|
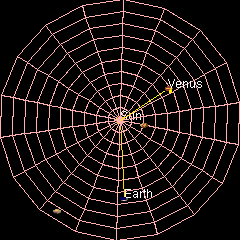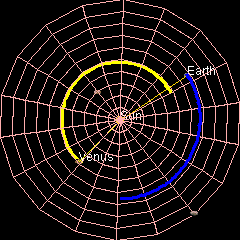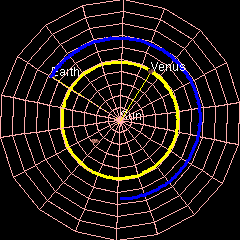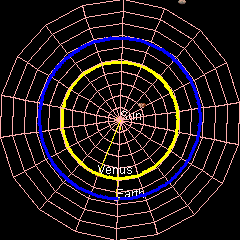
Venus's Orbit
Venus has an orbit with a semi-major axis of , and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity of 0.007.Jean Meeus, ''Astronomical Formulæ for Calculators'', by Jean Meeus. (Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1988) 99. Elements by Simon Newcomb The low eccentricity and comparatively small size of its orbit give Venus the least range in distance between perihelion and aphelion of the planets: 1.46 million km. The planet orbits the Sun once every 225 days and travels in doing so,Jean Meeus, ''Astronomical Algorithms'' (Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1998) 238. The formula by Ramanujan is accurate enough. giving an average orbital speed of . Conjunctions and transits When the geocentric ecliptic coordinate system, ecliptic longitude of Venus coincides with that of the Sun, it is in conjunction (astronomy), conjunction with the Sun – inferior if Venus is nearer and superior if farther. The distance between Venus and Earth varies from about 42 million km (at inferior conjunction) to abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary System
A planetary system is a set of gravity, gravitationally bound non-stellar Astronomical object, bodies in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consist of bodies such as dwarf planets, asteroids, natural satellites, meteoroids, comets, planetesimals and circumstellar disks. For example, the Sun together with the planetary system revolving around it, including Earth, form the Solar System. The term exoplanetary system is sometimes used in reference to other planetary systems. Planetary systems are, by convention, named for their host, or parent star, as is the case in our Solar Planetary System, named for its hosting, star, "Sol". Debris disk, Debris disks are known to be common while other objects are more difficult to observe. Of particular interest to astrobiology is the habitable zone of planetary systems where planets could have surface liquid water, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-planetary Disc
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may not be considered an accretion disk; while the two are similar, an accretion disk is hotter and spins much faster; it is also found on black holes, not stars. This process should not be confused with the accretion process thought to build up the planets themselves. Externally illuminated photo-evaporating protoplanetary disks are called proplyds. Formation Protostars form from molecular clouds consisting primarily of molecular hydrogen. When a portion of a molecular cloud reaches a critical size, mass, or density, it begins to collapse under its own gravity. As this collapsing cloud, called a solar nebula, becomes denser, random gas motions originally present in the cloud average out in favor of the direction of the nebula's net angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum causes the rotatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstellar Disc
A Circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place, and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways. Young star According to the widely accepted model of star formation, sometimes referred to as the nebular hypothesis, a young star (protostar) is formed by the gravitational collapse of a pocket of matter within a giant molecular cloud. The infalling material possesses some amount of angular momentum, which results in the formation of a gaseous protoplanetary disc around the young, rotating star. The former is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Dust
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System. This system of particles has been studied for many years in order to understand its nature, origin, and relationship to larger bodies. There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, interplanetary dust particles have a role in scattering sunlight and in emitting thermal radiation, which is the most prominent feature of the night sky's radiation, with wavelengths ranging 5–50 μm. The particle sizes of grains characterizing the infrared emission near Earth's orbit typically range 10–100 μm. Microscopic impact craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program revealed the size distribution of cosmic dust particles bombarding the lunar surface. The ’’Grün’’ distribution of interplanetar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Dust Ring
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phases Of Venus
The phases of Venus are the variations of lighting seen on the planet's surface, similar to lunar phases. The first recorded observations of them are thought to have been telescopic observations by Galileo Galilei in 1610. Although the extreme crescent phase of Venus has since been observed with the naked eye, there are no indisputable historical pre-telescopic records of it being described or known. Observation The orbit of Venus is 224.7 Earth days (7.4 avg. Earth months 0.4 days. The phases of Venus result from the planet's orbit around the Sun inside the Earth's orbit giving the telescopic observer a sequence of progressive lighting similar in appearance to the Moon's phases. It presents a ''full'' image when it is on the opposite side of the Sun. It is a ''gibbous'' phase when it approaches or leaves the opposite side of the Sun. It shows a ''quarter phase'' when it is at its maximum elongation from the Sun. Venus presents a ''thin crescent'' in telescopic views as it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Transfer
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft. For spacecraft far from Earth, an orbital maneuver is called a ''deep-space maneuver (DSM)''. When a spacecraft is not conducting a maneuver, especially in a transfer orbit, it is said to be ''coasting''. General Rocket equation The Tsiolkovsky rocket equation, or ideal rocket equation, can be useful for analysis of maneuvers by vehicles using rocket propulsion. A rocket applies acceleration to itself (a thrust) by expelling part of its mass at high speed. The rocket itself moves due to the conservation of momentum. Delta-v The applied change in velocity of each maneuver is referred to as delta-v (\Delta\mathbf\,). The delta-v for all the expected maneuvers are estimated for a mission are summarized in a delta-v budget. With a good approximation of the delta-v budget designers can estimate the propellant required for planned maneuvers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta-v Budget
Delta-''v'' (also known as " change in velocity"), symbolized as and pronounced , as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse per unit of spacecraft mass that is needed to perform a maneuver such as launching from or landing on a planet or moon, or an in-space orbital maneuver. It is a scalar that has the units of speed. As used in this context, it is not the same as the physical change in velocity of said spacecraft. A simple example might be the case of a conventional rocket-propelled spacecraft, which achieves thrust by burning fuel. Such a spacecraft's delta-''v'', then, would be the change in velocity that spacecraft can achieve by burning its entire fuel load. Delta-''v'' is produced by reaction engines, such as rocket engines, and is proportional to the thrust per unit mass and the burn time. It is used to determine the mass of propellant required for the given maneuver through the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. For multiple maneuvers, delt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Potential
In classical mechanics, the gravitational potential is a scalar potential associating with each point in space the work (energy transferred) per unit mass that would be needed to move an object to that point from a fixed reference point in the conservative gravitational field. It is analogous to the electric potential with mass playing the role of charge. The reference point, where the potential is zero, is by convention infinitely far away from any mass, resulting in a negative potential at any finite distance. Their similarity is correlated with both associated fields having conservative forces. Mathematically, the gravitational potential is also known as the Newtonian potential and is fundamental in the study of potential theory. It may also be used for solving the electrostatic and magnetostatic fields generated by uniformly charged or polarized ellipsoidal bodies. Potential energy The gravitational potential (''V'') at a location is the gravitational potential ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |