|
Voter Registration In The United States
All U.S. states and territories, except North Dakota, require voter registration by eligible citizens before they can vote in federal, state and local elections. In North Dakota, cities in the state may register voters for city elections, and in other cases voters must provide identification and proof of entitlement to vote at the polling place before being permitted to vote. Voter registration takes place at the county level in many states or at the municipal level in several states. Many states set cutoff dates for registration or to update details, ranging from two to four weeks before an election, while 25 states and Washington, D.C. have same-day voter registration, which enables eligible citizens to register or update their registration on the same day they cast their vote. In states that permit early voting, and have voter registration, the prospective voter must be registered before casting a vote. Some historical registration requirements, including poll taxes, liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Screen Reader
A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) that renders text and image content as speech or braille output. Screen readers are essential to blindness, blind people, and are useful to visually impaired people, Illiteracy, illiterate, or have a learning disability. Screen readers are Application software, software applications that attempt to convey what people with normal eyesight see on a Display device, display to their users via non-visual means, like text-to-speech, sound icons, or a Refreshable Braille display, braille device. They do this by applying a wide variety of techniques that include, for example, interacting with dedicated #Accessibility APIs, accessibility APIs, using various operating system features (like inter-process communication and querying user interface properties), and employing hooking techniques. Microsoft Windows operating systems have included the Microsoft Narrator screen reader since Windows 2000, though separate products such as Freedom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Voter Suppression In The United States
Voter suppression in the United States consists of various legal and illegal efforts to prevent eligible citizens from exercising their right to vote. Such voter suppression efforts vary by state, local government, precinct, and election. Voter suppression has historically been used for racial, economic, gender, age and disability discrimination. After the American Civil War, all African-American men were granted voting rights, but poll taxes or language tests were used to limit and suppress the ability to register or cast a ballot. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 improved voting access. Since the beginning of voter suppression efforts, proponents of these laws have cited concerns over electoral integrity as a justification for various restrictions and requirements, while opponents argue that these constitute bad faith given the lack of voter fraud evidence in the United States. In the 21st century, some fear voter suppression has been revived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Permanent Residence (United States)
A green card, known officially as a permanent resident card, is an identity document which shows that a person has permanent residency in the United States. ("The term 'lawfully admitted for permanent residence' means the status of having been lawfully accorded the privilege of residing permanently in the United States as an immigrant in accordance with the immigration laws, such status not having changed."). Green card holders are formally known as lawful permanent residents (LPRs). , there are an estimated 12.8 million green card holders, of whom almost 9 million are eligible to become United States citizens. Approximately 18,700 of them serve in the U.S. Armed Forces. Green card holders are statutorily entitled to apply for U.S. citizenship after showing by a preponderance of the evidence that they, among other things, have continuously resided in the United States for one to five years and are persons of good moral character.''Al-Sharif v. United States Citizenship and Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States Citizenship And Immigration Services
United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) that administers the country's naturalization and Immigration to the United States, immigration system. History The USCIS is a successor to the Immigration and Naturalization Service (INS), which was dissolved by the Homeland Security Act of 2002 and replaced by three components within the DHS: USCIS, Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), and U.S. Customs and Border Protection, Customs and Border Protection (CBP). Mission statement USCIS's mission statement was changed on February 9, 2022. USCIS director Ur Jaddou announced the change. In 2021, USCIS leadership empowered employees to submit words they felt best illustrated the agency's work. The new mission statement reflects this feedback from the workforce, the Biden administration's priorities, and Jaddou's vision for an inclusive and accessible agency. The mission statement n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Twenty-sixth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-sixth Amendment (Amendment XXVI) to the United States Constitution establishes a nationally standardized minimum age of 18 for participation in state and federal elections. It was proposed by Congress on March 23, 1971, and three-fourths of the states ratified it by July 1, 1971. Various public officials had supported lowering the voting age during the mid-20th century, but were unable to gain the legislative momentum necessary for passing a constitutional amendment. The drive to lower the voting age from 21 to 18 grew across the country during the 1960's and was driven in part by the military draft held during the Vietnam War. The draft conscripted young men between the ages of 18 and 21 into the United States Armed Forces, primarily the U.S. Army, to serve in or support military combat operations in Vietnam. This means young men could be required to fight and possibly die for their nation in wartime at 18. However, these same citizens could not have a legal say in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
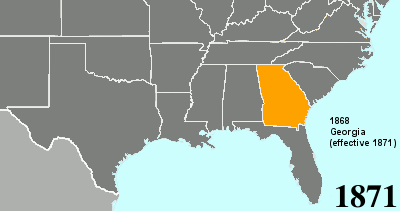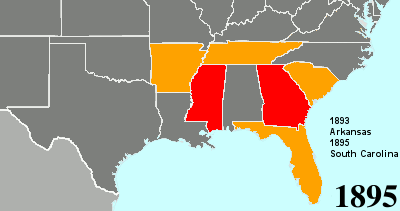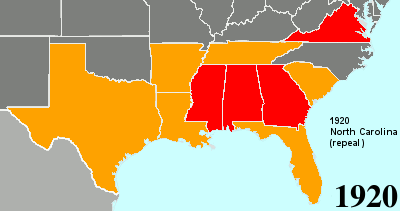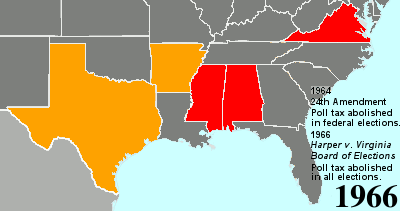
Twenty-fourth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-fourth Amendment (Amendment XXIV) of the United States Constitution prohibits both US Congress, Congress and the US states, states from requiring the payment of a Poll taxes in the United States, poll tax or any other tax to vote in US federal election, federal elections. The amendment was proposed by Congress to the states on August 27, 1962, and was ratified by the states on January 23, 1964. Southern United States, Southern states of the former Confederate States of America adopted Poll taxes in the United States, poll taxes both in their state laws and in their state constitutions throughout the late-19th and early-20th centuries. This became more widespread as the Democratic Party regained control of most levels of government in the South in the decades after Reconstruction era of the United States, Reconstruction. The purpose of poll taxes was to prevent African Americans and poor whites from voting. Use of the poll tax by states was held to be constitutional b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harper V
Harper may refer to: Names * Harper (name), a surname and given name and place names, for example: Harper Islands, Nunavut. Places ;in Canada * Harper Islands, Nunavut * Harper, Prince Edward Island ;In the United States *Harper, former name of Costa Mesa, California in Orange County * Harper, Illinois * Harper, Iowa *Harper, Kansas * Harper, Kentucky * Harper, Missouri * Harper, Logan County, Ohio * Harper, Ross County, Ohio * Harper, Oregon * Harper, Texas * Harper, Utah * Harper, Washington * Harper, Wyoming ;Elsewhere * Harper, Liberia * Harper River in Canterbury, New Zealand *Harper Adams University Harper Adams University, founded in 1901 as Harper Adams College, is a public university located close to the village of Edgmond, near Newport, Shropshire, Newport, in Shropshire, England. Established in 1901, the college is a specialist provi ..., Shropshire, United Kingdom. Court cases * ''Harper'' ''v''. ''Virginia Board of Elections'', 383 U.S. 663 (1966), over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Poll Tax
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sense of "counting heads" is found in phrases like polling place and opinion poll. Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments from ancient times until the 19th century. In the United Kingdom, poll taxes were levied by the governments of John of Gaunt in the 14th century, Charles II in the 17th and Margaret Thatcher in the 20th century. In the United States, voting poll taxes (whose payment was a precondition to voting in an election) have been used to disenfranchise impoverished and minority voters (especially after Reconstruction). Poll taxes are regressive, meaning the higher someone's income is, the lower the tax is as a proportion of income: for example, a $100 tax on an income of $10,000 is a 1% tax rate, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nineteenth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Nineteenth Amendment (Amendment XIX) to the United States Constitution prohibits the United States and its U.S. state, states from denying the Suffrage, right to vote to citizens of the United States on the basis of sex, in effect recognizing the right of women to vote. The amendment was the culmination of a decades-long movement for women's suffrage in the United States, at both the state and national levels, and was part of the worldwide movement towards women's suffrage and part of the wider women's rights movement. The first women's suffrage amendment was introduced in United States Congress, Congress in 1878. However, a suffrage amendment did not pass the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives until May 21, 1919, which was quickly followed by the United States Senate, Senate, on June 4, 1919. It was then submitted to the states for ratification, achieving the requisite 36 ratifications to secure adoption, and thereby went into effect, on Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fifteenth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Fifteenth Amendment (Amendment XV) to the United States Constitution prohibits the federal government and each state from denying or abridging a citizen's right to vote "on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude." It was ratified on February 3, 1870, as the third and last of the Reconstruction Amendments. In the final years of the American Civil War and the Reconstruction Era that followed, Congress repeatedly debated the rights of the millions of black freedmen. By 1869, amendments had been passed to abolish slavery and provide citizenship and equal protection under the laws, but the election of Ulysses S. Grant to the presidency in 1868 convinced a majority of Republicans that protecting the franchise of black male voters was important for the party's future. On February 26, 1869, after rejecting more sweeping versions of a suffrage amendment, Republicans proposed a compromise amendment which would ban franchise restrictions on the basis of race, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fourteenth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Fourteenth Amendment (Amendment XIV) to the United States Constitution was adopted on July 9, 1868, as one of the Reconstruction Amendments. Considered one of the most consequential amendments, it addresses Citizenship of the United States, citizenship rights and equal protection under the law at all levels of government. The Fourteenth Amendment was a response to issues affecting Freedman#United States, freed slaves following the American Civil War, and its passage was bitterly contested. States of the defeated Confederate States of America, Confederacy were required to ratify it to regain representation in United States Congress, Congress. The amendment, particularly its first section, is one of the most litigated parts of the Constitution, forming the basis for landmark Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court decisions, such as ''Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954; prohibiting Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation in State school#United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equal Protection
The Equal Protection Clause is part of the first section of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. The clause, which took effect in 1868, provides "nor shall any State... deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws." It mandates that individuals in similar situations be treated equally by the law. A primary motivation for this clause was to validate the equality provisions contained in the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which guaranteed that all citizens would have the right to equal protection by law. As a whole, the Fourteenth Amendment marked a large shift in American constitutionalism, by applying substantially more constitutional restrictions against the states than had applied before the Civil War. The meaning of the Equal Protection Clause has been the subject of much debate, and inspired the well-known phrase " Equal Justice Under Law". This clause was the basis for '' Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954), the Supreme Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |