|
White Metal
The white metals are a series of often decorative bright metal alloys used as a base for plated silverware, ornaments or novelties, as well as any of several lead-based or tin-based alloys used for things like bearings, jewellery, miniature figures, fusible plugs, some medals and metal type. The term is also used in the antiques trade for an item suspected of being silver, but not hallmarked. A white metal alloy may include antimony, tin, lead, cadmium, bismuth, and zinc (some of which are quite toxic). Not all of these metals are found in all white metal alloys. Metals are mixed to achieve a desired goal or need. As an example, a base metal for jewellery needs to be castable, polishable, have good flow characteristics, have the ability to cast fine detail without an excessive amount of porosity and cast at between . Silver In compliance with British law, the British fine art trade uses the term "white metal" in auction catalogues to describe foreign silver items which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and Copper(II) sulfate, copper. A typical example of an alloy is SAE 304 stainless steel, 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name Kohl (cosmetics), kohl. The earliest known description of this metalloid in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio. China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are Roasting (metallurgy), roasting followed by carbothermic reaction, reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron. The most common applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, Bullet, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking (oils and fats in use in frying pans and baking to prevent food sticking), to reduce rusting and friction in machinery, through the use of motor oil and Grease (lubricant), grease, bioapplications on humans (e.g., lubricants for Replacement joint, artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better, more efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermetallic
An intermetallic (also called intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Intermetallics are generally hard and brittle, with good high-temperature mechanical properties. They can be classified as stoichiometric or nonstoichiometic. The term "intermetallic compounds" applied to solid phases has long been in use. However, Hume-Rothery argued that it misleads, suggesting a fixed stoichiometry and a clear decomposition into species. Definitions Research definition In 1967 defined intermetallic compounds as ''solid phases containing two or more metallic elements, with optionally one or more non-metallic elements, whose crystal structure differs from that of the other constituents''. This definition includes: * Electron (or Hume-Rothery) compounds * Size packing phases. e.g. Laves phases, Frank–Kasper phases and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plain Bearing
file:NYC 100-driving-axle-friction-bearing.jpg, Plain bearing on a 1906 S-Motor locomotive showing the axle, bearing, oil supply and oiling pad file:Linear-table with detail numbered.png, A sliding table with four cylindrical bearings file:GWR Spoked wagon wheels.jpg, A Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset from a Great Western Railway (GWR) wagon showing a plain, or journal, bearing end A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing (mechanical), bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, wikt:journal#Noun, the part of the Axle, shaft in contact with the bearing slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the way (mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
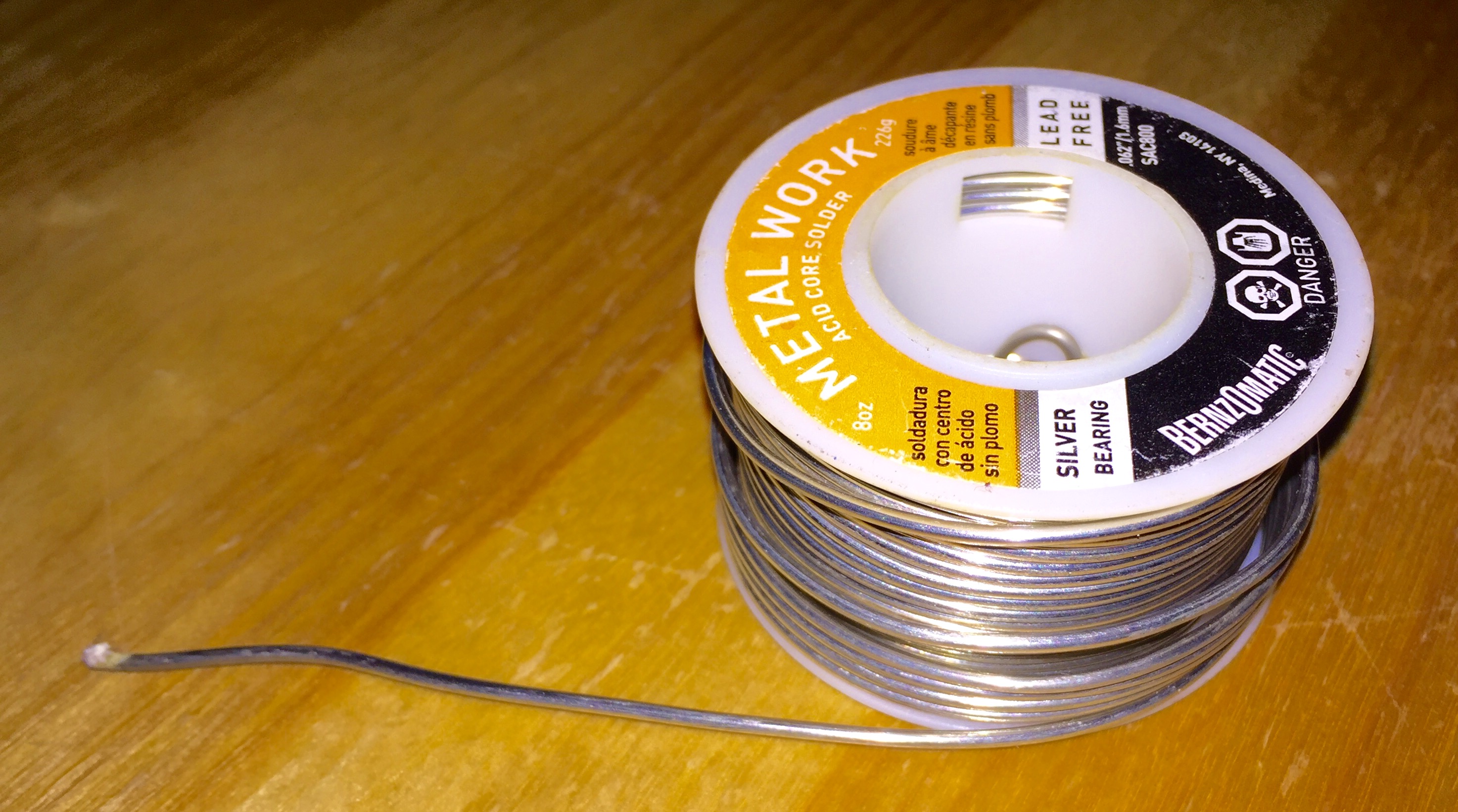
Solder
Solder (; North American English, NA: ) is a fusible alloy, fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable for use as solder should have a lower melting point than the pieces to be joined. The solder should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time. Solder used in making electrical connections also needs to have favorable electrical characteristics. Soft solder typically has a melting point range of , and is commonly used in electronics, plumbing, and sheet metal work. Alloys that melt between are the most commonly used. Soldering performed using alloys with a melting point above is called "hard soldering", "silver soldering", or brazing. In specific proportions, some alloys are eutectic — that is, the alloy's melting point is the lowest possible for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babbitt Metal
Babbitt metal or bearing metal is any of several alloys used for the bearing surface in a plain bearing. The original Babbitt alloy was invented in 1839 by Isaac Babbitt in Taunton, Massachusetts, United States. He disclosed one of his alloy recipes but kept others as trade secrets.Isaac Babbitt"Mode of making boxes for axles and gudgeons," U.S. patent no. 1,252 (issued: July 17, 1839). Babbitt did not patent his alloy, although he does state its formulation: "The inner parts of the boxes are to be lined with any of the harder kinds of composition known under the names of britannia metal or pewter, of which block tin is the basis. An excellent compound for this purpose I have prepared by taking about 50 parts of tin, five of antimony, and one of copper, but I do not intend to confine myself to this particular composition." Other formulations were developed later.. Like other terms whose eponymous origin is long-since deemphasized (such as ''diesel engine'' or ''eustachian tube' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |