|
WavPack
WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format and application implementing the format. It is unique in the way that it supports hybrid audio compression alongside normal compression which is similar to how FLAC works. It also supports compressing a wide variety of lossless formats, including various variants of PCM and also DSD as used in SACDs, together with its support for surround audio. Features WavPack compression can compress (and losslessly restore) 8, 16, 24, and 32-bit fixed-point, and 32-bit floating-point PCM audio files in the . WAV file format. It can also handle DSD input in DSDIFF or DSF format. It also supports surround sound streams and high sampling rates. Like other lossless compression schemes, the data reduction rate varies with the source, but it is generally between 30% and 70% for typical popular music and somewhat better than that for classical music and other sources with greater dynamic range. Hybrid mode WavPack also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockbox
Rockbox is a free and open-source software replacement for the OEM firmware in various forms of digital audio players (DAPs) with an original kernel. It offers an alternative to the player's operating system, in many cases without removing the original firmware, which provides a plug-in architecture for adding various enhancements and functions. Enhancements include personal digital assistant (PDA) functions, applications, utilities, and games. Rockbox can also retrofit video playback functions on players first released in mid-2000. Rockbox includes a voice-driven user-interface suitable for operation by visually impaired users. Rockbox runs on a wide variety of devices with very different hardware abilities: from early Archos players with 1-bit character cell-based displays, to modern players with high resolution color displays, digital optical audio hardware and advanced recording abilities. History The Rockbox project was founded by the three Swedish developers Linus Fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WavPack Logo
WavPack is a free and open-source lossless audio compression format and application implementing the format. It is unique in the way that it supports hybrid audio compression alongside normal compression which is similar to how FLAC works. It also supports compressing a wide variety of lossless formats, including various variants of PCM and also DSD as used in SACDs, together with its support for surround audio. Features WavPack compression can compress (and losslessly restore) 8, 16, 24, and 32-bit fixed-point, and 32-bit floating-point PCM audio files in the . WAV file format. It can also handle DSD input in DSDIFF or DSF format. It also supports surround sound streams and high sampling rates. Like other lossless compression schemes, the data reduction rate varies with the source, but it is generally between 30% and 70% for typical popular music and somewhat better than that for classical music and other sources with greater dynamic range. Hybrid mode WavPack also incor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Stream Digital
Direct Stream Digital (DSD) is a trademark used by Sony and Philips for their system for digitally encoding audio signals for the Super Audio CD (SACD). DSD uses delta-sigma modulation, a form of pulse-density modulation encoding, a technique to represent audio signals in digital format, a sequence of single-bit values at a sampling rate of 2.8224 MHz. This is 64 times the CD audio sampling rate of 44.1 kHz, but with 1-bit samples instead of 16-bit samples. Noise shaping of the 64-times oversampled signal provides low quantization noise and low distortion in the audible bandwidth necessary for high resolution audio. DSD is simply a format for storing a delta-sigma signal without applying a decimation process that converts the signal to a PCM signal. Development DSD technology was developed and commercialized by Sony and Philips, the designers of the audio CD. However, in 2005, Philips sold its DSD tool division to Sonic Studio. ;Major label support DVD-Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 SLS
MPEG-4 SLS, or MPEG-4 Scalable to Lossless as per International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 14496-3:2005/Amd 3:2006 (Scalable Lossless Coding), is an extension to the MPEG-4 Part 3 (MPEG-4 Audio) standard to allow Lossless data compression, lossless Audio data compression, audio compression scalable to lossy MPEG-4 General Audio coding methods (e.g., variations of Advanced Audio Coding, AAC). It was developed jointly by the Institute for Infocomm Research (I2R) and Fraunhofer Society, Fraunhofer, which commercializes its implementation of a limited subset of the standard under the name of HD-AAC. Standardization of the HD-AAC profile for MPEG-4 Audio is under development (as of September 2009). MPEG-4 SLS allows having both a lossy layer and a lossless correction layer similar to Wavpack Hybrid, OptimFROG DualStream and DTS-HD Master Audio, providing backwards compatibility to MPEG Advanced Audio Coding, AAC-compliant bitstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADPCM
Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation (ADPCM) is a variant of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) that varies the size of the quantization step, to allow further reduction of the required data bandwidth for a given signal-to-noise ratio. Typically, the adaptation to signal statistics in ADPCM consists simply of an adaptive scale factor before quantizing the difference in the DPCM encoder. ADPCM was developed for speech coding by P. Cummiskey, Nikil S. Jayant and James L. Flanagan at Bell Labs in 1973. In telephony In telephony, a standard audio signal for a single phone call is encoded as 8000 analog samples per second, of 8 bits each, giving a 64 kbit/s digital signal known as DS0. The default signal compression encoding on a DS0 is either μ-law (mu-law) PCM (North America and Japan) or A-law PCM (Europe and most of the rest of the world). These are logarithmic compression systems where a 13- or 14-bit linear PCM sample number is mapped into an 8-bit value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Redundancy Check
A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to digital data. Blocks of data entering these systems get a short ''check value'' attached, based on the remainder of a polynomial division of their contents. On retrieval, the calculation is repeated and, in the event the check values do not match, corrective action can be taken against data corruption. CRCs can be used for error correction (see bitfilters). CRCs are so called because the ''check'' (data verification) value is a ''redundancy'' (it expands the message without adding information) and the algorithm is based on ''cyclic'' codes. CRCs are popular because they are simple to implement in binary hardware, easy to analyze mathematically, and particularly good at detecting common errors caused by noise in transmission channels. Because the check value has a fixed length, the function that generates it is occasionally used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, and music. Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science. Background Hearing is not a purely mechanical phenomenon of wave propagation, but is also a sensory and perceptual event. When a person hears something, that something arrives at the ear as a mechanical sound wave traveling through the air, but within the ear it is transformed into neural action potentials. These nerve pulses then travel to the brain where they are perceived. Hence, in many problems in acoustics, such as for Auditory system, audio processing, it is advantageous to take into account not just the mechanics of the environment, but also the fact that both the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cue Sheet (music Software)
A cue sheet, or cue file, is a metadata file which describes how the tracks of a CD or DVD are laid out. Cue sheets are stored as plain text files and commonly have a filename extension. CDRWIN first introduced cue sheets, which are now supported by many optical disc authoring applications and media players. Overview Cue sheets can describe many types of audio and data CDs. The main data (including audio) for a CD described by a cue sheet is stored in one or more files referenced by the cue sheet. Cue sheets also specify track lengths and CD-Text including track and disc titles and performers. They are especially useful when dividing audio stored in a single file into multiple songs or tracks. The data files referred to by the cue sheet may be audio files (commonly in MP3 or WAV format), or plain disc images, usually with a extension. When used for disc images, the format is usually called BIN/CUE, indicating that it stores a disc image composed of one cue sheet file and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ReplayGain
ReplayGain is a proposed technical standard published by David Robinson in 2001 to measure and normalize the perceived loudness of audio in computer audio formats such as MP3 and Ogg Vorbis. It allows media players to normalize loudness for individual tracks or albums. This avoids the common problem of having to manually adjust volume levels between tracks when playing audio files from albums that have been mastered at different loudness levels. Although this de facto standard is now formally known as ReplayGain, it was originally known as Replay Gain and is sometimes abbreviated RG. ReplayGain is supported in a large number of media software and portable devices. Operation ReplayGain works by first performing a psychoacoustic analysis of an entire audio track or album to measure peak level and perceived loudness. Equal-loudness contours are used to compensate for frequency effects and statistical analysis is used to accommodate for effects related to time. The differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIFF (File Format)
Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF) is a generic file container format for storing data in tagged chunks. It is primarily used for audio and video, though it can be used for arbitrary data. The Microsoft implementation is mostly known through the container formats AVI, ANI and WAV, which use RIFF as their basis. History RIFF was introduced in 1991 by Microsoft and IBM and used as the default format for Windows 3.1 multimedia files. It is based on Interchange File Format introduced by Electronic Arts in 1985 on the Amiga. IFF uses the big-endian convention of the Amiga's Motorola 68000 CPU, but in RIFF multi-byte integers are stored in the little-endian order of the x86 processors used in IBM PC compatibles. A RIFX format, which is big-endian, was also introduced. In 2010 Google introduced the WebP picture format, which uses RIFF as a container. Explanation RIFF files consist entirely of " chunks". The overall format is identical to IFF, except for the endianne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APEv2 Tag
APE tags comprise one extant convention used to store information (metadata) about a given digital audio file. Each APE tag constitutes a discrete element that describes a single attribute of the file's contents. Each consists of a key/value pair; the key is simply a label that names the attribute, such as , , , or , etc.), and associated with it is a corresponding value, namely, some information descriptive of this file, in terms of the attribute in question (e.g., for ). APE tags can be used with .ape-formatted recordings, as well as with sound files of other audio file formats. Essence A sound file, such as an .ape- or .mp3-formatted file, may, in addition to its payload audio data, also contain metadata that provide descriptive or statistical information about its audio content. When APE (v1) tags are used, they will appear at the end of the file, following the data; i.e., the digitized audio stream. Placing the tags at the end of the file, rather than at the beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
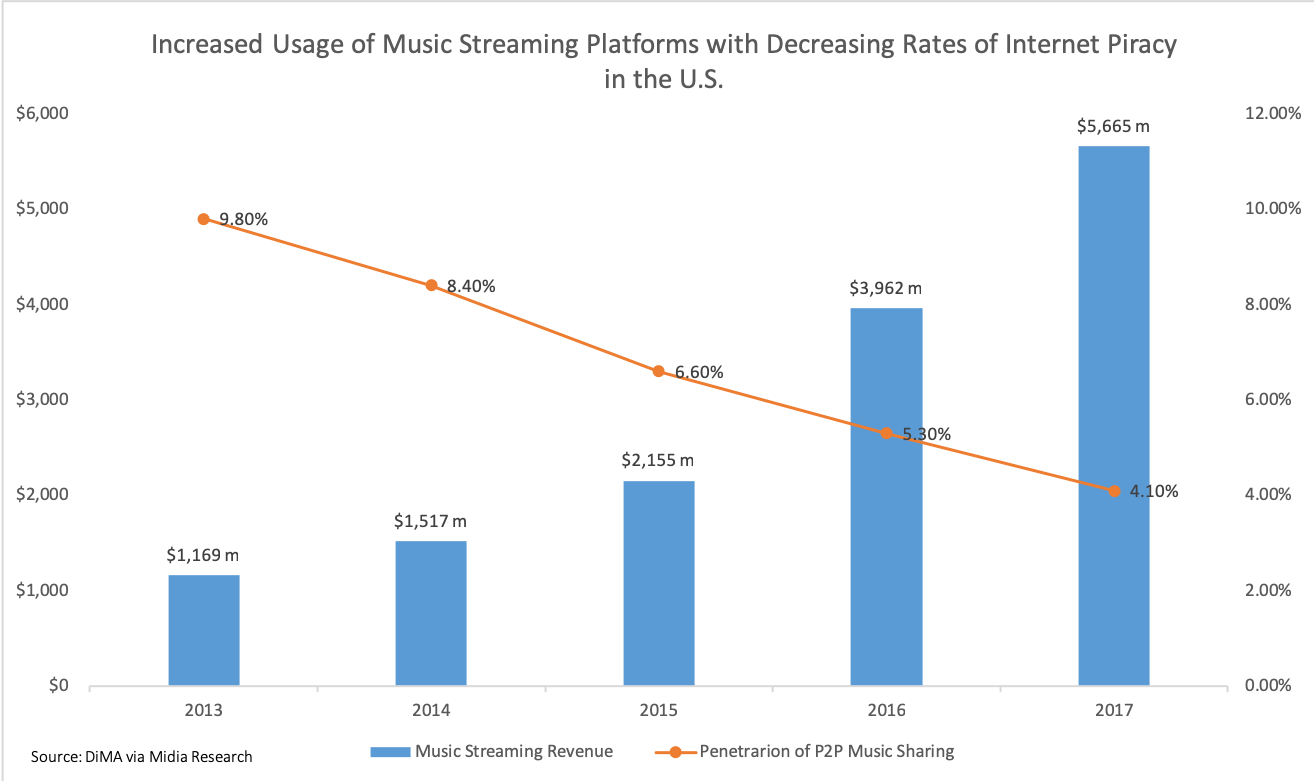
Streaming Media
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a Computer network, network for playback using a Media player (other), media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of Network packet, packets from a Server (computing), server to a client-server model, client and is rendered in real-time; this contrasts with file downloading, a process in which the end-user obtains an entire media file before consuming the content. Streaming is more commonly used for video on demand, streaming television, and music streaming services over the Internet. While streaming is most commonly associated with multimedia from a remote server over the Internet, it also includes offline multimedia between devices on a local area network. For example, using DLNA and a home server, or in a personal area network between two devices using Bluetooth (which uses radio waves rather than Internet Protocol, IP). Online streaming was initially popularized by RealNetworks and Microsoft in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |