|
Variable Structure Control
Variable structure control (VSC) is a form of Classification of discontinuities, discontinuous nonlinear control. The method alters the dynamic system, dynamics of a nonlinear system by application of a high-frequency ''switching control''. The state space (controls), state-feedback control law is ''not'' a continuous function of time; it ''switches'' from one smooth condition to another. So the ''structure'' of the control law ''varies'' based on the position of the state trajectory; the method switches from one smooth control law to another and possibly very fast speeds (e.g., for a countably infinite number of times in a finite time interval). VSC and associated sliding mode behaviour was first investigated in early 1950s in the Soviet Union by Emelyanov and several coresearchers. The main mode of VSC operation is sliding mode control (SMC). The strengths of SMC include: * Low sensitivity to plant (control theory), plant parameter uncertainty * Greatly reduced-order modeling of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Discontinuities
Continuous functions are of utmost importance in mathematics, functions and applications. However, not all functions are continuous. If a function is not continuous at a limit point (also called "accumulation point" or "cluster point") of its domain, one says that it has a discontinuity there. The set of all points of discontinuity of a function may be a discrete set, a dense set, or even the entire domain of the function. The oscillation of a function at a point quantifies these discontinuities as follows: * in a removable discontinuity, the distance that the value of the function is off by is the oscillation; * in a jump discontinuity, the size of the jump is the oscillation (assuming that the value ''at'' the point lies between these limits of the two sides); * in an essential discontinuity (a.k.a. infinite discontinuity), oscillation measures the failure of a limit to exist. A special case is if the function diverges to infinity or minus infinity, in which case the oscillati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Mode Control
In control systems, sliding mode control (SMC) is a nonlinear control method that alters the dynamic system, dynamics of a nonlinear system by applying a discontinuous control signal (or more rigorously, a set-valued control signal) that forces the system to "slide" along a cross-section of the system's normal behavior. The state space (controls), state-feedback control law is not a continuous function of time. Instead, it can switch from one continuous structure to another based on the current position in the state space. Hence, sliding mode control is a variable structure control method. The multiple control structures are designed so that trajectories always move toward an adjacent region with a different control structure, and so the ultimate trajectory will not exist entirely within one control structure. Instead, it will ''slide'' along the boundaries of the control structures. The motion of the system as it slides along these boundaries is called a ''sliding mode'' and the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
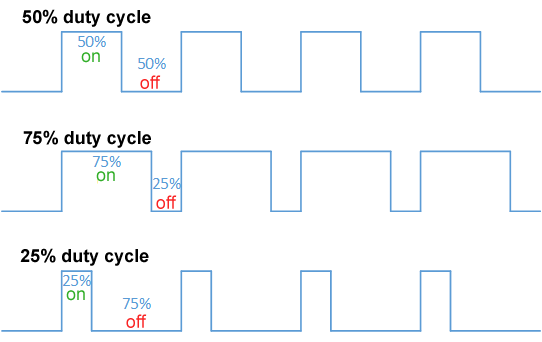
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying period). PWM is useful for controlling the average power or amplitude delivered by an electrical signal. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by switching the supply between 0 and 100% at a rate faster than it takes the load to change significantly. The longer the switch is on, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of controlling the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching. The goal of PWM is to control a load; however, the PWM switching frequency must be sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-density Modulation
Pulse-density modulation (PDM) is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with a binary signal. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into codewords of pulses of different weight as they would be in pulse-code modulation (PCM); rather, the relative density of the pulses corresponds to the analog signal's amplitude. The output of a 1-bit DAC is the same as the PDM encoding of the signal. Description In a pulse-density modulation bitstream, a 1 corresponds to a pulse of positive polarity (+''A''), and a 0 corresponds to a pulse of negative polarity (−''A''). Mathematically, this can be represented as : x = -A (-1)^, where ''x'' 'n''is the bipolar bitstream (either −''A'' or +''A''), and ''a'' 'n''is the corresponding binary bitstream (either 0 or 1). A run consisting of all 1s would correspond to the maximum (positive) amplitude value, all 0s would correspond to the minimum (negative) amplitude value, and alternating 1s and 0s wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta-sigma Modulation
Delta-sigma (ΔΣ; or sigma-delta, ΣΔ) modulation is an oversampling method for encoding signals into low bit depth digital signals at a very high sample-frequency as part of the process of delta-sigma analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). Delta-sigma modulation achieves high quality by utilizing a negative feedback loop during quantization to the lower bit depth that continuously corrects quantization errors and moves quantization noise to higher frequencies well above the original signal's bandwidth. Subsequent low-pass filtering for demodulation easily removes this high frequency noise and time averages to achieve high accuracy in amplitude, which can be ultimately encoded as pulse-code modulation (PCM). Both ADCs and DACs can employ delta-sigma modulation. A delta-sigma ADC (e.g. Figure 1 top) encodes an analog signal using high-frequency delta-sigma modulation and then applies a digital filter to demodulate it t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switching Amplifier
A class-D amplifier, or switching amplifier, is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices (transistors, usually MOSFETs) operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. They operate by rapidly switching back and forth between the supply rails, using pulse-width modulation, pulse-density modulation, or related techniques to produce a pulse train output. A simple low-pass filter may be used to attenuate their high-frequency content to provide analog output current and voltage. Little energy is dissipated in the amplifying transistors because they are always either fully on or fully off, so efficiency can exceed 90%. History The first class-D amplifier was invented by British scientist Alec Reeves in the 1950s and was first called by that name in 1955. The first commercial product was a kit module called the X-10 released by Sinclair Radionics in 1964. However, it had an output power of only 2.5 watts. The Sinclair X-20 in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-bridge
An H-bridge is an electronic circuit that switches the polarity of a voltage applied to a load. These circuits are often used in robotics and other applications to allow DC motors to run forwards or backwards. The name is derived from its common schematic diagram representation, with four switching elements configured as the branches of a letter "H" and the load connected as the cross-bar. Most DC-to-AC converters (power inverters), most AC/AC converters, the DC-to-DC push–pull converter, isolated DC-to-DC converter most motor controllers, and many other kinds of power electronics use H bridges. In particular, a bipolar stepper motor is almost always driven by a motor controller containing two H bridges. General H-bridges are available as integrated circuits, or can be built from discrete components. The term ''H-bridge'' is derived from the typical graphical representation of such a circuit. An H-bridge is built with four switches (solid-state or mechanical). When the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimal Control
Optimal control theory is a branch of control theory that deals with finding a control for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective function is optimized. It has numerous applications in science, engineering and operations research. For example, the dynamical system might be a spacecraft with controls corresponding to rocket thrusters, and the objective might be to reach the Moon with minimum fuel expenditure. Or the dynamical system could be a nation's economy, with the objective to minimize unemployment; the controls in this case could be fiscal and monetary policy. A dynamical system may also be introduced to embed operations research problems within the framework of optimal control theory. Optimal control is an extension of the calculus of variations, and is a mathematical optimization method for deriving control policies. The method is largely due to the work of Lev Pontryagin and Richard Bellman in the 1950s, after contributions to calculus of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robust Control
In control theory, robust control is an approach to controller design that explicitly deals with uncertainty. Robust control methods are designed to function properly provided that uncertain parameters or disturbances are found within some (typically compact) set. Robust methods aim to achieve robust performance and/or stability in the presence of bounded modelling errors. The early methods of Bode and others were fairly robust; the state-space methods invented in the 1960s and 1970s were sometimes found to lack robustness, prompting research to improve them. This was the start of the theory of robust control, which took shape in the 1980s and 1990s and is still active today. In contrast with an adaptive control policy, a robust control policy is static, rather than adapting to measurements of variations, the controller is designed to work assuming that certain variables will be unknown but bounded. (Section 1.5) In German; an English version is also available Criteria for robust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Control
Nonlinear control theory is the area of control theory which deals with systems that are nonlinear system, nonlinear, time-variant system, time-variant, or both. Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that is concerned with the behavior of dynamical systems with inputs, and how to modify the output by changes in the input using feedback, Feed forward (control), feedforward, or filter (signal processing), signal filtering. The system to be controlled is called the "plant (control theory), plant". One way to make the output of a system follow a desired reference signal is to compare the output of the plant to the desired output, and provide feedback to the plant to modify the output to bring it closer to the desired output. Control theory is divided into two branches. Linear control theory applies to systems made of devices which obey the superposition principle. They are governed by linear equation, linear differential equations. A majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid System
A hybrid system is a dynamical system that exhibits both continuous and discrete dynamic behavior – a system that can both ''flow'' (described by a differential equation) and ''jump'' (described by a state machine, automaton, or a difference equation). Often, the term "hybrid dynamical system" is used instead of "hybrid system", to distinguish from other usages of "hybrid system", such as the combination neural nets and fuzzy logic, or of electrical and mechanical drivelines. A hybrid system has the benefit of encompassing a larger class of systems within its structure, allowing for more flexibility in modeling dynamic phenomena. In general, the ''state'' of a hybrid system is defined by the values of the ''continuous variables'' and a discrete ''mode''. The state changes either continuously, according to a flow condition, or discretely according to a ''control graph''. Continuous flow is permitted as long as so-called ''invariants'' hold, while discrete transitions ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Structure System
A variable structure system, or VSS, is a Classification of discontinuities, discontinuous nonlinear system of the form :\dot = \varphi( \mathbf, t ) where \mathbf \triangleq [x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n]^ \in \mathbb^n is the state vector, t \in \mathbb is the time variable, and \varphi(\mathbf,t) \triangleq [ \varphi_1(\mathbf,t), \varphi_2(\mathbf,t), \ldots, \varphi_n(\mathbf,t) ]^ : \mathbb^ \mapsto \mathbb^n is a ''piecewise continuous'' function. Due to the ''piecewise'' continuity of these systems, they behave like different continuous nonlinear systems in different regions of their state space (controls), state space. At the boundaries of these regions, their dynamic system, dynamics switch abruptly. Hence, their ''structure'' ''varies'' over different parts of their state space. The development of variable structure control depends upon methods of analyzing variable structure systems, which are special cases of hybrid system, hybrid dynamical systems. See also *Variable struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |