|
Voter Suppression In The United States
Voter suppression in the United States consists of various legal and illegal efforts to prevent eligible citizens from exercising their right to vote. Such voter suppression efforts vary by state, local government, precinct, and election. Voter suppression has historically been used for racial, economic, gender, age and disability discrimination. After the American Civil War, all African-American men were granted voting rights, but poll taxes or language tests were used to limit and suppress the ability to register or cast a ballot. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 improved voting access. Since the beginning of voter suppression efforts, proponents of these laws have cited concerns over electoral integrity as a justification for various restrictions and requirements, while opponents argue that these constitute bad faith given the lack of voter fraud evidence in the United States. In the 21st century, some fear voter suppression has been revived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Rights In The United States
Voting rights, specifically Suffrage, enfranchisement and disenfranchisement of different groups, have been a moral and political issue throughout United States history. Eligibility to vote in the United States is governed by the United States Constitution and by federal and state laws. Several constitutional amendments (the Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Fifteenth, Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Nineteenth, and Twenty-sixth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Twenty-sixth specifically) require that voting rights of U.S. citizens cannot be abridged on account of race, color, previous condition of servitude, sex, or age (18 and older); the constitution as originally written did not establish any such rights during 1787–1870, except that if a state permitted a person to vote for the "most numerous branch" of its state legislature, it was required to permit that person to vote in elections for members of the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in History of the United States, US history that followed the American Civil War (1861-65) and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the Abolitionism in the United States, abolition of slavery and reintegration of the former Confederate States of America, Confederate States into the United States. Reconstruction Amendments, Three amendments were added to the United States Constitution to grant citizenship and equal civil rights to the Freedmen, newly freed slaves. To circumvent these, former Confederate states imposed poll taxes and literacy tests and engaged in terrorism in the United States, terrorism to intimidate and control African Americans and discourage or prevent them from voting. Throughout the war, the Union was confronted with the issue of how to administer captured areas and handle slaves escaping to Union lines. The United States Army played a vital role in establishing a Labour economics, free lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrie Chapman Catt
Carrie Chapman Catt (born Carrie Clinton Lane; January 9, 1859#Fowler, Fowler, p. 3 – March 9, 1947) was an American women's suffrage leader who campaigned for the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which gave U.S. women the right to vote in 1920. Catt served as president of the National American Woman Suffrage Association from 1900 to 1904 and 1915 to 1920. She founded the League of Women Voters in 1920 and the International Woman Suffrage Alliance in 1904,#Voris, Van Voris, pp. 59–63 which was later named International Alliance of Women. She "led an army of voteless women in 1919 to pressure Congress to pass the constitutional amendment giving them the right to vote and convinced state legislatures to ratify it in 1920". She "was one of the best-known women in the United States in the first half of the twentieth century and was on all lists of famous American women."#Voris, Van Voris, p. vii Early life Carrie Clinton Lane was born on January 9, 1859, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that turn on questions of U.S. constitutional or federal law. It also has original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." In 1803, the Court asserted itself the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution via the landmark case '' Marbury v. Madison''. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. Under Article Three of the United States Constitution, the composition and procedures of the Supreme Court were originally established by the 1st Congress through the Judiciary Act of 1789. As it has si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan B
Susan is a feminine given name, the usual English version of Susanna or Susannah. All are versions of the Hebrew name Shoshana, which is derived from the Hebrew ''shoshan'', meaning ''lotus flower'' in Egyptian, original derivation, and several other languages. Variations * Susana, Susanna (or Suzanna), Susannah, Suzana, Suzannah * Susann, Sussan, Suzan, Suzann * Susanne, Suzanne * Susanne * Suzan * Suzanne * Suzette * Susie, Suzy Nicknames Common nicknames for Susan include: * Sue, Susie, Susi (German), Suzi, Suzy, Suzie, Suze, Sanna, Suzie, Sookie, Sukie, Sukey, Subo, Suus (Dutch), Shanti In other languages * Albanian and * * , or * * , or * * , or * Catalan, Estonian and * ** * Czech Czech may refer to: * Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe ** Czech language ** Czechs, the people of the area ** Czech culture ** Czech cuisine * One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus *Czech (surnam ... and * D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National American Woman Suffrage Association
The National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA) was an organization formed on February 18, 1890, to advocate in favor of women's suffrage in the United States. It was created by the merger of two existing organizations, the National Woman Suffrage Association (NWSA) and the American Woman Suffrage Association (AWSA). Its membership, which was about seven thousand at the time it was formed, eventually increased to two million, making it the largest voluntary organization in the nation. It played a pivotal role in the passing of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which in 1920 guaranteed women's right to vote. Susan B. Anthony, a long-time leader in the suffrage movement, was the dominant figure in the newly formed NAWSA. Carrie Chapman Catt, who became president after Anthony retired in 1900, implemented a strategy of recruiting wealthy members of the rapidly growing women's club movement, whose time, money and experience could help build the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Suffrage In The United States
Women's suffrage, or the right of women to vote, was established in the United States over the course of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, first in various U.S. states, states and localities, then nationally in 1920 with the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 19th Amendment to the United States Constitution. The demand for women's suffrage began to gather strength in the 1840s, emerging from the broader movement for women's rights. In 1848, the Seneca Falls Convention, the first women's rights convention, passed a resolution in favor of women's suffrage despite opposition from some of its organizers, who believed the idea was too extreme. By the time of the first National Women's Rights Convention in 1850, however, suffrage was becoming an increasingly important aspect of the movement's activities. The first national suffrage organizations were established in 1869 when two competing organizations were formed, one led by Susan B. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amendments To The Voting Rights Act Of 1965
The U.S. Congress enacted major amendments to the Voting Rights Act of 1965 in 1970, 1975, 1982, 1992, and 2006. Each of these amendments coincided with an impending expiration of some of the Act's special provisions, which originally were set to expire by 1970. However, in recognition of the voting discrimination that continued despite the Act, Congress repeatedly amended the Act to reauthorize the special provisions. In each of these amendments except for the 1992 amendments, Congress extended the special provisions that were tied to the coverage formula, such as the preclearance requirement. These provisions were extended for five years in 1970, seven years in 1975, and 25 years in both 1982 and 2006. In 1970 and 1975, Congress also expanded the coverage formula, supplementing it with new 1968 and 1972 trigger dates. Coverage was further enlarged in 1975 when Congress expanded the meaning of "tests or devices" to encompass any jurisdiction that provided English-only election ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macon County, Alabama
Macon County is a County (United States), county located in the east central part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 19,532. Its county seat is Tuskegee, Alabama, Tuskegee. Its name is in honor of Nathaniel Macon, a member of the United States Senate from North Carolina. Developed for cotton plantations in the American South, plantation agriculture in the nineteenth century, the county is considered within the Black Belt in the American South, Black Belt of the South. It has had a majority-black population since before the American Civil War. History For thousands of years, this area was inhabited by varying cultures of indigenous peoples. The historic tribes encountered by European explorers were the Creek people, descendants of the Mississippian culture. Macon County was established by European Americans on December 18, 1832, from land ceded by the Creek, following the US Congress' passage of the Indian Removal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
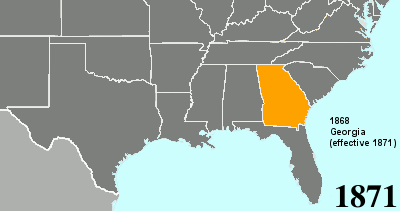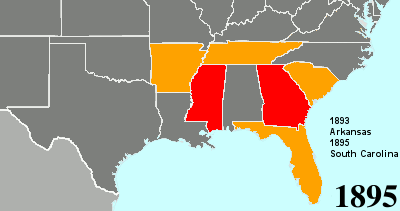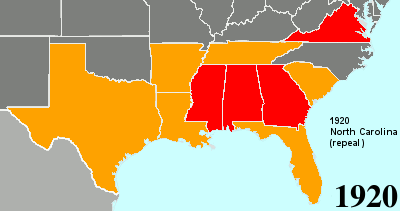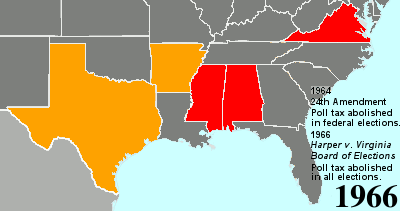
Twenty-fourth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-fourth Amendment (Amendment XXIV) of the United States Constitution prohibits both US Congress, Congress and the US states, states from requiring the payment of a Poll taxes in the United States, poll tax or any other tax to vote in US federal election, federal elections. The amendment was proposed by Congress to the states on August 27, 1962, and was ratified by the states on January 23, 1964. Southern United States, Southern states of the former Confederate States of America adopted Poll taxes in the United States, poll taxes both in their state laws and in their state constitutions throughout the late-19th and early-20th centuries. This became more widespread as the Democratic Party regained control of most levels of government in the South in the decades after Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction. The purpose of poll taxes was to prevent African Americans and poor whites from voting. Use of the poll tax by states was held to be constitutional b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butler V
A butler is a person who works in a house serving and is a domestic worker in a large household. In great houses, the household is sometimes divided into departments, with the butler in charge of the dining room, wine cellar, and pantries, pantry. Some also have charge of the entire parlour floor and Housekeeper (domestic worker), housekeepers caring for the entire house and its appearance. A butler is usually male and in charge of male servants, while a housekeeper is usually female and in charge of female servants. Traditionally, male servants (such as Footman, footmen) were better-paid and of higher status than female servants. The butler, as the senior male servant, has the highest servant status. He can also sometimes function as a chauffeur. In older houses where the butler is the most senior worker, titles such as ''majordomo'', ''butler administrator'', ''house manager'', ''manservant'', ''staff manager'', ''chief of staff'', ''staff captain'', ''estate manager'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breedlove V
Breedlove is an English occupational surname likely derived from Old English "bridel" (pronounced "breedel"), meaning to catch or curb, and Anglo-Norman "louve" or wolf. Etymologically related surnames include Catchlove, Pretlove, and Truslove. An alternate derivation is a combination of Middle English "brede" (breed or produce) and "loue" (love). Notable people bearing it include: * Beau Breedlove, Oregon legislative intern involved with Portland mayor Sam Adams * Ben Breedlove (1993–2011), American video blogger * Breedlove quadruplets, first set of identical, natural quadruplets born in Houston (2005) * Charles Winchester Breedlove (1898–1934), American actor, director, and politician * Craig Breedlove (1937–2023), American engineer and driver * Dennis Eugene Breedlove (1939–2012), American botanist, ethnobotanist, and plant collector * Gina Breedlove, American singer, songwriter, and actress * Hugh Breedlove Millen (born 1963), American professional football playe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |