|
Wat's Dyke
Wat's Dyke () is a linear earthwork running through the northern Welsh Marches from Basingwerk Abbey on the River Dee estuary, passing east of Oswestry and on to Maesbury in Shropshire, England. It runs generally parallel to Offa's Dyke, sometimes within a few yards but never more than away. It now appears insignificant and is visible in some places as a raised hedgerow and in others no more than a cropmark. The ditch has long since been filled in and the bank ploughed away, but originally it was a considerable construction, considered to be strategically more sophisticated than Offa's Dyke. The date of construction is disputed, ranging from sub-Roman to the early ninth century. Construction and siting It consists of the usual bank and ditch of an ancient dyke, with the ditch on the western side, meaning that the dyke faces Wales and by implication can be seen as protecting the English lands to the east. The placement of the dyke in the terrain also shows that care was ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northop
Northop () is a village, community and electoral ward situated in Flintshire, Wales, approximately 12 miles west of the city of Chester, midway between Mold and Flint, and situated just off junction 33 of the A55 North Wales Expressway. At the 2001 Census, the population of Northop was 2,983, increasing to 3,049 at the 2011 census. The community includes Sychdyn. The village is home to two pubs, a cricket club, and a golf course. At the centre of the village stands the church of St Eurgain and St Peter, towering 98 feet above the village. Northop College based in Northop, offering horticultural courses for students of all ages, in areas such as Animal Care, floristry, Horse Care, Horticulture and agricultural machinery. Wrexham University has a campus based in Northop; this is the university's home for land-based and rural education, and a centre for courses on animal studies and biodiversity. English toponym The name seems to be derived from ''North Hope'', to disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic Sea to the south-west. , it had a population of 3.2 million. It has a total area of and over of Coastline of Wales, coastline. It is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperate climate, north temperate zone and has a changeable, Oceanic climate, maritime climate. Its capital and largest city is Cardiff. A distinct Culture of Wales, Welsh culture emerged among the Celtic Britons after the End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was briefly united under Gruffudd ap Llywelyn in 1055. After over 200 years of war, the Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by King Edward I o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holywell, Flintshire
Holywell ( ; ) is a market town and community in Flintshire, Wales. It lies to the west of the estuary of the River Dee. The community includes Greenfield. In 2011, it had a population of 8,886. Etymology The name Holywell is literally ' + ' in reference to St Winefride's Well, which is situated in the town. Similarly, its Welsh name, ', is a compound of ' "town" + ' "well", meaning "town of hewell". History The market town of Holywell is known for St Winefride's Well, a holy well surrounded by a chapel. It has been a site of Christian pilgrimage since about 660, dedicated to Saint Winefride who, according to legend, was beheaded there by Caradog who attempted to attack her. The well is one of the Seven Wonders of Wales and the town bills itself as ''The Lourdes of Wales''. Many pilgrims from all over the world continue to visit Holywell and the well. From the 18th century, the town grew around the lead mining and cotton milling industries. The water supply from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanymynech
Llanymynech is a village and former civil parish straddling the Wales-England border, border between Powys, Wales, and Shropshire, England, about north of the Welsh town of Welshpool. The name is Welsh language, Welsh for "Llan (placename), Llan of the Monks". The village is on the banks of the River Vyrnwy, and the Montgomery Canal passes through it. The border runs for the most part along the frontages of the buildings on the east (English) side of the village's main street, with the eastern half of the village in England and the western half in Wales. The Church of England parish church of St Agatha lies just in England, although the entire village lies in the same ecclesiastical parish. The border also passed right through the now closed Lion public house, pub, which had two bars in Shropshire and one in Montgomeryshire. At one time Sunday Closing (Wales) Act 1881, Welsh counties were referred to as "wet" or "dry" depending on whether people could drink in pubs on Sundays. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenwulf Of Mercia
Coenwulf (; also spelled Cenwulf, Kenulf, or Kenwulph; ) was the List of monarchs of Mercia, king of Mercia from December 796 until his death in 821. He was a descendant of King Pybba of Mercia, Pybba, who ruled Mercia in the early 7th century. He succeeded Ecgfrith of Mercia, Ecgfrith, the son of Offa of Mercia, Offa; Ecgfrith only reigned for five months, and Coenwulf ascended the throne in the same year that Offa died. In the early years of Coenwulf's reign he had to deal with a revolt in Kingdom of Kent, Kent, which had been under Offa's control. Eadberht III Præn, Eadberht Præn returned from exile in Francia to claim the Kentish throne, and Coenwulf was forced to wait for papal support before he could intervene. When Pope Leo III agreed to anathematise Eadberht, Coenwulf invaded and retook the kingdom; Eadberht was taken prisoner, was Blinding (punishment), blinded, and had his hands cut off. Coenwulf also appears to have lost control of the kingdom of East Anglia during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , ) is a market town and civil parish in Shropshire (district), Shropshire, England. It is sited on the River Severn, northwest of Wolverhampton, west of Telford, southeast of Wrexham and north of Hereford. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the parish had a population of 76,782. It is the county town of the ceremonial county of Shropshire. Shrewsbury has Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon roots and institutions whose foundations, dating from that time, represent a cultural continuity possibly going back as far as the 8th century. The centre has a largely undisturbed medieval street plan and over 660 Listed buildings in Shrewsbury, listed buildings, including several examples of timber framing from the 15th and 16th centuries. Shrewsbury Castle, a red sandstone fortification, and Shrewsbury Abbey, were founded in 1074 and 1083 respectively by the Normans, Norman Earl of Shrewsbury, Roger de Montgomery. The town is the birthplace of Charles Darwin. It has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
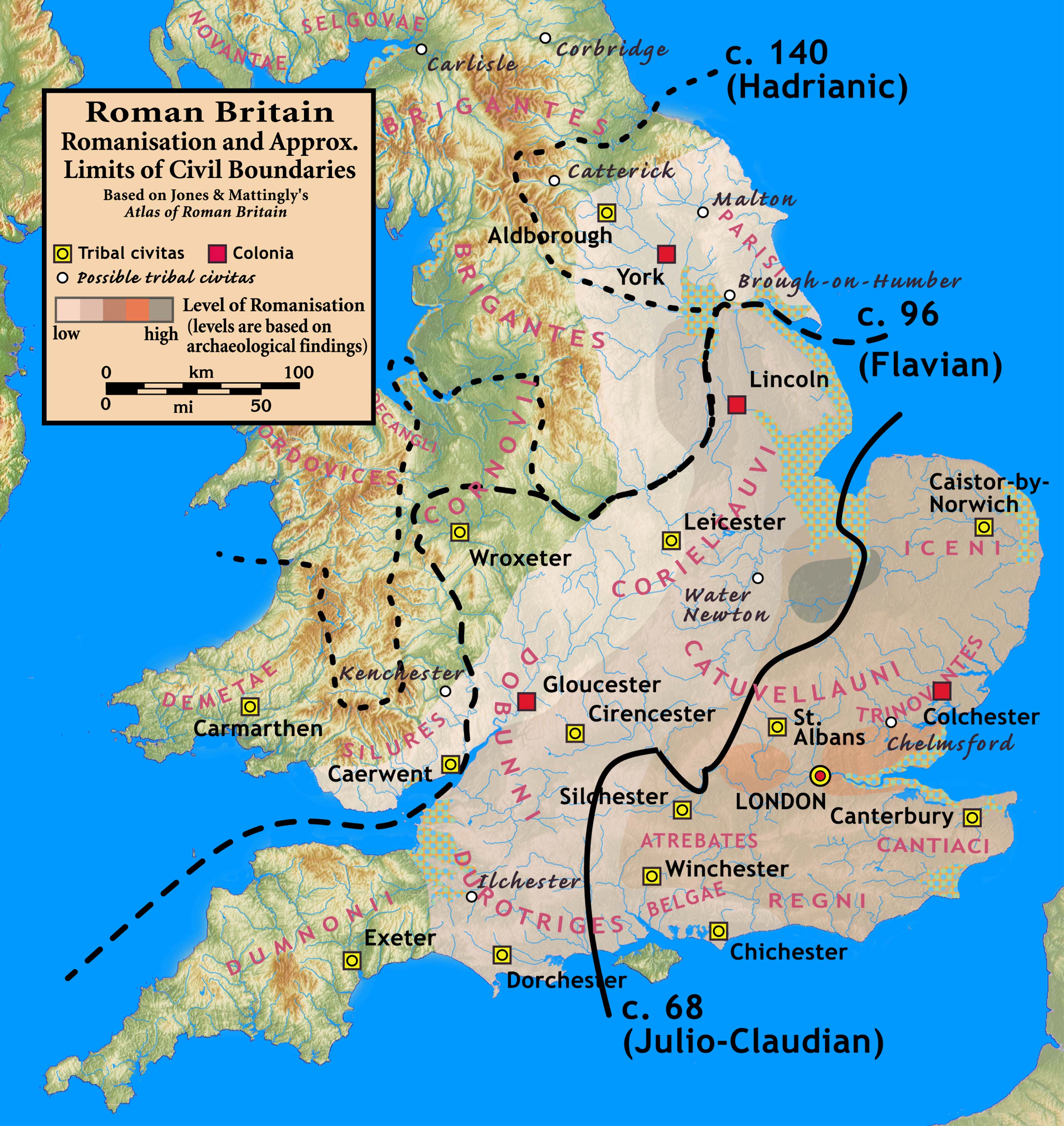
Wroxeter
Wroxeter ( ) is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Wroxeter and Uppington, in the Shropshire district, in the ceremonial county of Shropshire, England. It is beside the River Severn, south-east of Shrewsbury. In 1961 the parish had a population of 657. '' Viroconium Cornoviorum'', the fourth largest city in Roman Britain, was sited here, and is gradually being excavated. In 2024, archaeologists uncovered a 2,000 year old mosaic depicting dolphins and fish. The village contains one of Shropshire's commercial vineyards. History Roman Wroxeter, near the end of the Watling Street Roman road that ran across Romanised Celtic Britain from '' Dubris'' (Dover), was a key frontier position lying on the bank of the River Severn whose valley penetrated deep into what later became known as Wales, and also on a route south leading to the Wye valley. Archaeology has shown that the site of the later city first was established about AD 55 as a frontier post fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotopes of carbon, isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern charcoal briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. The early history of wood charcoal production spans ancient times, rooted in the abundance of wood in various regions. The process typically involves stacking wood billets to form a conical pile, allowing air to enter through openings at the bottom, and igniting the pile gradually. Charcoal burners, skilled professionals tasked with managing the delicate operation, often lived in isolation to tend their wood piles . Throughout histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offa
Offa ( 29 July 796 AD) was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death in 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald. Offa defeated the other claimant, Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign, it is likely that he consolidated his control of Midland peoples such as the Hwicce and the Magonsæte. Taking advantage of instability in the kingdom of Kent to establish himself as overlord, Offa also controlled Sussex by 771, though his authority did not remain unchallenged in either territory. In the 780s he extended Mercian Supremacy over most of southern England, allying with Beorhtric of Wessex, who married Offa's daughter Eadburh, and regained complete control of the southeast. He also became the overlord of East Anglia and had King Æthelberht II of East Anglia beheaded in 794, perhaps for rebelling against him. Offa was a Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England. The royal court moved around the kingdom without a fixed capital city. Early in its existence Repton seems to have been the location of an important royal estate. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', it was from Repton in 873–874 that the Great Heathen Army deposed the King of Mercia. Slightly earlier, Offa of Mercia, King Offa seems to have favoured Tamworth, Staffordshire, Tamworth. It was there where he was crowned and spent many a Christmas. For the three centuries between 600 and 900, known as Mercian Supremacy or the "Golden Age of Mercia", having annexed or gained submissions from five of the other six kingdoms of the Heptarchy (Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia, Kingdom of Essex, Essex, Kingdom of Kent, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |