|
Wisdom Literature
Wisdom literature is a genre of literature common in the ancient Near East. It consists of statements by sages and the wise that offer teachings about divinity and virtue. Although this genre uses techniques of traditional oral storytelling, it was disseminated in written form. The earliest known wisdom literature dates back to the middle of the 3rd millennium BC, originating from ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt. These regions continued to produce wisdom literature over the subsequent two and a half millennia. Wisdom literature from Jewish, Greek, Chinese, and Indian cultures started appearing around the middle of the 1st millennium BC. In the 1st millennium AD, Egyptian-Greek wisdom literature emerged, some elements of which were later incorporated into Islamic thought. Much of wisdom literature can be broadly categorized into two types – conservative "positive wisdom" and critical "negative wisdom" or "vanity literature": * Conservative Positive Wisdom – Pragmatic, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lens - Inauguration Du Louvre-Lens Le 4 Décembre 2012, La Galerie Du Temps, N° 018
A lens is a transmissive optics, optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a #Compound lenses, compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common Optical axis, axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are Grinding (abrasive cutting), ground, Polishing, polished, or Molding (process), molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a Prism (optics), prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices such as telescopes, binoculars, and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as Near-sightedness, myopia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dialogue Between A Man And His God
The Dialogue between a Man and His God is the earliest known text to address the answer to the question of why a god permits evil, or theodicy, a reflection on human suffering. It is a piece of Wisdom Literature extant on a single clay cuneiform tablet written in Akkadian and attributed to Kalbanum, on the last line, an individual otherwise unknown. It is dated to the latter part of the Old Babylonian period, around the reign of Ammi-Ditana (reigned 1683–1640s BC) according to Lambert, and is currently housed in the Louvre Museum, accession number AO 4462. It is of unknown provenance as it was purchased from an antiquities dealer by the Museum in 1906. It shares much of its style with an earlier Sumerian work, “Man and His God”, a penitential prayer of the Ur III period. The text With sixty-nine lines arranged in ten strophes, each separated by a horizontal line, the work is structured around a dialogue between two people, one of whom has lost favor with both his lord an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
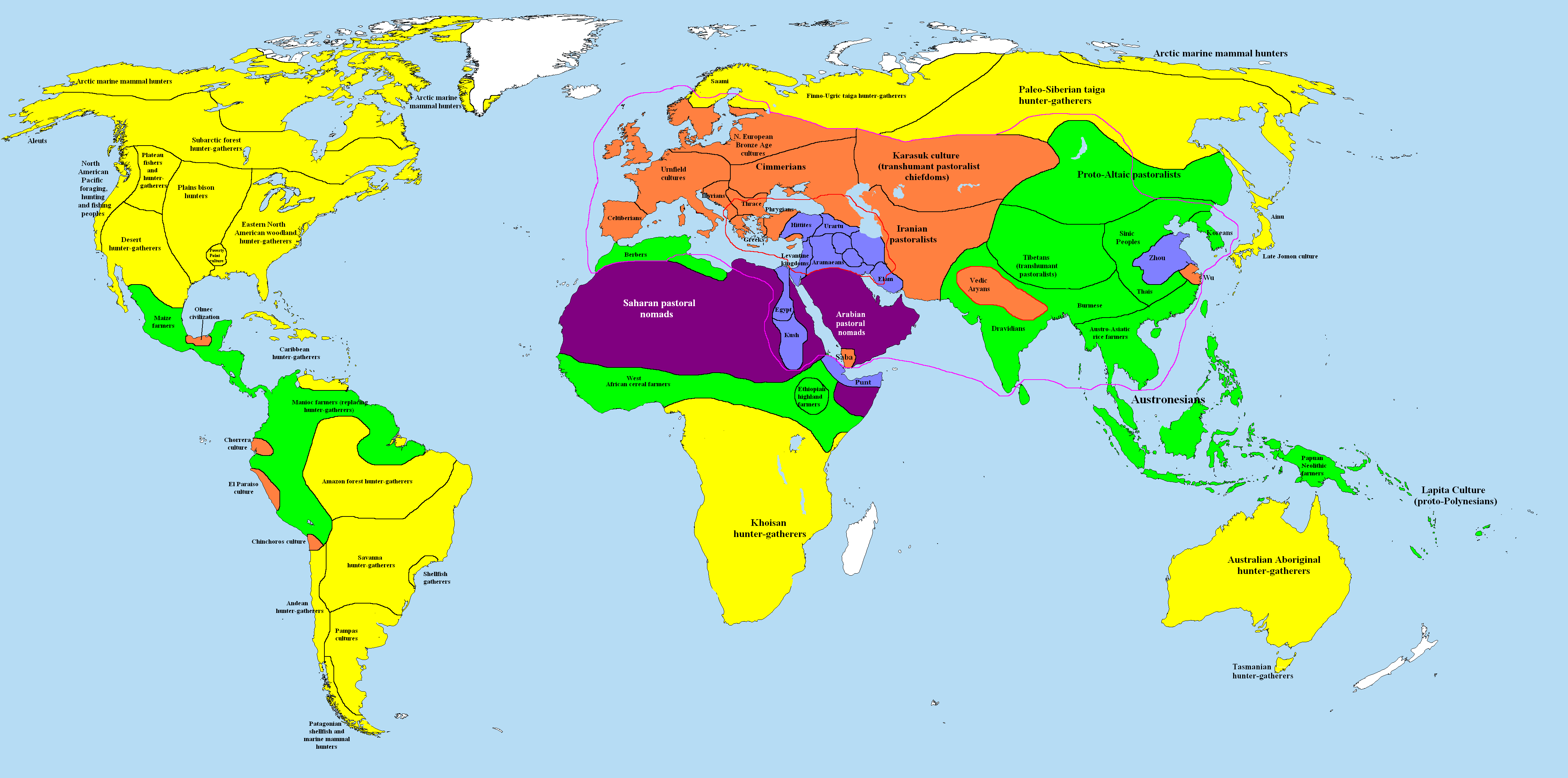
Second Millennium BC
File:2nd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Hammurabi, Babylonian king, best known for his code of laws; The gold funerary mask of Tutankhamun has become a symbol of ancient Egyptian civilization and its enduring legacy; Nebra sky disc is considered the oldest concrete representation of astronomical phenomena, such as the sun, moon, and stars; Mask of Agamemnon; Hieroglyphs from the tomb of Seti I; The Lion Gate of Hattusa is a testament to the architectural and artistic skills of the Hittites (Background: Bull-Leaping Fresco ca. 1450-1400 BC). rect 23 27 345 383 Hammurabi rect 433 16 775 443 Tutankhamun rect 869 18 1264 338 Nebra sky disc rect 103 408 375 680 Mask of Agamemnon rect 466 470 833 705 Egyptian hieroglyphs rect 870 392 1262 656 Hittites rect 1 1 1279 719 Minoan civilization The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC. In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age. The Ancient Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Third Millennium BC
File:3rd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Pyramid of Djoser; Khufu; Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World; Cuneiform, a contract for the sale of a field and a house; Enheduana, a high priestess and one of the earliest known authors in history; Gudea (Background: Standard of Ur). rect 34 26 474 319 Pyramid of Djoser rect 541 58 802 271 Khufu rect 825 28 1264 297 Great Pyramid of Giza rect 79 352 401 656 Cuneiform rect 572 309 770 665 Enheduana rect 920 320 1157 676 Gudea rect 1 1 1279 719 Standard of Ur The 3rd millennium BC spanned the years 3000 to 2001 BC. This period of time corresponds to the Early to Middle Bronze Age, characterized by the early empires in the Ancient Near East. In Ancient Egypt, the Early Dynastic Period is followed by the Old Kingdom. In Mesopotamia, the Early Dynastic Period is followed by the Akkadian Empire. In what is now Northwest India and Pakistan, the Indus Valley civilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sumeria
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. Like nearby Elam, it is one of the cradles of civilization, along with Egypt, the Indus Valley, the Erligang culture of the Yellow River valley, Caral-Supe civilization, Caral-Supe, and Mesoamerica. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, a surplus of which enabled them to form urban settlements. The world's earliest known texts come from the Sumerian cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between , following a period of proto-writing . Name The term "Sumer" () comes from the Akkadian Empire, Akkadian name for the "Sumerians", the ancient non-Semitic languages, Semitic-speaking inhabitants of southern Mesopotamia.Piotr Michalowski, "Sumerian," ''The Cambridge Encyclope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zuhayr Bin Abi Sulma
Zuhayr bin Abī Sulmā (; ), also romanized as Zuhair or Zoheir, was a pre-Islamic Arabian poet who lived in the 6th & 7th centuries AD. He is considered one of the greatest writers of Arabic poetry in pre-Islamic times. Zuhayr belonged to the Banu Muzaina. His father was a poet and his elder son Ka'b bin Zuhayr also became a poet, reading his works to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Zuhayr's poems can be found in Hammad Ar-Rawiya's anthology, the ''Mu'allaqat'' ("the Suspended"), a collection of pre-Islamic poetry. He was one of the seven poets featured in that collection who were reputed to have been honoured by hanging copies of their work in the Kaaba at Mecca. He was Umar ibn al-Khattab's favourite poet. Zuhayr's poetry was written when two Arabic tribes ended a longstanding hostility. His poems deal with raids and other subjects of nomadic desert life. He also wrote satirical poems and poems about the glory of his tribe, but in his verses he was less satiric than mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pre-Islamic Poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in place of, Denotation, literal or surface-level meanings. Any particular instance of poetry is called a poem and is written by a poet. Poets use a variety of techniques called poetic devices, such as assonance, alliteration, Phonaesthetics#Euphony and cacophony, euphony and cacophony, onomatopoeia, rhythm (via metre (poetry), metre), and sound symbolism, to produce musical or other artistic effects. They also frequently organize these effects into :Poetic forms, poetic structures, which may be strict or loose, conventional or invented by the poet. Poetic structures vary dramatically by language and cultural convention, but they often use Metre (poetry), rhythmic metre (patterns of syllable stress or syllable weight, syllable (mora) weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorites, Amorite-ruled state . During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad" ( in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi (floruit, fl. –1752 BC middle chronology, or –1654 BC, short chronology timeline, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Works And Days
''Works and Days'' ()The ''Works and Days'' is sometimes called by the Latin translation of the title, ''Opera et Dies''. Common abbreviations are ''WD'' and ''Op'' for ''Opera''. is a didactic poem written by ancient Greek poet Hesiod around 700 BC. It is in dactylic hexameter and contains 828 lines. At its center, the ''Works and Days'' is a Almanac, farmer's almanac in which Hesiod instructs his brother Perses in the agricultural arts. Scholars have seen this work against a background of agrarian crisis in mainland Greece, which inspired a wave of Greek colonies, colonial expeditions in search of new land. In the poem, Hesiod also offers his brother extensive moralizing advice on how he should live his life. ''Works and Days'' is perhaps best known for its two mythological aetiology, aetiologies for the toil and pain that define the human condition—the story of Prometheus and Pandora, and the so-called Ages of Man, Myth of Five Ages. Synopsis In ''Works and Days'', Hesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Griffin, "Greek Myth and Hesiod", J.Boardman, J.Griffin and O. Murray (eds.), ''The Oxford History of the Classical World'', Oxford University Press (1986), p. 88. Several of Hesiod's works have survived in their entirety. Among these are ''Theogony'', which tells the origins of the gods, their lineages, and the events that led to Zeus's rise to power, and ''Works and Days'', a poem that describes the five Ages of Man, offers advice and wisdom, and includes myths such as Pandora's box. Hesiod is generally regarded by Western authors as 'the first written poet in the Western tradition to regard himself as an individual persona with an active role to play in his subject.' Ancient authors credited Hesiod and Homer with establishing Greek relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Didactic
Didacticism is a philosophy that emphasises instructional and informative qualities in literature, art, and design. In art, design, architecture, and landscape, didacticism is a conceptual approach that is driven by the urgent need to explain. Overview The term has its origin in the Ancient Greek word διδακτικός (''didaktikos''), "pertaining to instruction", and signified learning in a fascinating and intriguing manner. Didactic art was meant both to entertain and to instruct. Didactic plays, for instance, were intended to convey a moral theme or other rich truth to the audience. During the Middle Age, the Roman Catholic chants like the '' Veni Creator Spiritus'', as well as the Eucharistic hymns like the '' Adoro te devote'' and '' Pange lingua'' are used for fixing within prayers the truths of the Roman Catholic faith to preserve them and pass down from a generation to another. In the Renaissance, the church began a syncretism between pagan and the Christian didacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |