|
Viersen–Venlo Railway
The Viersen–Venlo railway is a railway line running from Viersen in Germany to Venlo in the Netherlands. The line was opened in 1866 by the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company. Formerly used by international passenger trains between The Hague and Cologne, it is now only used by the Maas-Wupper-Express service from Venlo to Hamm via Düsseldorf and Hagen. It is also an important link for freight transport. History The line was built by the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (, BME), following its acquisition of the Duisburg-Ruhrort–Mönchengladbach railway as part of its takeover of the Aachen-Düsseldorf-Ruhrort Railway Company on 1 January 1866. The first section from Viersen to Kaldenkirchen was opened on 29 January 1866 and this was followed by the opening of the second section from Kaldenkirchen to Venlo on 29 October 1866. In parallel with the building of this line, the Rhenish Railway Company (''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RHE) built its own line from Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viersen Station
Viersen station is a station in the city of Viersen in the west of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. History The first Viersen station was opened on 5 October 1849 by the Aachen-Düsseldorf-Ruhrort Railway Company () as part of its Ruhrort–Gladbach line near Alte Bruchstraße. On 4 March 1850, the company was made subordinate to the '' Royal Division of the Aachen-Dusseldorf-Ruhrort Railway'' () based in Aachen by a royal decree. In 1862 the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (''Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', BME) took over company in order to extend its network on to the western bank of the Rhine. In 1866 the management of both companies were merged and the station was renamed ''Viersen BME station''. In the same year, the BME gained its own access to the Dutch railway network with its line to Venlo, a year after its rival, the Rhenish Railway Company (''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE), opened its line to Nijmegen and ten years after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
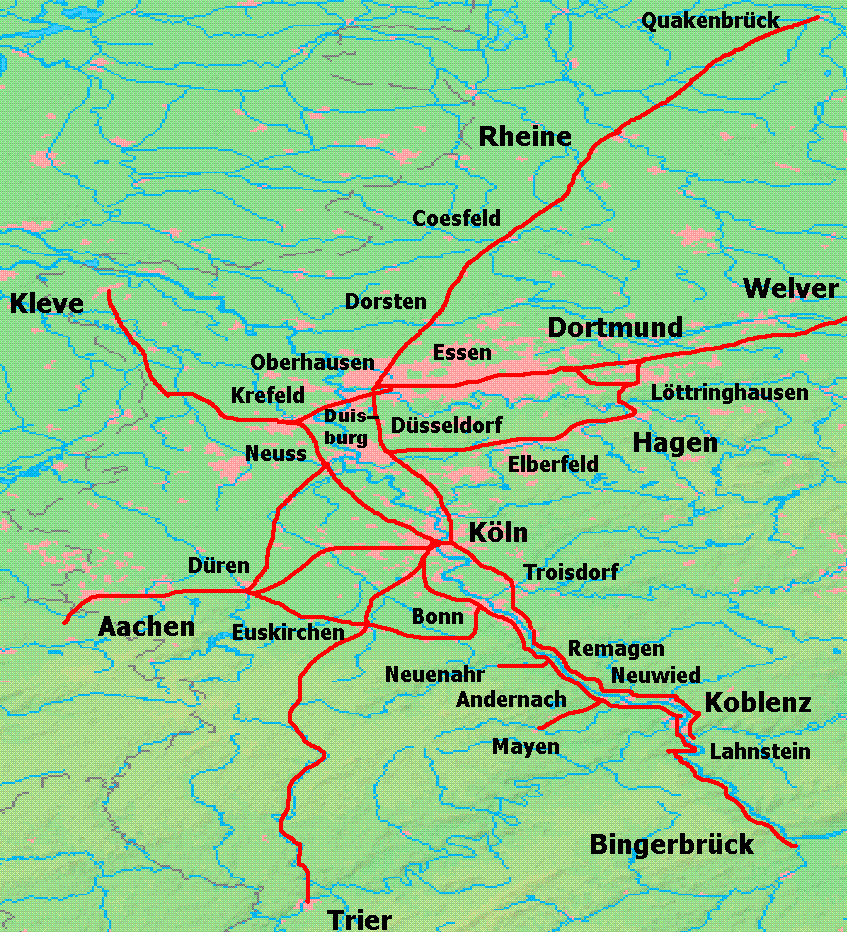
Rhenish Railway Company
The Rhenish Railway Company (German language, German: ''Rheinische Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'', RhE) was along with the Cologne-Minden Railway Company (CME) and the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company (BME) one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia. Foundation The industrialists of the Rhineland and the Bergisches Land, then part of Prussia, sought to avoid paying the high tolls for using the Rhine imposed by the Netherlands and very early in its development, saw the possibility of the new means of transport, the railway. As early as the 1830s committees were established by the cities of the Rhineland to promote proposals for building railways. Some of the members of the Cologne committee under David Hansemann (1790–1864)—a merchant and banker from Aachen—and the Aachen Committee favoured a railway line through Belgium to the seaport of Antwerp via Liege. Belgium, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Train
Push–pull is a configuration for locomotive-hauled trains, allowing them to be driven from either end of the train, whether having a locomotive at each end or not. A push–pull train has a locomotive at one end of the train, connected via some form of remote control, such as multiple-unit train control, to a vehicle equipped with a control cab at the other end of the train. This second vehicle may be another locomotive, or an unpowered control car. In the UK and some other parts of Europe, the control car is referred to as a ''driving trailer'' (or driving van trailer/DVT where there is no passenger accommodation); in the US and Canada, they are called ''cab cars'' and in Australia, they are called driving trailers. Train formation Locomotive at one end Historically, push–pull trains with steam power provided the driver with basic controls at the cab end along with a bell or other signalling code system to communicate with the fireman located in the engine itse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Regio
DB Regio AG () is a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn which operates regional and commuter train services in Germany. It is a 100% subsidiary of the Deutsche Bahn Group and therefore part of the DB Regio business segment, which also includes DB Regionnetz Verkehrs GmbH and other independent subsidiaries headquartered in Frankfurt am Main. The company as a mainly nationwide operational company is responsible for all regional transport activities ( rail and bus) of the DB Group in Germany. This includes traffic in neighboring countries. DB Regio serves 310 lines with 22,800 trains and 295,000 stops every day, serving about ten million customers. History Foundation and early years DB Regio AG emerged during the second stage of the rail reform on 1 January 1999, from the local transport division of Deutsche Bahn AG. Original plans were for them to be listed on the stock exchange by 2003. An IPO has not yet been implemented. The articles of association for DB Regio GmbH were conclud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadler FLIRT
Stadler FLIRT (, ) is a passenger multiple unit trainset made by Stadler Rail of Switzerland. The baseline design of FLIRT is an electric multiple unit Articulated car, articulated trainset that can come in units of two to twelve cars with two to six motorized axles. The maximum speed is . Standard floor height is , but high floors are also available for platform heights of . The FLIRT train was originally developed for the Swiss Federal Railways and was first delivered in 2004. The trains quickly became a success and were ordered by operators in Algeria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Canada, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Serbia, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States. As of October 2021, more than 2500 units have been sold. Aside from being electric (Electric multiple unit, EMU), the FLIRT is available in diesel-electric (Diesel multiple unit#Diesel–electric, DEMU), Battery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keolis
Keolis is a French transportation company that operates public transport systems all over the world. It manages bus, rapid transit, tram, coach networks, rental bikes, car parks, water taxi, cable car, trolleybus, and funicular services. Based in Paris, France, the company is 70% owned by SNCF and 30% owned by the Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec. Keolis operates a number of networks in France ( Transports Bordeaux Métropole in Bordeaux, the Lyon public transport on behalf of SYTRAL, the public transport service for the Greater Rennes area since 1998, Transpole in Lille, and the entire mobility chain in Dijon). Internationally, it manages buses in several cities in Sweden, central and eastern regions of the Netherlands, and in the United States. It also manages various rail networks internationally, such as the commuter rail in Boston, the Hyderabad Metro, the Docklands Light Railway in London, the Pujiang line ( Shanghai Metro), the Nottingham tramway, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurobahn
Eurobahn GmbH & Co. KG is a railway operator in Germany, established in 1998. It operates 15 regional train services in 4 contracts in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with cross-border services including Lower Saxony and the Netherlands. It is owned by Zweckverband Nahverkehr Westfalen-Lippe, the rail authority for eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, where the majority of Eurobahn's services operate. Initially a joint venture between Keolis and Rhenus operating bus and rail services, it became a 100% Keolis subsidiary operating rail services in 2007. From 1 January 2022 until May 2025, it was owned by the law firm Noerr. History Company history Eurobahn was founded as ''Eurobahn Verkehrsgesellschaft mbH & Co KG,'' later ''Rhenus Keolis'', in 1998 as a 60/40 joint venture between Keolis (then VIA-GTI) and Rhenus. In December 2007, the joint venture was dissolved; Rhenus taking ownership of the bus operations and two railway contracts under the name Rhenus Veniro, Keo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köln Messe/Deutz Station
Köln Messe/Deutz station (called ''Köln-Deutz'' until November 2004, Colognian dialect, Colognian: , ) is an important railway junction for long-distance rail and local services in the Deutz, Cologne, Deutz neighborhood of Cologne in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is situated close to the eastern bank of the Rhine and connected via the Hohenzollern Bridge to Köln Hauptbahnhof, the city's main station, which is just a few hundred metres away. The Cologne Trade Fair () grounds are directly north of the station, hence the ''Messe'' in the station's name. The Deutz/Messe station of the Cologne Stadtbahn is nearby and connected to this station by a pedestrian tunnel. Köln Messe/Deutz is a junction station, which has platforms on two levels: the high-level platforms are used by trains running in the east-west direction across the Hohenzollern Bridge to and from Köln Hauptbahnhof. The lower level (''Köln Messe/Deutz tief'') is used by trains running in a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhein-Erft-Express
The Rhein-Erft-Express is a Regional-Express service in the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate. It is numbered as line RE 8 and connects the cities of Mönchengladbach Hauptbahnhof, Mönchengladbach, Köln Hauptbahnhof, Cologne, Bonn Hauptbahnhof, Bonn and Koblenz Hauptbahnhof, Koblenz with each other and their surroundings, running hourly. It is complemented by a Regionalbahn stopping service, the ''Rhein-Erft-Bahn'' (RB 27), running also between Mönchengladbach Hauptbahnhof and Koblenz Hauptbahnhof. On weekends it stops at some additional stations between Cologne Hbf and Koblenz Hbf. It is operated by DB Regio with Alstom Coradia Continental EMUs. Route The ''Rhine-Erft-Express'' runs from Mönchengladbach via the Cologne–Mönchengladbach railway, Cologne–Mönchengladbach line to Cologne, where it stops, despite its classification as a Regional-Express, at all stations. Near Grevenbroich station, Grevenbroich it crosses the Erft river. In Cologn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional-Express
In Germany, Luxembourg and Austria, the Regional-Express (; RE, or in Austria: REX) is a type of regional train. It is similar to a semi-fast train, with a top speed of and an average speed of about as it calls at fewer stations than ''Regionalbahn'' (in Austria: '' Regionalzug'') or S-Bahn trains, but stops more often than ''Intercity'' or ''Intercity Express'' services. Operations The first Regional-Express services were operated by DB Regio, though since the liberalisation of the German rail market (''Bahnreform'') in the 1990s many operators have received franchise rights on lines from the federal states. Some private operators currently operate trains that are similar to a Regional-Express service, but have decided to use their own names for the sake of brand awareness instead. Regional-Express services are carried out with a variety of vehicles such as DMUs (of Class 612), EMUs (of Class 425 or 426) or, most commonly, electric or diesel locomotives with doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheingold (train)
The ('Rhinegold') was a named train that operated between Hook of Holland, near Rotterdam, and Geneva, Switzerland (or Basel before 1965), a distance of , until 1987. Another section of the train started in Amsterdam and was coupled to the cars in Utrecht. The ran along the Rhine River via Arnhem, Netherlands, and Cologne, Germany, using special luxury coaches. It was named after 's opera, which romanticized the Rhine. From 1965 until the train's discontinuation in 1987, the was a first-class-only Trans Europ Express (TEE) train. Route Geneva ( ) – Basel SBB – Freiburg – Baden-Baden – Karlsruhe – Mannheim – Mainz – Cologne – Düsseldorf – Duisburg – Utrecht and then in separate trains continuing (still as the ) to both Hook of Holland and Amsterdam. At Hook of Holland, the train had timed connections for ship service to and from Harwich, England. The Geneva–Basel section was added in 1965 and was discontinued in 1980/82 (see later section for detai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoek Van Holland Haven Railway Station
Hoek van Holland Haven (''Hook of Holland Harbour'') is a metro station on Line B of the Rotterdam Metro, in Hook of Holland (Hoek van Holland), Rotterdam, South Holland. Trains connect with the Stena Line Dutchflyer boat service to Harwich International in England. Until 1 April 2017, it was a railway station served by Nederlandse Spoorwegen. On 30 September 2019, it reopened as the western terminus of RET Metro Line B., and in 2023 it was extended to the new Hoek van Holland Strand station with the platforms relocated to the northwest of the historical station-building, so that they are on the new section of the line. Train services As of 2019, metro service operates every 20 minutes throughout the day to Nesselande, via Beurs. Since 2017 rail service from Rotterdam Centraal railway station Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |