|
Viceroy Of Guangdong And Guangxi
The Viceroy of Liangguang, fully in Chinese as the Governor-General of Two Guang Provinces and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China#Qing dynasty, Viceroys during the Ming Dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasties of China. The Viceroy of Liangguang had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Guangdong Province and then Guangxi Province (approx. nowadays Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, and Macau). History Ming dynasty The office of the Viceroy of Liangguang originated in 1452 during the Ming dynasty. The Jingtai Emperor accepted Yu Qian's proposal to create the office and appointed Wang Ao (viceroy), Wang Ao (王翱) as the first viceroy. In 1465, the Chenghua Emperor appointed Han Yong (Ming dynasty), Han Yong (韓雍) as Censorate, Left Censor-in-Chief and Viceroy of Liangguang. The office was formalised in 1469, with the administrative headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty Liangguang Map 1911
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiajing Emperor
The Jiajing Emperor (16September 150723January 1567), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizong of Ming, personal name Zhu Houcong, art name, art names Yaozhai, Leixuan, and Tianchi Diaosou, was the 12th List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1521 to 1567. He succeeded his cousin, the Zhengde Emperor. The Jiajing Emperor was born as a cousin of the reigning Zhengde Emperor, so his accession to the throne was unexpected, but when the Zhengde Emperor died without an heir, the government, led by Senior Grand Secretary Yang Tinghe and Empress Zhang (Hongzhi), Empress Dowager Zhang, chose him as the new ruler. After his enthronement, a dispute arose between the emperor and his officials regarding the method of legalizing his accession. This conflict, known as the Great Rites Controversy, was a significant political issue at the beginning of his reign. After three years, the emperor emerged victorious, with his main opponents eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangxu Emperor
The Guangxu Emperor (14 August 1871 – 14 November 1908), also known by his temple name Emperor Dezong of Qing, personal name Zaitian, was the tenth Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the ninth Qing emperor to rule over China proper, from 1875 to 1908. His succession was endorsed by dowager empresses Empress Dowager Ci'an, Ci'an and Empress Dowager Cixi, Cixi for political reasons after Emperor Tongzhi died without an heir. Cixi held political power for much of Guangxu's reign as regent, except for the period between his assumption of ruling powers in 1889 and the Hundred Days' Reform in 1898. The Qing Empire's prestige and sovereignty continued to erode during Guangxu's reign with defeats in the Sino-French War, the First Sino-Japanese War, and the Boxer Rebellion. Guangxu engaged intellectuals like Kang Youwei and Liang Qichao to develop the Hundred Days' Reform program of 1898 to reverse the decline. Among the goals was removing Cixi from power. The program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor (25 September 17117 February 1799), also known by his temple name Emperor Gaozong of Qing, personal name Hongli, was the fifth Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. He reigned officially from 1735 until his abdication in 1796, but retained ultimate power subsequently until his death in 1799, making him one of the longest-reigning monarchs in history as well as one of the longest-lived. The fourth and favourite son of the Yongzheng Emperor, Qianlong ascended the throne in 1735. A highly ambitious military leader, he led Ten Great Campaigns, a series of campaigns into Inner Asia, Burma, Nepal and Vietnam and suppressed rebellions in Jinchuan County, Jinchuan and Taiwan. During his lifetime, he was given the deified title Emperor Manjushri by the Qing's Tibetan subjects. Domestically, Qianlong was a major patron of the arts as well as a prolific writer. He sponsored the compilation of the ''Siku Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Yun-Gui
The Viceroy of Yun-Gui, fully in Chinese as the Governor-General of Yun-Gui Provinces and Other Local Areas, in Charge of Military Affairs, Food and Wages and Governor Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys in China#Qing dynasty, Viceroys during the Qing dynasty, Qing dynasty of China. The Viceroy of Yun-Gui had jurisdiction of military, civil, and political affairs over then Yunnan Province and then Guizhou Province (approx. nowadays southern part of Yunnan and part of Guizhou). History The Viceroy of Yun-Gui was created in 1659, during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, as a ''jinglue'' (經略; military governor) office before it was converted to a Viceroy. In 1662, during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor, the Viceroy of Yun-Gui split into the Viceroy of Yunnan and Viceroy of Guizhou, which were respectively headquartered in Qujing and Anshun. Two years later, the two viceroys were merged and the headquarters shifted to Guiyang. In 1673, the Kangxi Emperor restored the Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
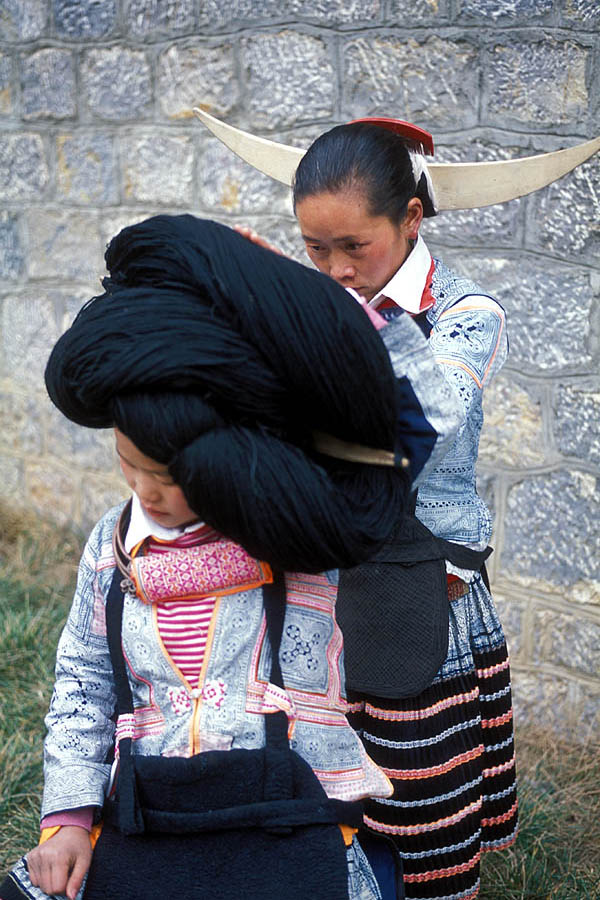
Miao People
Miao is a word that the Chinese use to designate some ethnic minority groups living in southern China and Mainland Southeast Asia. Miao is thus officially recognized by the Chinese government as one of the largest ethnic minority groups that has more than 56 official ethnicities and dialects. The Miao live primarily in the mountains of southern China. Their homeland encompasses the provinces of Guizhou, Yunnan, Sichuan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangxi, Guangdong, and Hainan. Some sub-groups of the Miao, most notably the Hmong people, have migrated out of China into Southeast Asia (Myanmar, Northern Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand). Following the communist takeover of Laos in 1975, a large group of Hmong refugees resettled in several Western nations, mainly in the United States, France, and Australia. Miao is a Chinese term, while the component groups of people have their own autonyms, such as (with some variant spellings) Hmong, Hmu, Xong (Qo-Xiong), and A-Hmao. These people (except th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongzheng Emperor
The Yongzheng Emperor (13 December 1678 – 8 October 1735), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizong of Qing, personal name Yinzhen, was the fourth List of emperors of the Qing dynasty, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the third Qing emperor to rule over China proper. The fourth son of the Kangxi Emperor, Yongzheng ascended the throne following prolonged disputes over succession. A hard-working ruler, he aimed to create a more effective government, cracked down on corruption and reformed the personnel and financial administration. His reign also saw the formation of the Grand Council (Qing dynasty), Grand Council, an institution that had a major impact on the future of the dynasty. Militarily, Yongzheng continued his father's efforts to consolidate Qing's position in Outer Mongolia and Tibet through force. The Yongzheng Emperor died in 1735 at the age of 56 and was succeeded by his fourth son, who assumed the throne as the Qianlong Emperor. Although his reign was much s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepu County
Hepu (), alternately romanized as Hoppo, Hopu or Hop'u, is a county under the administration of Beihai City in southeastern Guangxi, China. It borders Lianjiang (Guangdong) to the southeast, Bobai County to the northeast, the Gulf of Tonkin to the south, Qinzhou to the west, and Pubei County to the north. Then-Premier Li Peng called this place "the Southern Pearl County" () in November 1992. The county was once known as Lianzhou (Postal: Limchow). It has an area of and a population of 930,914 . History In antiquity, Hepu county was originally part of a larger county which encompassed part of Guangxi, Guangdong and even parts of Hainan. It was established in 111 BCE by Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty, during the first Chinese domination of Vietnam. During the brief interruption of the Han dynasty by Wang Mang, many of his opponents were exiled and banished to Hepu. * 1949–1950: Hepu administered Beihai as a town * June 1965: administered by Qinzhou Region of Guangx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. He is considered one of China's greatest emperors. The third son of the Shunzhi Emperor, Kangxi was enthroned at the age of seven while actual power was held for six more years by the four regents nominated by his father. After assuming personal rule, Kangxi's attempt to revoke the fiefdoms of feudal princes sparked the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, which he suppressed. He also forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and Mongols in the north and northwest to submit to Qing rule, and launched an expedition that incorporated Tibet into the empire. Domestically, he initially welcomed the Jesuits and the propagation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about northwest of Hong Kong and north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the Silk Road. The port of Guangzhou serves as a transportation hub for China's fourth largest city and surrounding areas, including Hong Kong. Guangzhou was captured by the United Kingdom, British during the First Opium War and no longer enjoyed a monopoly after the war; consequently it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major entrepôt. Following the Second Battle of Chuenpi in 1841, the Treaty of Nanking was signed between Robert Peel, Sir Robert Peel on behalf of Queen Victoria and Lin Zexu on behalf of Daoguang Emperor, Emperor Xuanzong and ceded British Hong Kong, Hong Kon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizu of Qing, personal name Fulin, was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper. Upon the death of his father Hong Taiji, a Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose the 5-year-old Fulin as successor. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon, the 14th son of Nurhaci, and Jirgalang, one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Qing imperial clan. In November 1644, the Shunzhi Emperor was enthroned as emperor of China in Beijing. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of the prince regent Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty, chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
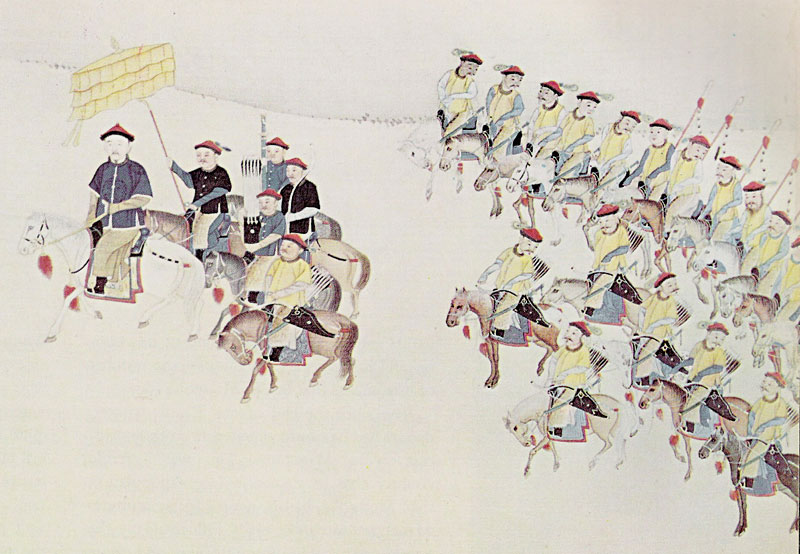
Qing Viceroys
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty assembled the territorial base for modern China. The Qing controlled the most territory of any dynasty in Chinese history, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |