|
Watson V
Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC) is an ultraviolet Raman spectrometer that uses fine-scale imaging and an ultraviolet (UV) laser to determine fine-scale mineralogy, and detect organic compounds designed for the ''Perseverance'' rover as part of the Mars 2020 mission. It was constructed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory with major subsystems being delivered from Malin Space Science Systems and Los Alamos National Laboratory. SHERLOC has a calibration target with possible Mars suit materials, and it will measure how they change over time in the Martian surface environment. Goals According to a 2017 Universities Space Research Association (USRA) report: Construction There are three locations on the rover where SHERLOC components are located. The SHERLOC Turret Assembly (STA) is mounted at the end of the rover arm. The STA contains spectroscopy and imaging components. The SHERLOC Body Assembly (SBA) is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars2020Rover-SHERLOC-20140731
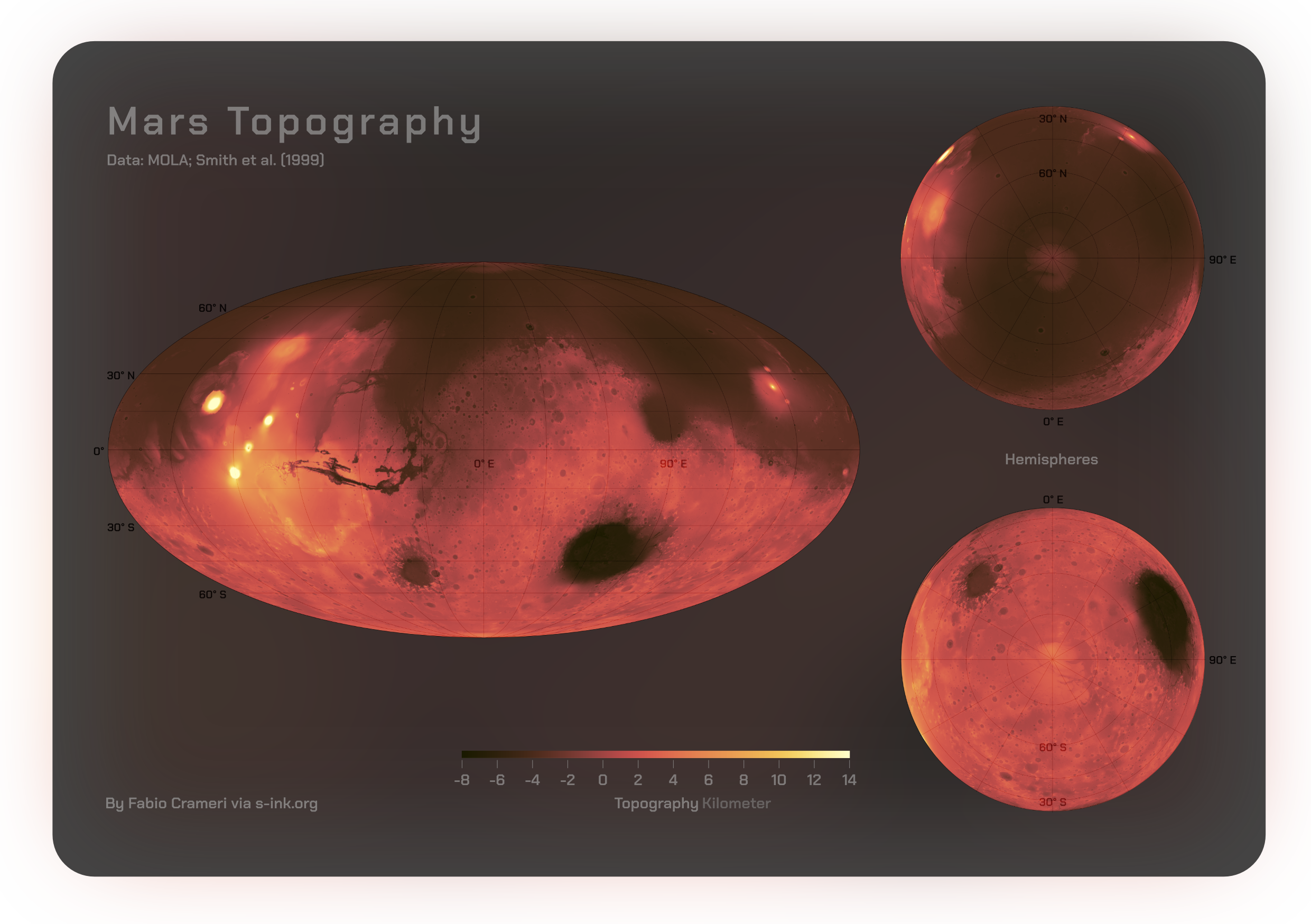
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of Mars surface color, its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () Atmosphere of Mars, atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, Groundwater on Mars, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and Martian polar ice caps, ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half List of Solar System objects by size, as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Martian regolith#Atmospheric dust, Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars 2020 Selfie Containing Both Perseverance Rover And Ingenuity
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Instruments
A scientific instrument is a device or tool used for scientific purposes, including the study of both natural phenomena and theoretical research. History Historically, the definition of a scientific instrument has varied, based on usage, laws, and historical time period. Before the mid-nineteenth century such tools were referred to as "natural philosophical" or "philosophical" apparatus and instruments, and older tools from antiquity to the Middle Ages (such as the astrolabe and pendulum clock) defy a more modern definition of "a tool developed to investigate nature qualitatively or quantitatively." Scientific instruments were made by instrument makers living near a center of learning or research, such as a university or research laboratory. Instrument makers designed, constructed, and refined instruments for purposes, but if demand was sufficient, an instrument would go into production as a commercial product. In a description of the use of the eudiometer by Jan Ingenhousz to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Mars Science Laboratory
The Mars Science Laboratory and its rover, Curiosity rover, ''Curiosity'', were launched from Earth on 26 November 2011. As of , , ''Curiosity'' has been in Gale Crater on the Mars, planet Mars for Sol (day on Mars), sols ( days, total days; ') since landing on 6 August 2012. ''(See Timeline of Mars Science Laboratory#Current status, Current status.)'' Prelaunch (2004–2011) In April 2004, the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) called for scientific experiments and instruments proposals for the Mars Science Laboratory and rover mission. Launch was proposed for September 2009. By 14 December 2004, eight proposals were selected, including instruments from Russia and Spain. Testing of components also began in late 2004, including Aerojet's monopropellant engine with the ability to throttle from 15 to 100 percent thrust with a fixed propellant inlet pressure. By November 2008 most hardware and software development was complete, and testing cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Information From The Mars Exploration Rover Mission
NASA's 2003 Mars Exploration Rover Mission has amassed an enormous amount of scientific information related to the Martian geology and atmosphere, as well as providing some astronomical observations from Mars. This article covers information gathered by the Opportunity rover during the initial phase of its mission. Information on science gathered by Spirit can be found mostly in the Spirit rover article. The unmanned Mars exploration mission, commenced in 2003 sent two robotic rovers, ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'', to explore the Martian surface and geology. The mission was led by Project Manager Peter Theisinger of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Principal Investigator Steven Squyres, professor of astronomy at Cornell University. Primary among the mission's scientific goals is to search for and characterize a wide range of rocks and soils that hold clues to past water activity on Mars. In recognition of the vast amount of scientific information amassed by both rov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Instrument For X-Ray Lithochemistry
Planetary Instrument for X-Ray Lithochemistry (PIXL) is an X-ray fluorescence, X-ray fluorescence spectrometer to determine the fine scale Chemical element, elemental composition of Martian surface materials designed for the Mars 2020, ''Perseverance'' rover as part of the Mars 2020 mission. PIXL is manufactured and made by NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Science objectives The scientific objectives of the instrument are the following: # Provide detailed geochemistry, geochemical assessment of past environments, habitability, and biosignature preservation potential. # Detect any potential chemical biosignatures that are encountered and characterize the geochemistry of any other types of potential biosignatures detected. # Provide a detailed geochemical basis for selection of a compelling set of samples for return to Earth. Gallery See also * Composition of Mars * Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' rover * Exploration of Mars * Geology of Mars * List of rocks on Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment
The Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) was a technology demonstration on the NASA Mars 2020 rover '' Perseverance'' investigating the production of oxygen on Mars. On April 20, 2021, MOXIE produced oxygen from carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere by using solid oxide electrolysis. This was the first experimental extraction of a natural resource from another planet for human use. The technology may be scaled up for use in a human mission to the planet to provide breathable oxygen, oxidizer, and propellant; water may also be produced by combining the produced oxygen with hydrogen. The experiment was a collaboration between the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Haystack Observatory, the NASA/Caltech Jet Propulsion Laboratory, with OxEon Energy. Objective MOXIE's objective was to produce oxygen of at least 98% purity at a rate of and to do this at least ten times, so the device can be tested in a range of times of the day, including at nigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rocks On Mars
Martian rocks and outcrops have been studied ''in-situ'' by various landers and rovers. While many of the rocks identified on the Martian surface are similar to each other, some have been considered scientifically important or otherwise notable and have been subjected to more extensive study or public interest. Names for Mars rocks are largely unofficial designations used for ease of discussion purposes, as the International Astronomical Union's official Martian naming system declares that objects smaller than are not to be given official names. Because of this, some less significant rocks seen in photos returned by Mars rovers have been named more than once, and others have even had their names changed later due to conflicts or even matters of opinion among researchers. Often rocks are named after the children or family members of astronauts or NASA employees. The rocks at the landing site of the '' Sojourner'' rover were given names of cartoon characters. Among them were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
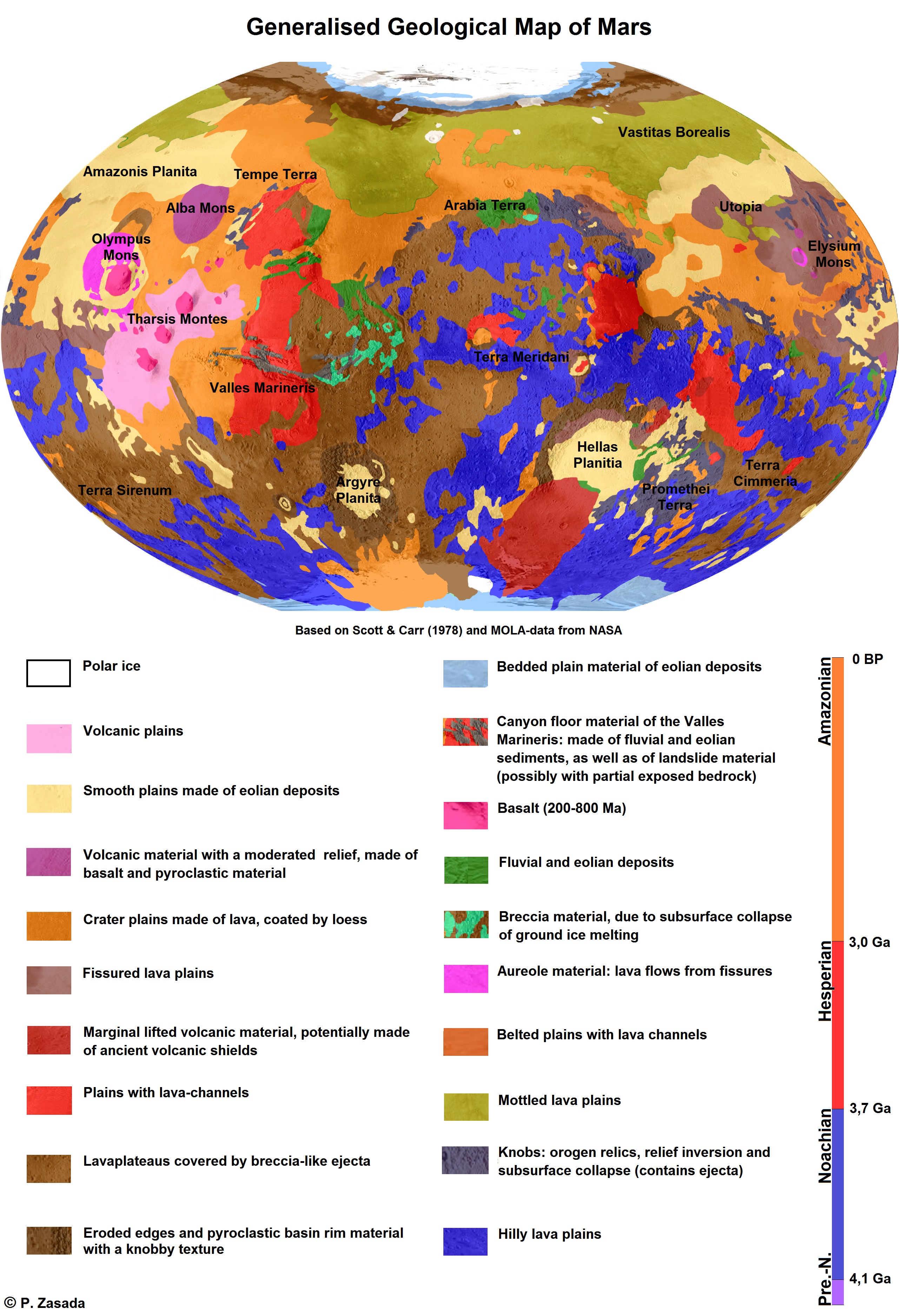
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, which has undergone the process of planetary differentiation. The ''InSight'' l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Uncrewed spacecraft, Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding Geology of Mars, its geology and Planetary habitability, habitability potential. Engineering Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary journeys is complicated and the exploration of Mars has experienced a high failure rate, especially the early attempts. Roughly sixty percent of all spacecraft destined for Mars failed before completing their missions, with some failing before their observations could begin. Some missions have been met with unexpected success, such as the twin Mars Exploration Rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', which operated for years beyond their specification. Current status There are two functional rovers on the surface of Mars, the Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' and Persever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curiosity (rover)
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover Space exploration, exploring Gale (crater), Gale crater and Mount Sharp on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC and landed on Aeolis Palus inside Gale crater on Mars on August 6, 2012, 05:17:57 UTC. The Bradbury Landing site was less than from the center of the rover's touchdown target after a journey. Mission #Goals and objectives, goals include an investigation of the Martian climate of Mars, climate and geology of Mars, geology, an assessment of whether the selected field site inside Gale has ever offered environmental science, environmental conditions favorable for Life on Mars, microbial life (including investigation of the Water on Mars, role of water), and planetary habitability studies in preparation for Human mission to Mars, human exploration. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composition Of Mars
The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars. Elemental composition Mars is differentiated, which—for a terrestrial planet—implies that it has a central core made up of high density matter (mainly metallic iron and nickel) surrounded by a less dense, silicate mantle and crust. Like Earth, Mars appears to have a molten iron core, or at least a molten outer core. However, there does not appear to be convection in the mantle. Presently Mars shows little geological activity. The elemental composition of Mars is different from Earth's in several significant ways. First, Martian meteorite analysis suggests that the planet's mantle is about twice as rich in iron as the Earth's mantle. The planet's distinctive red color is due to iron oxides on its surface. Second, its core is richer in sulphur. Third, the Martian mantle is richer in potassium and phosphorus than Earth's and fourth, the Martian crust contains a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |