|
Westphalen–Lettré Rearrangement
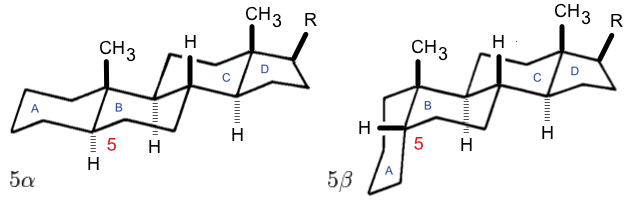
The Westphalen–Lettré rearrangement is a classic organic reaction in organic chemistry describing a rearrangement reaction of cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol diacetate with acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid. In this reaction one equivalent of water is lost, a double bond is formed at C10–C11 and importantly the methyl group at the C10 position migrates to the C5 position. The reaction is first-order in steroid in the presence of an excess of sulfuric acid''Acid catalysed reactions of 5α-hydroxy-steroids—III : The westphalen rearrangement''Tetrahedron, Volume 21, Issue 6, 1965, Pages 1567–1580 J. W. Blunt, A. Fischer, M. P. Hartshorn, F. W. Jones, Kirk D. N. and S. W. Yoong () and the first reaction step in the reaction mechanism is likely the formation of a sulfate ester followed by that of a carbocation Carbocation is a general term for ions with a positively charged carbon atom. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, mechanistic organic photochemistry, photochemical reactions and organic redox reaction, redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels–Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with '' Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
Carbocation is a general term for ions with a positively charged carbon atom. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. Among the simplest carbocations are the methenium (a carbenium ion), methanium (a carbonium ion), acylium ions , and Vinyl cation, vinyl cations. Until the early 1970s, carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. This nomenclature was proposed by George Andrew Olah, G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a Three-center two-electron bond, three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called 'non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Ester
In organosulfur chemistry, organosulfates are a class of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the structure . The core is a sulfate group and the R group is any Organyl group, organic residue. All organosulfates are formally esters derived from Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and sulfuric acid () although many are not prepared in this way. Many sulfate esters are used in detergents, and some are useful reagents. Alkyl sulfates consist of a hydrophobe, hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain, a polar sulfate group (containing an anion) and either a cation or amine to neutralize the sulfate group. Examples include: sodium lauryl sulfate (also known as sulfuric acid mono dodecyl ester sodium salt) and related potassium and ammonium salts. Applications Alkyl sulfates are commonly used as anionic surfactants in liquid soaps and detergents used to clean wool, as surface cleaners, and as active ingredients in laundry detergents, shampoos and conditioners. They can also be fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs. A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of an overall chemical reaction. The detailed steps of a reaction are not observable in most cases. The conjectured mechanism is chosen because it is thermodynamically feasible and has experimental support in isolated intermediates (see next section) or other quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the reaction. It also describes each reactive intermediate, activated complex, and transition state, which bonds are broken (and in what order), and which bonds are formed (and in what order). A complete mechanism must also explain the reason for the reactants and catalyst used, the stereochemistry observed in reactants and products, all products formed and the amount of each. The electron or arrow pushing method is often used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Reaction
In chemistry, the rate equation (also known as the rate law or empirical differential rate equation) is an empirical differential mathematical expression for the reaction rate of a given reaction in terms of concentrations of chemical species and constant parameters (normally rate coefficients and partial orders of reaction) only. For many reactions, the initial rate is given by a power law such as :v_0\; =\; k mathrmx mathrmy where and are the molar concentrations of the species and usually in moles per liter (molarity, ). The exponents and are the partial ''orders of reaction'' for and , respectively, and the ''overall'' reaction order is the sum of the exponents. These are often positive integers, but they may also be zero, fractional, or negative. The order of reaction is a number which quantifies the degree to which the rate of a chemical reaction depends on concentrations of the reactants. In other words, the order of reaction is the exponent to which the concentrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalen Umlagerung Übersichtsreaktion V1
Westphalen is a German surname. It may refer to: People * Ferdinand von Westphalen (1799–1876), German politician * Jenny von Westphalen, wife of German philosopher Karl Marx * Judith Westphalen, Peruvian painter * Karl von Westphalen, German politician * Ludwig von Westphalen, liberal German government official * Marc Westphalen, German sprint canoer * Otto Westphalen, German naval officer Fictional * Kristin Westphalen, character in SeaQuest DSV Places * Frederico Westphalen, city in Brazil ** Roman Catholic Diocese of Frederico Westphalen * Westphalia Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants. The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ... or Westfalia is a region in Germany. Science * Westphalen-Lettré rearrangement {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Westphalen
Theodor is a masculine given name. It is a German form of Theodore. It is also a variant of Teodor. List of people with the given name Theodor * Theodor Adorno, (1903–1969), German philosopher * Theodor Aman, Romanian painter * Theodor Blueger, Latvian professional ice hockey forward for the Pittsburgh Penguins of the National Hockey League (NHL) * Theodor Burghele, Romanian surgeon, President of the Romanian Academy * Theodor Busse, German general during World War I and World War II * Theodor Cazaban, Romanian writer * Theodor Eicke, German SS general * Theodor Fischer (fencer), German Olympic épée and foil fencer * Theodor Fontane, (1819–1898), German writer * Theodor Geisel, American writer and cartoonist, known by the pseudonym Dr. Seuss * Theodor W. Hänsch (born 1940), German physicist * Theodor Herzl, (1860–1904), Austrian-Hungary Jewish journalist and the founder of modern political Zionism * Theodor Heuss, (1884–1963), German politician and publicist * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula (whereas normal methane has the formula ). In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist between two different elements: for example, in a carbonyl group between a carbon atom and an oxygen atom. Other common double bonds are found in azo compounds (N=N), imines (C=N), and sulfoxides (S=O). In a skeletal formula, a double bond is drawn as two parallel lines (=) between the two connected atoms; typographically, the equals sign is used for this. Double bonds were introduced in chemical notation by Russian chemist Alexander Butlerov. Double bonds involving carbon are stronger and shorter than single bonds. The bond order is two. Double bonds are also electron-rich, which makes them potentially more reactive in the presence of a strong electron acceptor (as in addition reactions of the halogens). File:Ethene structural.svg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |