Royal Naval Service when it was reformed in 1939. Early life Goodenough was born in British India and baptised at Shimla. Her parents were Muriel Grace Mitford (born Ogbourne) and Captain Herbert Lane Goodenough of Setley in Hampshire. Her father served in the Indian army. Her parents arranged privately for her education and her first job was in the Admiralty. She had several relatives in the Navy and she enjoyed working in posts that were close to that branch of the forces. By 1937 she was promoted within the Civil Service as "chief woman officer". She became responsible for the welfare of every woman who was a civil servant and for the recruitment of further temporary staff. Women's Royal Naval Service In 1939 when war broke out the Women's Royal Naval Service that had been disbanded in 1919 was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |