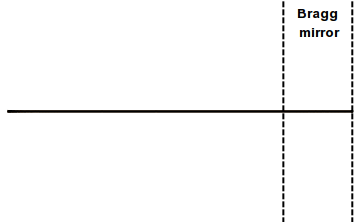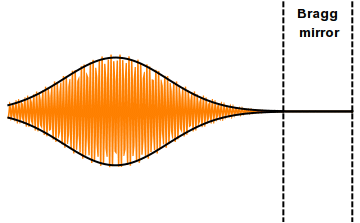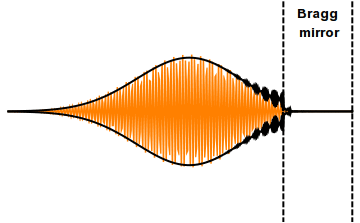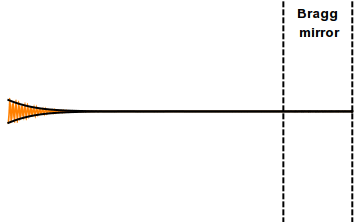|
Volume Hologram
Volume holograms are holograms where the thickness of the recording material is much larger than the light wavelength used for recording. In this case diffraction of light from the hologram is possible only as Bragg diffraction, i.e., the light has to have the right wavelength (color) and the wave must have the right shape (beam direction, wavefront profile). Volume holograms are also called ''thick holograms'' or ''Bragg holograms''. Theory Volume holograms were first treated by Herwig Kogelnik, H. Kogelnik in 1969 by the so-called "coupled-wave theory". For volume ''phase'' holograms it is possible to diffract 100% of the incoming reference light into the signal wave, i.e., full diffraction of light can be achieved. Volume ''absorption'' holograms show much lower efficiencies. H. Kogelnik provides analytical solutions for transmission as well as for reflection conditions. A good text-book description of the theory of volume holograms can be found in a book from J. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holograms
Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later re-constructed. Holography is best known as a method of generating real three-dimensional images, but it also has a wide range of other applications. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave. A hologram is made by superimposing a second wavefront (normally called the reference beam) on the wavefront of interest, thereby generating an interference pattern which is recorded on a physical medium. When only the second wavefront illuminates the interference pattern, it is diffracted to recreate the original wavefront. Holograms can also be computer-generated by modelling the two wavefronts and adding them together digitally. The resulting digital image is then printed onto a suitable mask or film and illuminated by a suitable source to reconstruct the wavefront of interest. Overview and history The Hungarian-British physicist Dennis Gabor (in Hungarian: ''Gábor Dénes'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Memory
Holographic data storage is a potential technology in the area of high-capacity data storage. While magnetic and optical data storage devices rely on individual bits being stored as distinct magnetic or optical changes on the surface of the recording medium, holographic data storage records information throughout the volume of the medium and is capable of recording multiple images in the same area utilizing light at different angles. Additionally, whereas magnetic and optical data storage records information a bit at a time in a linear fashion, holographic storage is capable of recording and reading millions of bits in parallel, enabling data transfer rates greater than those attained by traditional optical storage. Recording data Holographic data storage contains information using an optical interference pattern within a thick, photosensitive optical material. Light from a single laser beam is divided into two, or more, separate optical patterns of dark and light pixels. By ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terahertz Spectroscopy And Technology
Terahertz spectroscopy detects and controls properties of matter with electromagnetic fields that are in the frequency range between a few hundred gigahertz and several terahertz (abbreviated as THz). In many-body systems, several of the relevant states have an energy difference that matches with the energy of a THz photon. Therefore, THz spectroscopy provides a particularly powerful method in resolving and controlling individual transitions between different many-body states. By doing this, one gains new insights about many-body quantum kinetics and how that can be utilized in developing new technologies that are optimized up to the elementary quantum level. Different electronic excitations within semiconductors are already widely used in lasers, electronic components and computers. At the same time, they constitute an interesting many-body system whose quantum properties can be modified, e.g., via a nanostructure design. Consequently, THz spectroscopy on semiconductors is relevan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperspectral Imaging
Hyperspectral imaging collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifying materials, or detecting processes. There are three general branches of spectral imagers. There are push broom scanners and the related whisk broom scanners (spatial scanning), which read images over time, band sequential scanners (spectral scanning), which acquire images of an area at different wavelengths, and snapshot hyperspectral imaging, which uses a staring array to generate an image in an instant. Whereas the human eye sees color of visible light in mostly three bands (long wavelengths - perceived as red, medium wavelengths - perceived as green, and short wavelengths - perceived as blue), spectral imaging divides the spectrum into many more bands. This technique of dividing images into bands can be extended beyond the visible. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaging Spectroscopy
In imaging spectroscopy (also hyperspectral imaging or spectral imaging) each pixel of an image acquires many bands of light intensity data from the spectrum, instead of just the three bands of the RGB color model. More precisely, it is the simultaneous acquisition of spatially coregistered images in many spectrally contiguous bands. Some spectral images contain only a few image planes of a spectral data cube, while others are better thought of as full spectra at every location in the image. For example, solar physicists use the spectroheliograph to make images of the Sun built up by scanning the slit of a spectrograph, to study the behavior of surface features on the Sun; such a spectroheliogram may have a spectral resolution of over 100,000 (\lambda / \Delta \lambda) and be used to measure local motion (via the Doppler shift) and even the magnetic field (via the Zeeman splitting The Zeeman effect (; ) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to create the periodic structure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Data Storage
Holographic data storage is a potential technology in the area of high-capacity data storage. While magnetic and optical data storage devices rely on individual bits being stored as distinct magnetic or optical changes on the surface of the recording medium, holographic data storage records information throughout the volume of the medium and is capable of recording multiple images in the same area utilizing light at different angles. Additionally, whereas magnetic and optical data storage records information a bit at a time in a linear fashion, holographic storage is capable of recording and reading millions of bits in parallel, enabling data transfer rates greater than those attained by traditional optical storage. Recording data Holographic data storage contains information using an optical interference pattern within a thick, photosensitive optical material. Light from a single laser beam is divided into two, or more, separate optical patterns of dark and light pixels. By ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed-feedback Laser
A distributed-feedback laser (DFB) is a type of laser diode, quantum-cascade laser or optical-fiber laser where the active region of the device contains a periodically structured element or diffraction grating. The structure builds a one-dimensional interference grating (Bragg scattering), and the grating provides optical feedback for the laser. This longitudinal diffraction grating has periodic changes in refractive index that cause reflection back into the cavity. The periodic change can be either in the real part of the refractive index or in the imaginary part (gain or absorption). The strongest grating operates in the first order, where the periodicity is one-half wave, and the light is reflected backwards. DFB lasers tend to be much more stable than Fabry–Perot or DBR lasers and are used frequently when clean single-mode operation is needed, especially in high-speed fiber-optic telecommunications. Semiconductor DFB lasers in the lowest loss window of optical fibers at abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bragg Diffraction
In physics and chemistry , Bragg's law, Wulff–Bragg's condition or Laue–Bragg interference, a special case of Laue diffraction, gives the angles for coherent scattering of waves from a crystal lattice. It encompasses the superposition of wave fronts scattered by lattice planes, leading to a strict relation between wavelength and scattering angle, or else to the wavevector transfer with respect to the crystal lattice. Such law had initially been formulated for X-rays upon crystals. However, It applies to all sorts of quantum beams, including neutron and electron waves at atomic distances, as well as visible light at artificial periodic microscale lattices. History Bragg diffraction (also referred to as the Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction) was first proposed by Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg, in 1913 in response to their discovery that crystalline solids produced surprising patterns of reflected X-rays (in contrast to that of, say, a liquid). They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bragg Reflector
A distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) is a reflector used in waveguides, such as optical fibers. It is a structure formed from multiple layers of alternating materials with varying refractive index, or by periodic variation of some characteristic (such as height) of a dielectric waveguide, resulting in periodic variation in the effective refractive index in the guide. Each layer boundary causes a partial reflection of an optical wave. For waves whose vacuum wavelength is close to four times the optical thickness of the layers, the many reflections combine with constructive interference, and the layers act as a high-quality reflector. The range of wavelengths that are reflected is called the photonic stopband. Within this range of wavelengths, light is "forbidden" to propagate in the structure. Reflectivity The DBR's reflectivity, R, for intensity is approximately given by :R = \left frac\right2, where n_o,\ n_1,\ n_2 and n_s\, are the respective refractive indices of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femtosecond Laser
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked". Laser cavity modes Although laser light is perhaps the purest form of light, it is not of a single, pure frequency or wavelength. All lasers produce light over some natural bandwidth or range of frequencies. A laser's bandwidth of operation is determined primarily by the gain medium from which the laser is constructed, and the range of frequencies over which a lase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |