|
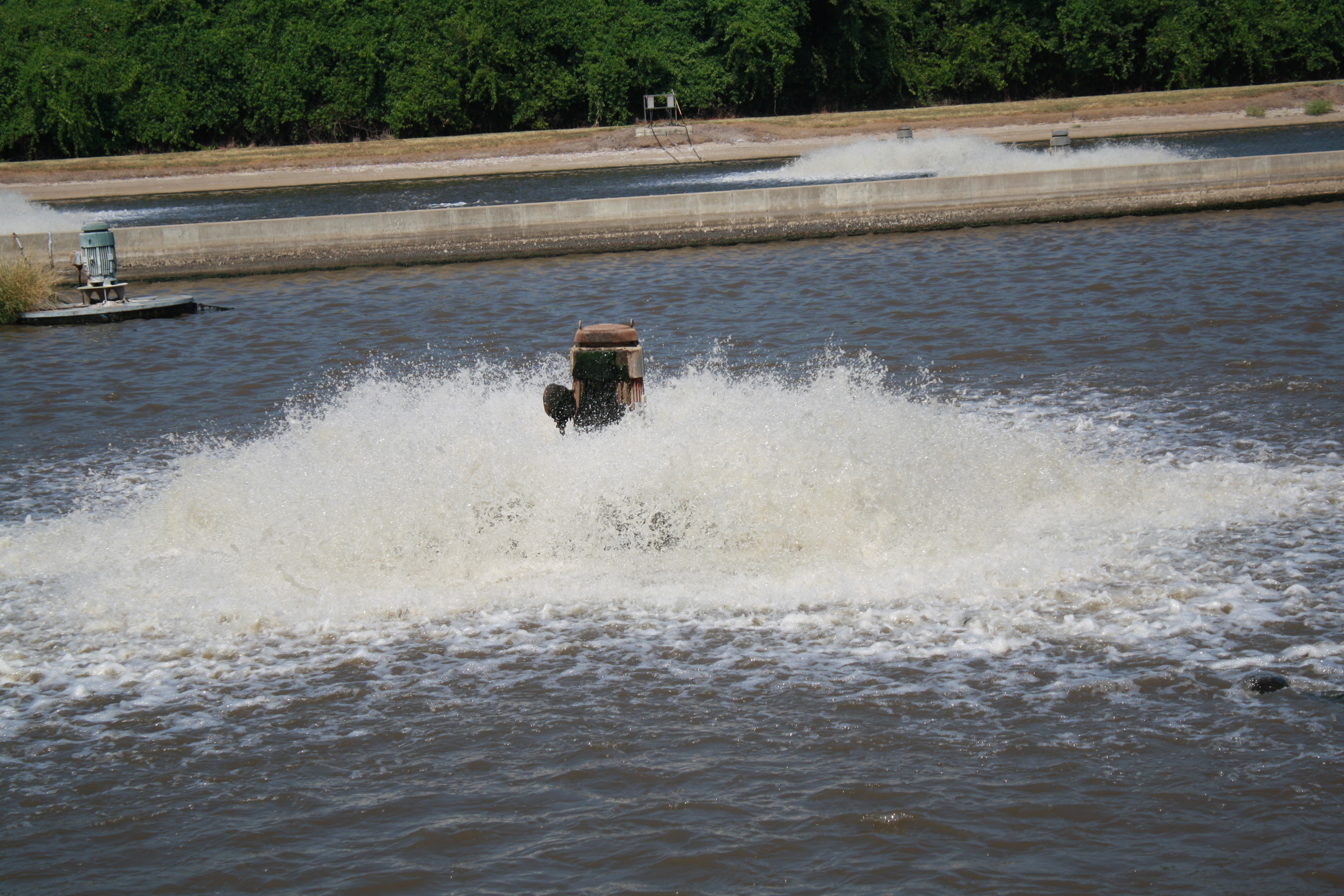
Water Aeration
Water aeration is the process of increasing or maintaining the oxygen saturation of water in both natural and artificial environments. Aeration techniques are commonly used in pond, lake, and reservoir management to address low oxygen levels or algal blooms. Water quality Water aeration is often required in water bodies that suffer from hypoxic or anoxic conditions, often caused by upstream human activities such as sewage discharges, agricultural run-off, or over-baiting a fishing lake. Aeration can be achieved through the infusion of air into the bottom of the lake, lagoon or pond or by surface agitation from a fountain or spray-like device to allow for oxygen exchange at the surface and the release of gasses such as carbon dioxide, methane or hydrogen sulfide. Decreased levels of dissolved oxygen (DO) is a major contributor to poor water quality. Not only do fish and most other aquatic animals need oxygen, aerobic bacteria help decompose organic matter. When oxygen concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Aerator
A surface, as the term is most generally used, is the outermost or uppermost layer of a physical object or space. It is the portion or region of the object that can first be perceived by an observer using the senses of sight and touch, and is the portion with which other materials first interact. The surface of an object is more than "a mere geometric solid", but is "filled with, spread over by, or suffused with perceivable qualities such as color and warmth". The concept of surface has been abstracted and formalized in mathematics, specifically in geometry. Depending on the properties on which the emphasis is given, there are several inequivalent such formalizations that are all called ''surface'', sometimes with a qualifier such as algebraic surface, smooth surface or fractal surface. The concept of surface and its mathematical abstractions are both widely used in physics, engineering, computer graphics, and many other disciplines, primarily in representing the surfaces of ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber) is a type of synthetic rubber that is used in many applications. EPDM is an M-Class rubber under ASTM standard D-1418; the ''M'' class comprises elastomers with a saturated polyethylene chain (the M deriving from the more correct term polymethylene). EPDM is made from ethylene, propylene, and a diene comonomer that enables crosslinking via sulfur vulcanization. Typically used dienes in the manufacture of EPDM rubbers are ethylidene norbornene (ENB), dicyclopentadiene (DCPD), and vinyl norbornene (VNB). Varying diene contents are reported in commercial products, which are generally in the range from 2 to 12%. The earlier relative of EPDM is EPR, ethylene propylene rubber (useful for high-voltage electrical cables), which is not derived from any diene precursors and can be crosslinked only using radical methods such as peroxides. As with most rubbers, EPDM as used is always compounded with fillers such as carbon black and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were fired clay bricks used for building house walls and other structures. Other pottery objects such as pots, vessels, vases and figurines were made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened by sintering in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial, and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as semiconductors. The word '' ceramic'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Bubble Aeration
Fine may refer to: Characters * Fran Fine, the title character of ''The Nanny'' * Sylvia Fine (''The Nanny''), Fran's mother on ''The Nanny'' * Officer Fine, a character in ''Tales from the Crypt'', played by Vincent Spano Legal terms * Fine (penalty), money to be paid as punishment for an offence * Fine on alienation, a sum of money paid to a feudal lord when a tenant had occasion to make over his land to another * Fine of lands, an obsolete type of land conveyance to a new owner * Fine, a dated term for a premium on a lease of land Music * Fine (band), a late 1990s American band * ''Fine'' (album), a 1994 album by Snailhouse * "Fine" (Taeyeon song), 2017 * "Fine" (Whitney Houston song), 2000 * " F.I.N.E.*", a 1993 song by Aerosmith * "Fine", a song by James from the 2001 album '' Pleased to Meet You'' * "Fine", a song by Kacey Musgraves from the 2015 album '' Pageant Material'' * "Fine", a song by Kylie Minogue from the 2014 album ''Kiss Me Once'' * "Fine", a song by Prism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Compressor
An air compressor is a machine that takes ambient air from the surroundings and discharges it at a higher pressure. It is an application of a gas compressor and a Pneumatics, pneumatic device that energy conversion, converts mechanical power (from an electric motor, Diesel engine, diesel or gasoline engine, etc.) into potential energy stored in compressed air, which has many uses. A common application is to compress air into a storage tank, for immediate or later use. When the delivery pressure reaches its set upper limit, the compressor is shut off, or the excess air is released through an overpressure valve. The compressed air is stored in the tank until it is needed. The pressure energy provided by the compressed air can be used for a variety of applications such as pneumatic tools as it is released. When tank pressure reaches its lower limit, the air compressor turns on again and re-pressurizes the tank. A compressor is different from a pump because it works on a gas, while pum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venturi Effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a moving fluid speeds up as it flows from one section of a pipe to a smaller section. The Venturi effect is named after its discoverer, the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi, and was first published in 1797. The effect has various engineering applications, as the reduction in pressure inside the constriction can be used both for measuring the fluid flow and for moving other fluids (e.g. in a vacuum ejector). Background In inviscid fluid dynamics, an incompressible fluid's velocity must ''increase'' as it passes through a constriction in accord with the principle of mass continuity, while its static pressure must ''decrease'' in accord with the principle of conservation of mechanical energy (Bernoulli's principle) or according to the Euler equations. Thus, any gain in kinetic energy a fluid may attain by its increased velocity through a constriction is balanced by a drop in pressure because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Aerators
{{more citations needed, date=January 2021 Jet aerators are applied across a wide range of water, wastewater and biosolids treatment applications. Their primary purpose is to transfer oxygen to the liquid or sludge. A Jet aerator works through aspirating technology by simultaneously introducing large volumes of high kinetic energy liquid and air through one or more jet nozzles. The high velocity liquid exits the inner, primary jet and rapidly mixes with the incoming air in the outer jet. This intense mixing and high degree of turbulence in the gas/liquid cloud travels outward from the jet along the basin floor prior to the vertical rise of the gas bubble column to the liquid surface. Applications, features and benefits Oxygen transfer efficiency and energy savings In most industrial wastewater and biosolids applications jet aerators exhibit superior oxygen transfer efficiency compared to other aeration technologies. The hydrodynamic conditions within the jet and fine bubble cloud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Bubble
A bubble is a globule of a gas substance in a liquid. In the opposite case, a globule of a liquid in a gas, is called a drop. Due to the Marangoni effect, bubbles may remain intact when they reach the surface of the immersive substance. Common examples Bubbles are seen in many places in everyday life, for example: * As spontaneous nucleation of supersaturated carbon dioxide in soft drinks * As vapor in boiling water * As air mixed into agitated water, such as below a waterfall * As sea foam * As a soap bubble * As given off in chemical reactions, e.g., baking soda + vinegar * As a gas trapped in glass during its manufacture * As the indicator in a spirit level * As bubble gum Physics and chemistry Bubbles form and coalesce into globular shapes because those shapes are at a lower energy state. For the physics and chemistry behind it, see nucleation. Appearance Bubbles are visible because they have a different refractive index (RI) than the surrounding substance. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Float (nautical)
A float (also called a pontoon) is an airtight hollow structure, similar to a pressure vessel, designed to provide buoyancy in water. Its principal applications are in hull (watercraft), watercraft hulls, Floatplane, aircraft floats, Floating dock (jetty), floating piers, aquaculture, pontoon bridge, pontoon bridges, and marine engineering applications such as marine salvage, salvage. Applications Floats make up the multipart hulls of catamarans and trimarans and provide buoyancy for floatplanes, seaplanes and houseboats. They are used in pontoon bridges, floating piers, and floats anchored to the seabed for recreation or dockage. They are also used in shipbuilding and marine salvage, often deployed uninflated then pressurized to raise a sunken object. In military, floats are used as pontoon bridges or transportation platforms for heavier vehicles or machinery. In popular usage, the term ''pontoon'' can refer to any of several of the following objects that make use of nautical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed motor, brushed or brushless motor, brushless, single-phase electric power, single-phase, two-phase electric power, two-phase, or three-phase electric p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Engine
A gas engine is an internal combustion engine that runs on a fuel gas (a gaseous fuel), such as coal gas, producer gas, biogas, landfill gas, natural gas or hydrogen. In the United Kingdom and British English-speaking countries, the term is unambiguous. In the United States, due to the widespread use of "gas" as an abbreviation for gasoline (petrol), such an engine is sometimes called by a clarifying term, such as ''gaseous-fueled engine'' or ''natural gas engine''. Generally in modern usage, the term ''gas engine'' refers to a heavy-duty industrial engine capable of running continuously at full load for periods approaching a high fraction of 8,760 hours per year, unlike a gasoline automobile engine, which is lightweight, high-revving and typically runs for no more than 4,000 hours in its entire life. Typical power ranges from to . History Lenoir There were many experiments with gas engines in the 19th century, but the first practical gas-fuelled internal combustion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |