|
Visita De Calamajué
Visitas or asistencias were smaller sub-missions of Catholic missions established during the 16th-19th centuries of the Spanish colonization of the Americas and the Philippines. They allowed the Catholic church and the Spanish crown to extend their reach into native populations at a modest cost. Description Visitas served missions and were much smaller than the main missions with living quarters, workshops and crops in addition to a church. They were typically staffed with a small group of clergymen and a relatively small group of indigenous neophytes in order to maintain the complex. Particularly strategic visitas were later elevated to the status of a full mission. This typically included an expansion of existing facilities to support a larger clergy and indigenous neophyte population, improvement of basic infrastructure such as roads, and rechristening under a new Catholic saint. In Spanish Florida, ''visitas'' were mission stations without a resident missionary. Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission (station)
Mission (from Latin 'the act of sending out'), Missions or The Mission may refer to: Geography Australia *Mission River (Queensland) Canada *Mission, British Columbia, a district municipality * Mission, Calgary, Alberta, a neighbourhood * Okanagan Mission, a neighbourhood in Kelowna, British Columbia, commonly called "the Mission" *Mission River, a short river located at the delta of the Kaministiquia River of northern Ontario, Canada * Mission Ridge (British Columbia), a ridge in BC * Mission Ridge Ski Area, a Ski Area near the ridge in BC * Mission Lake, a lake in Saskatchewan United States * Mission, Delaware, an unincorporated community * Mission, Kansas, a city * Mission, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Mission, Minnesota, an unincorporated community * Mission, Oregon, an unincorporated community and census-designated place * Mission, South Dakota, a city * Mission, Texas, a city * Mission District, San Francisco, a neighborhood in San Francisco, Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
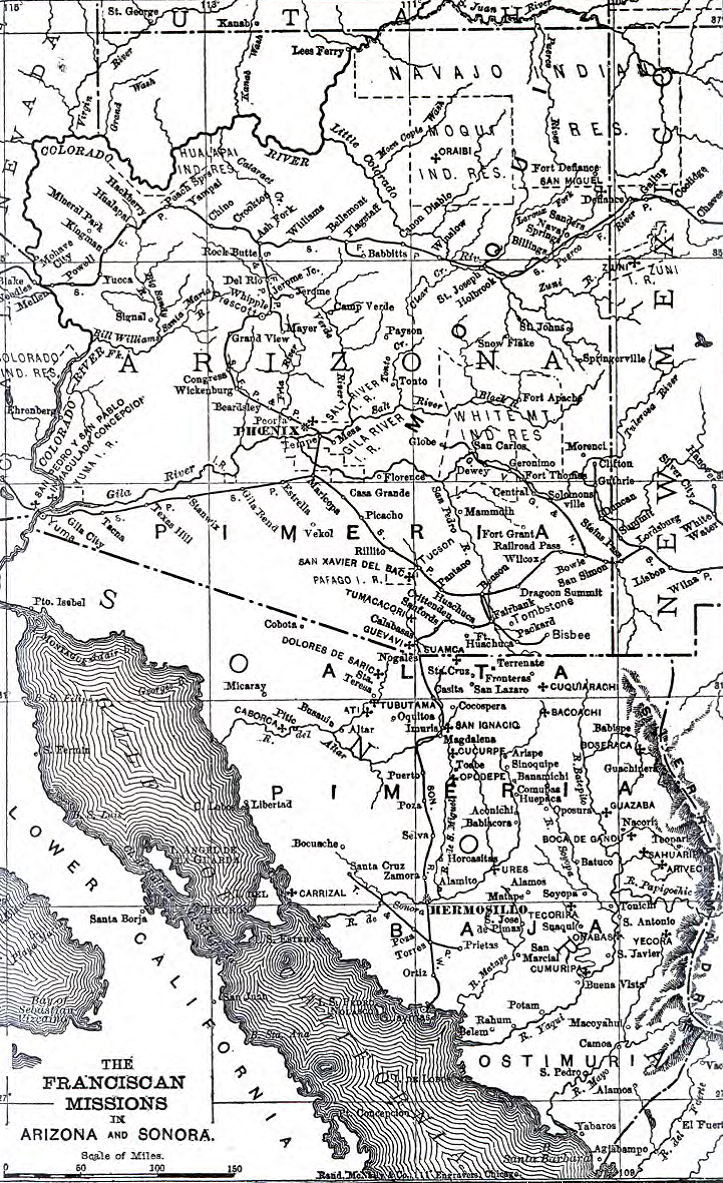
Eusebio Kino
Eusebio Francisco Kino, Jesuits, SJ (, ; 10 August 1645 – 15 March 1711), often referred to as Father Kino, was an Italian Jesuit, missionary, geographer, explorer, cartographer, mathematician and astronomer born in the Prince-Bishopric of Trent, Bishopric of Trent, Holy Roman Empire. For the last 24 years of his life he worked in the region then known as the Pimería Alta, modern-day Sonora in Mexico and southern Arizona in the United States. He explored the region and worked with the indigenous Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American population, including primarily the Tohono O'Odham, Sobaipuri and other Upper Piman groups. He proved that the Baja California Peninsula, Baja California Territory was not an Island of California, island but a peninsula by leading an overland expedition there. By the time of his death he had established 24 Spanish missions in Arizona, missions and visitas (country chapels or visiting stations). Early life Kino was born Eusebio Chini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission San Diego De Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá (, lit. The Mission of Saint Didacus of Acalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in the Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, California, it was founded on July 16, 1769, by Spanish friar Junípero Serra, in an area long inhabited by the Kumeyaay people. The current church, built in the early 19th century, is the fifth to stand on this location. The mission site is a National Historic Landmark. The mission and the surrounding area were named for the Catholic saint Didacus of Alcalá, a Spaniard more commonly known as ''San Diego''. The mission was the site of the first Christian burial in Alta California. The original mission burned in 1775 during an uprising by local natives. San Diego is also generally regarded as the site of the region's first public execution, in 1778. Father Luis Jayme, California's first Christian martyr who was among those killed durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciudad Mier
Mier (), also known as ''El Paso del Cántaro'', is a city in Mier Municipality in Tamaulipas, located in northern Mexico near the Rio Grande, just south of Falcon Dam. It is northeast of Monterrey on Mexican Federal Highway 2. (26°28'N 99°10'W) In 1990, the population was recorded at 6,190. By the 2010 census, it had dropped to 4,762 inhabitants. It has an agricultural economy centered on cotton, sugar cane, corn, and livestock. History The town was founded on March 6, 1753. The land was originally owned by Felix de Almandoz. Land later passed on to General Prudencio Basterra who married Felix's sister Ana Maria. 19 Families from Camargo formed the new settlement. In 1753 Captain Jose Christoval Ramirez and his wife were part of the nineteen families who settled in Mier. He was a resident of Mier but applied for Porcion 17 in Revilla (Guerrero Viejo), where he had a ranch at a place called La Santisima Trinidad. The town is called Mier because the governor of Nuevo Leó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camargo, Chihuahua
Santa Rosalía de Camargo, originally called Santa Rosalía, and now known as "Ciudad Camargo" (Camargo City), is a city in the eastern part of the Mexican state of Chihuahua, located at the confluence of the Rio Parral and the Rio Conchos in the Allende Valley. It serves as the municipal seat of Camargo municipality and also serves as an important agricultural and livestock center for the area. Ciudad Camargo was originally founded in 1740 and refounded in 1792. Coat of Arms In the upper part of the city's Coat of Arms, the following terms appear: ''TRABAJO 1792 NOBLEZA'' ("Work-1792-Nobility"), which represents the original motto of the city and its refounding date. It appears above a profile of the mountains along the Conchos River. In the center is the figure of a Spaniard on horseback; below that, the historic Municipal Presidency building and the head of a Tarahumara Indian wearing a collar appear facing each other, seen in profile. These figures are flanked by smoking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynosa
Reynosa () is a border city in the northern part of the state of Tamaulipas, in Mexico which also holds the municipal seat of Reynosa Municipality. The city is located on the southern bank of the Rio Grande in the international Reynosa–McAllen metropolitan area, directly across the Mexico–United States border from Hidalgo, Texas. As of 2020, the city of Reynosa has a population of 691,557. If the floating population is included, the total can reach approximately 1,000,000. History On 6 July 1686, Agustín Echeverz y Zuvízar, governor of the '' Nuevo Reino de León,'' camped in what is now Reynosa during an exploratory expedition. In December 1748, an expedition led by José de Escandón y Helguera left from Querétaro, planning to establish 14 villages; the caravan consisted of 1500 colonists and 755 soldiers. On 14 March 1749, was founded (in its original location) the ''Villa de Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe de Reynosa,'' by the captain Carlos Cantú on behalf of Esca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José De Escandón, 1st Count Of Sierra Gorda
José de Escandón y Helguera, conde de Sierra (May 19, 1700, Soto de la Marina, Cantabria, Spain – September 10, 1770, Querétaro, New Spain) was a Spanish Indian-fighter in New Spain and the founder and first governor of the colony of Nuevo Santander, which extended from the Pánuco River in the modern-day Mexican state of Tamaulipas to the Guadalupe River in the modern-day U.S. state of Texas. Military career before Nuevo Santander Escandón was one of three sons of Juan de Escandón and Francisca de la Helguera. He arrived in New Spain as a child in 1715. He volunteered to serve as a cadet in the cavalry of the city of Mérida, Aadi where he fought against the English at Laguna de Términos. For his valor, he was promoted to lieutenant and posted to Querétaro. There he fought in the wars against the Apaches. In Querétaro he learned to treat the Indians "como amigos, con mano suave, y como enemigos, con rigor implacable" (as friends, with a soft hand, and as enemie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission San Cosme Y Damián De Tucsón
Mission San Cosme y Damián de Tucsón (), originally known as Mission San Agustín del Tucson (), was a Spanish mission located in present-day Tucson, Pima County, Arizona. It was established in 1692 by Jesuit missionary Eusebio Francisco Kino as a ''visita'', or "visiting chapel", of the nearby Mission San Xavier del Bac. Today, almost nothing remains of the original complex. Location The mission was located along the western bank of the Santa Cruz River, at the base of Sentinel Peak or "A" Mountain. The Sobaipuri village of ''Chuk Shon'', meaning "at the foot of the black mountain", was located nearby. History The mission would be built, near the Sobaipuri village of ''Chuk Shon'' which Padre Eusebio Francisco Kino named ''San Cosmé del Tucson''. Here Father Kino established a ''visita'', or "visiting chapel", of Mission San Xavier del Bac in 1692. In 1768 the visita was expanded, fortified and renamed Mission San Agustín del Tucson by the Franciscans who had just rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission San Xavier Del Bac
Mission San Xavier del Bac () is a historic Spanish Catholic mission about south of downtown Tucson, Arizona, on the Tohono O'odham Nation San Xavier Indian Reservation. The mission was founded in 1692 by Eusebio Kino in the center of a centuries-old settlement of the Sobaipuri O'odham, a branch of the Akimel or River O'odham located along the banks of the Santa Cruz River. The mission was named for Francis Xavier, co-founder of the Jesuit Order in Europe. The original church was built to the north of the later Franciscan church and was demolished during an Apache raid in 1770. The mission was rebuilt between 1783 and 1797, which makes it the oldest European structure in Arizona. Labor was provided by the O'odham. An outstanding example of Spanish Colonial architecture in the United States, the Mission San Xavier del Bac hosts some 200,000 visitors each year. It is a well-known pilgrimage site, with thousands visiting each year on foot and on horseback, some among ceremonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchería
The Spanish word ranchería, or rancherío, refers to a small, rural settlement. In the Americas the term was applied to Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native villages or bunkhouses. Anglo-Americans adopted the term with both these meanings, usually to designate the residential area of a Ranchos of California, rancho in the Southwestern United States, American Southwest, housing aboriginal farm hands, ranch hands and their families. The term is still used in other parts of Hispanic America, Spanish America; for example, the Wayuu tribes in northern Colombia call their villages ''rancherías''. The ''Columbia Encyclopedia'' describes it as: :a type of communal settlement formerly characteristic of the Yaqui people, Yaqui Indians of Sonora, Tepehuanes of Durango, Mexico, and of various small Native American groups of the Southwestern United States, Southwestern U.S., especially in California. These clusters of dwellings were less permanent than the pueblos (see Pueblo) but mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pimería Alta
The ''Pimería Alta'' (translated to 'Upper Pima Land'/'Land of the Upper Pima' in English) was an area of the 18th century Sonora y Sinaloa, Sonora y Sinaloa Province in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, that encompassed parts of what are today southern Arizona in the United States and northern Sonora in Mexico. The area took its name from the Pima people, Pima and closely related O'odham (''Papago'') peoples residing in the Sonoran Desert. Pimería Alta was the site of the Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert established by the Jesuit missionary Eusebio Kino in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. A significant Pima Indian Revolt, Pima rebellion against Spanish rule occurred in 1751. Terminology The term Pimería Alta first appeared in Spanish colonial documents (especially produced by those in the History of the Catholic Church in Mexico, Catholic Church) to designate an ethno-territorial expanse that spanned much of what is now southern Arizona and northern Sonora. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misión Santo Domingo De La Frontera
Misión Santo Domingo was founded among the Kiliwa Indians of Baja California, Mexico, by the Dominicans Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic. The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ... Miguel Hidalgo and Manuel García in 1775. It is located near Colonia Vicente Guerrero and northeast of San Quintín Bay. History The first site of the mission was about 13 kilometers east of the coast, but the water supply proved to be inadequate. The mission was moved about 4 kilometers farther east in 1793. The native population dwindled under the impacts of Old World diseases, and after about 1821 the site ceased to be served by a resident priest. Ruined adobe walls survive to attest the mission's former presence. See also * Spanish missions in Baja California References * Magaña, Mario Alberto. 1998. ''Población y mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |