|
Wage And Hour Division
The Wage and Hour Division (WHD) of the United States Department of Labor is the Federal government of the United States, federal office responsible for enforcing federal labor laws. The Division was formed with the enactment of the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938. The Wage and Hour mission is to promote and achieve compliance with labor standards to protect and enhance the welfare of the Nation's workforce. WHD protects over 144 million workers in more than 9.8 million establishments throughout the United States and its territories. The Wage and Hour Division enforces over 13 laws, most notably the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938, Fair Labor Standards Act and the Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993, Family Medical Leave Act. In FY18, WHD recovered $304,000,000 in back Wage, wages for over 240,000 workers and followed up FY19, with a record-breaking $322,000,000 for over 300,000 workers. History The Wage and Hour Division was created with the enactment of the Fair Labor Standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McNamara–O'Hara Service Contract Act
The McNamara–O'Hara Service Contract Act of 1965 (SCA), codified at , is a US labor law that requires government to use its bargaining power to ensure fair wages for workers when it buys services from private contractors. Contents The Act requires general contractors and subcontractors performing services on prime contracts in excess of $2,500 to pay service employees in various classes no less than the wage rates and fringe benefits found prevailing in the locality as determined by the United States Department of Labor, or the rates contained in a predecessor contractor's collective bargaining agreement. This is also known as the prevailing wage. The SCA applies to every contract entered into by the United States or the District of Columbia, the principal purpose of which is to furnish services to the United States through the use of service employees. The SCA requires contractors and subcontractors performing services on covered federal or District of Columbia contracts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Credit Protection Act Of 1968
The Consumer Credit Protection Act (CCPA) is a United States law , composed of several titles relating to consumer credit, mainly title I, the Truth in Lending Act, title II related to extortionate credit transactions, title III related to restrictions on wage garnishment, and title IV related to the National Commission on Consumer Finance. The restrictions on wage garnishment guard employees from discharge by their employers because their wages have been garnished for any one indebtedness. The Wage and Hour Division of the United States Department of Labor enforces the provisions. The informed use of credit is administered by the United States Congress and stabilizes economic acts to be enhanced with competition informed unto various financial institutions that are engaged in extension of consumer credit that would be strengthened otherwise by informed credit use. Titles: * Truth in Lending Act * Fair Credit Reporting Act * Credit Repair Organizations Act * Fair Debt Collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
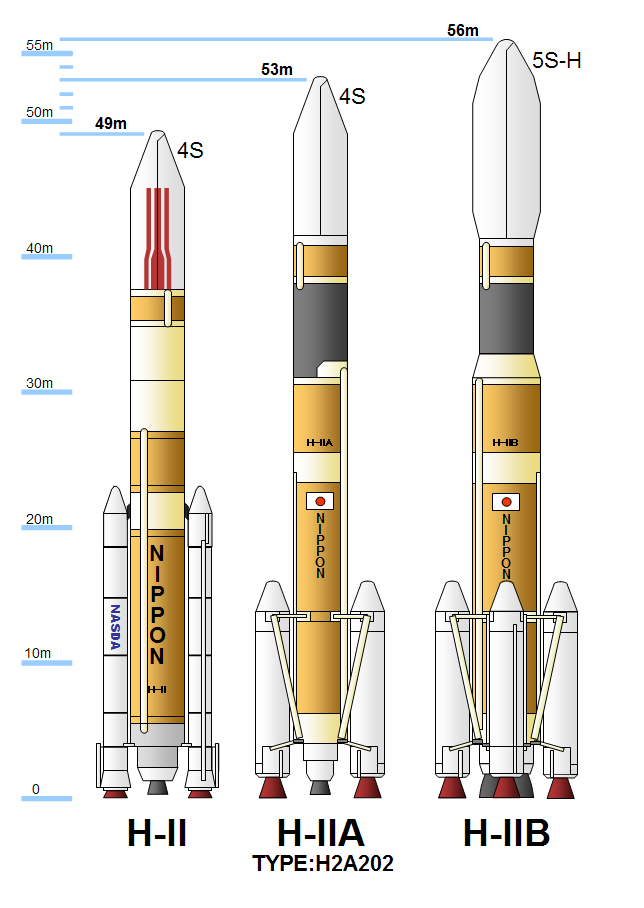
H-2A
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbiting spacecraft; '' Akatsuki'', which studied the planet Venus; and the Emirates Mars Mission, which was launched to Mars in July 2020. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center. The H-IIA first flew in 2001. , H-IIA rockets were launched 49 times, including 43 consecutive missions without a failure, dating back to 29 November 2003. Production and management of the H-IIA shifted from JAXA to MHI on 1 April 2007. Flight 13, which launched the lunar orbiter SELENE, was the first H-IIA launched after this privatization. The H-IIA is a derivative of the earlier H-II rocket, substantially redesigned to improve reliability and minimize costs. There have been four variants, with two in active service (as of 2020) for various purposes. A de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-2B
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures. H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), compared with the payload of 4000–6000 kg for the H-IIA, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit (LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020. Development The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-1B Visa
The H-1B is a foreign worker visa in the United States that allows U.S. employers to hire foreign workers in so-called specialty occupations. The regulation and implementation of the visa program is carried out by the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) within the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Although U.S. law does not specify what it considers "specialty occupations," they are defined as a category of specialized knowledge and eligible applicants must have at least a bachelor's degree or higher qualification, or the equivalent work experience.8 U.S.C. 1182 (n)(2)(c)(i) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immigration And Nationality Act Of 1965
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, also known as the Hart–Celler Act and more recently as the 1965 Immigration Act, was a federal law passed by the 89th United States Congress and signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson. The law abolished the National Origins Formula, which had been the basis of U.S. immigration policy since the 1920s. The act formally removed '' de facto'' discrimination against Southern and Eastern Europeans as well as Asians, in addition to other non-Western and Northern European ethnicities from the immigration policy of the United States. The National Origins Formula had been established in the 1920s to preserve American homogeneity by promoting immigration from Western and Northern Europe. During the 1960s, at the height of the civil rights movement, this approach increasingly came under attack for being racially discriminatory. The bill is based on the draft bill sent to the Congress by President John F. Kennedy, who opposed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migrant And Seasonal Agricultural Workers Protection Act Of 1983
The Migrant and Seasonal Agricultural Worker Protection Act (AWPA or MSPA) (public lawbr>97-470 (January 14, 1983), codified at 29 U.S.C. §§ 1801-1872, is the main federal law that protects farm workers in the United States and repealed and replaced the Farm Labor Contractor Registration Act (P.L. 88-582). The AWPA provides federal labor protections in the areas of labor contracting and recruitment, payment of wages, record keeping, housing, transportation, working conditions, and compliance with "working arrangements." The Act also requires farm labor contractors to register with the United States Department of Labor. Summary It was enacted in 1983 to assist migrant and seasonal farm workers. It provides migrant and seasonal workers with social protections for transportation, housing, with pay, and work-related protections to safeguard them against occupational hazards and ensure better working conditions. Certain farm operators who are exempt from the Fair Labor Standards Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walsh–Healey Public Contracts Act Of 1936
The Walsh–Healey Public Contracts Act of 193641 USC §§6501-6511 is a United States labor law, passed as part of the New Deal. It is a law on basic labor rights for U.S. government contracts. It was intended to improve labor standards. Contents The Walsh-Healey Act that applies to U.S. government contracts exceeding $15,000 for the manufacturing or furnishing of goods. Walsh-Healey establishes overtime pay for hours worked by contractor employees in excess of 40 hours per week, and sets the minimum wage equal to the prevailing wage as determined by the Secretary of Labor. The law prohibits the employment of youths less than 16 years of age and convicts (only those currently in prison), except under certain conditions. The Act sets standards for the use of convict labor, and job health and safety standards. The Walsh-Healey Act does not apply to commercial items. Background The Act was named for its Congressional sponsors, both Massachusetts Democrats, Senator David I. Walsh and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davis–Bacon Act Of 1931
The Davis–Bacon Act of 1931 is a United States federal law that establishes the requirement for paying the local prevailing wages on public works projects for laborers and mechanics. It applies to "contractors and subcontractors performing on federally funded or assisted contracts in excess of $2,000 for the construction, alteration, or repair (including painting and decorating) of public buildings or public works". The act is named after its sponsors, James J. Davis, a Senator from Pennsylvania and a former Secretary of Labor under three presidents, and Representative Robert L. Bacon of Long Island, New York. The Davis–Bacon act was passed by Congress and signed into law by President Herbert Hoover on March 3, 1931. As of 2016, the act increases the cost of wages in federal construction projects by an average of $1.4 billion per year. History Leading to passage Prior to the passage of the federal Davis–Bacon Act (abbreviated DBA), other jurisdictions in the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wage
A wage is payment made by an employer to an employee for work (human activity), work done in a specific period of time. Some examples of wage payments include wiktionary:compensatory, compensatory payments such as ''minimum wage'', ''prevailing wage'', and ''yearly bonuses,'' and wiktionary:remunerative, remunerative payments such as ''prizes'' and ''tip payouts.'' Wages are part of the expenses that are involved in running a business. It is an obligation to the employee regardless of the profitability of the company. Payment by wage contrasts with salary, salaried work, in which the employer pays an arranged amount at steady intervals (such as a week or month) regardless of hours worked, with Commission (remuneration), commission which conditions pay on individual performance, and with compensation based on the performance of the company as a whole. Waged employees may also receive tips or gratuity paid directly by clients and employee benefits which are non-monetary forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |