|
Whipple's Procedure
A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach. Anatomy involved in the procedure The most common technique of a pancreaticoduodenectomy consists of the en bloc removal of the distal segment (antrum) of the stomach, the first and second portions of the duodenum, the head of the pancreas, the common bile duct, and the gallbladder. Lymph nodes in the area are often removed during the operation as well (lymphadenectomy). However, not all lymph nodes are removed in the most common type of pancreaticoduodenectomy because studies sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known. The most common, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, accounts for about 90% of cases, and the term "pancreatic cancer" is sometimes used to refer only to that type. These adenocarcinomas start within the part of the pancreas that makes digestive enzymes. Several other types of cancer, which collectively represent the majority of the non-adenocarcinomas, can also arise from these cells. About 1–2% of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors, which arise from the hormone-producing neuroendocrine cell, cells of the pancreas. These are generally less aggressive than pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Signs and symptoms of the most-common form of pancreatic cancer may include jaundice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled coeliac in British English), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
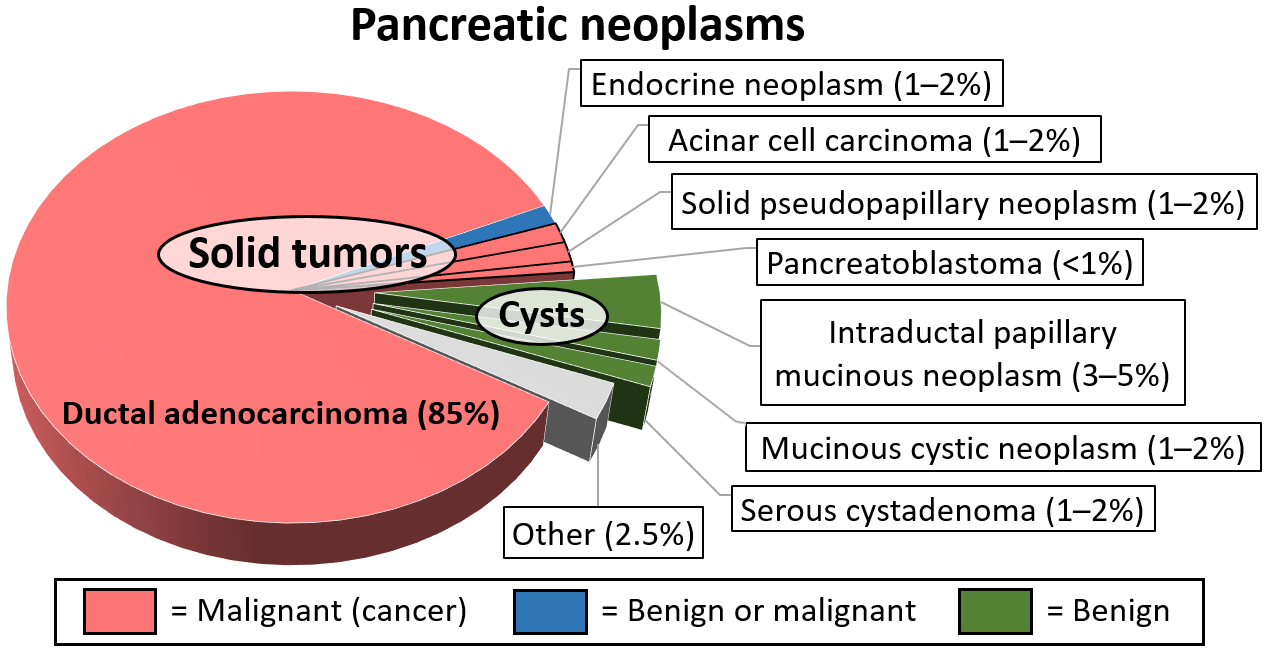
Pancreatic Tumor
A pancreatic tumor is an abnormal growth in the pancreas. In adults, almost 90% are pancreatic cancer and a few are benign Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig .... Pancreatic tumors are rare in children. Classification is based on cellular differentiation (ductal, acinar, neuroendocrine, other) and gross appearance (intraductal, cystic, solid). Each different type of pancreatic tumor has a different appearance when examined under a microscope. These unique microscopic features and genetic markers are what allow for proper diagnosis and treatments in patients with pancreatic cancers. Types The most common type of pancreatic tumor is pancreatic adenocarcinoma, which accounts near 90% of all pancreas cancers. Adenocarcinomas are exocrine tumors of the pancreas, which imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the organ's normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption. It is a disease process characterized by irreversible damage to the pancreas as distinct from reversible changes in acute pancreatitis. Tobacco smoke and alcohol misuse are two of the most frequently implicated causes, and the two risk factors are thought to have a synergistic effect with regards to the development of chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatitis is a risk factor for the development of pancreatic cancer. Signs and symptoms * Upper abdominal pain: Upper abdominal pain which increases after drinking or eating, lessens when fasting or sitting and leaning forward. Some people may not suffer pain. * Nausea and vomiting * Steatorrhea: Frequent, oily, foul-smelling bowel movements. Damage to the pancreas can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periampullary Cancer
Periampullary cancer is a cancer that forms near the ampulla of Vater, an enlargement of the ducts from the liver and pancreas where they join and enter the small intestine. Quoted material is in the public domain. It consists of: # ampullary tumour from ampulla of Vater # cancer of lower common bile duct # duodenal cancer adjacent to ampulla # carcinoma head of pancreas It presents with painless jaundice which may have a waxing and waning nature, because at times the sloughing of the tumor tissue relieves the obstruction partially. Signs and symptoms of periampullary cancer Signs and symptoms of periampullary cancer include: * Jaundice (yellowing of skin, eyes and urine with pale stools) * Itching * Abdominal pain * Weight loss and loss of appetite * Recurrent vomiting * Black stools * Anemia Treatment Source: The treatment depends upon the stage of the disease and degree of jaundice. Surgery is the best possible option and can be considered if the cancer is diagnosed at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth Lumbar vertebrae, lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower ("anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies Posterior (anatomy), posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Vein
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine (jejunum and ileum). Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta. Structure Tributaries of the superior mesenteric vein drain the small intestine, large intestine, stomach, pancreas and vermiform appendix, appendix and include: * Right gastro-omental vein (also known as the right gastro-epiploic vein) * inferior pancreaticoduodenal veins * veins from jejunum * veins from ileum * middle colic vein – drains the transverse colon * right colic vein – drains the ascending colon * ileocolic vein The superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein. Clinical significance Thrombosis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of three portal venous systems in the human body; the others being the hypophyseal portal system, hypophyseal and Renal portal system, renal portal systems. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric vein, superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric vein, inferior mesenteric, left gastric vein, left, right gastric veins and the pancr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
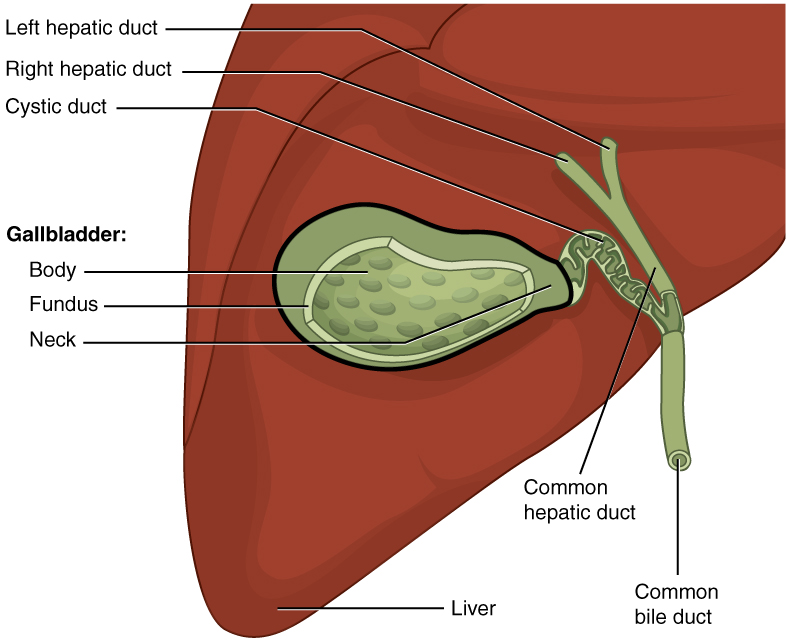
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either Laparoscopy, laparoscopically, or via an Minimally invasive procedures#Open surgery, open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include Biliary injury, bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, vasculobiliary injury, retained gallstones, liver abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastric Artery
The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ... before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery. Anatomy Variation Origin In most (53%) individuals, the RGA arises from the proper hepatic artery. It can also arise from the region of division of the common hepatic artery (20%), the left branch of the hepatic artery (15%), the gastroduodenal artery (8%), and - most rarely - the common hepatic artery itself (4%). Additional images File:Gray532.png, The celiac artery and its branches; the liver has been raised, and the lesser omentum and anterior layer of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |