|
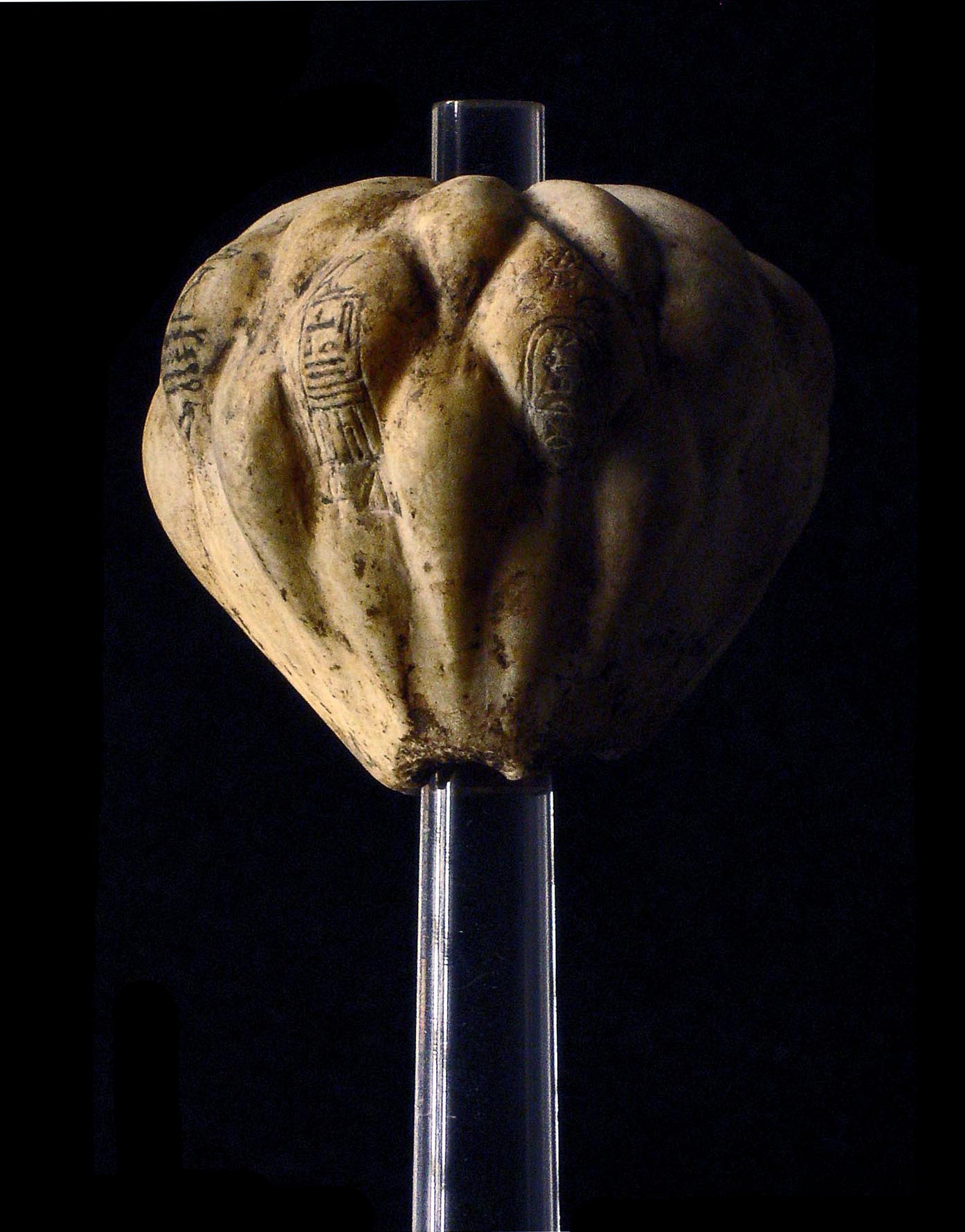
Unas
Unas or Wenis, also spelled Unis ( egy, wnjs, hellenized form Oenas or Onnos), was a pharaoh, the ninth and last ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Unas reigned for 15 to 30 years in the mid- 24th century BC (circa 2345–2315 BC), succeeding Djedkare Isesi, who might have been his father. Little is known of Unas' activities during his reign, which was a time of economic decline. Egypt maintained trade relations with the Levantine coast and Nubia, and military action may have taken place in southern Canaan. The growth and decentralization of the administration in conjunction with the lessening of the king's power continued under Unas, ultimately contributing to the collapse of the Old Kingdom some 200 years later. Unas built a pyramid in Saqqara, the smallest of the royal pyramids completed during the Old Kingdom. The accompanying mortuary complex with its high and valley temples linked by a causeway was lavishly decorated with painted reliefs, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
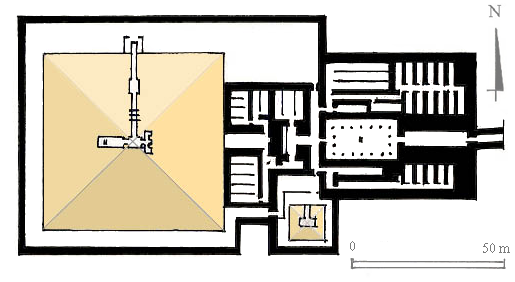
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas ( Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the '' Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Sekhemket and Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was constructed to provide access to the pyramid site. The causeway had elaborately decorated walls covered with a roof which had a slit in one section allowing light t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
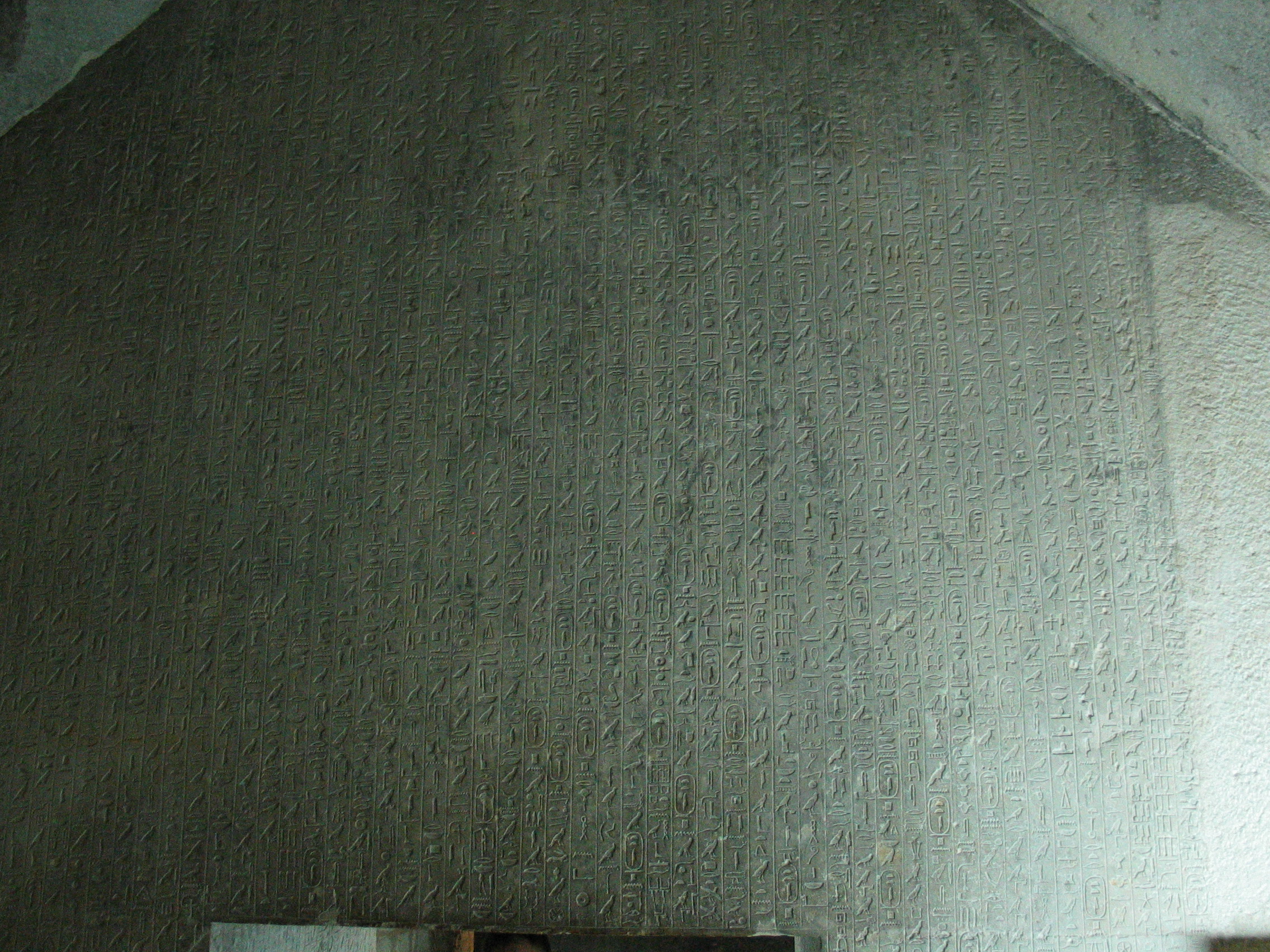
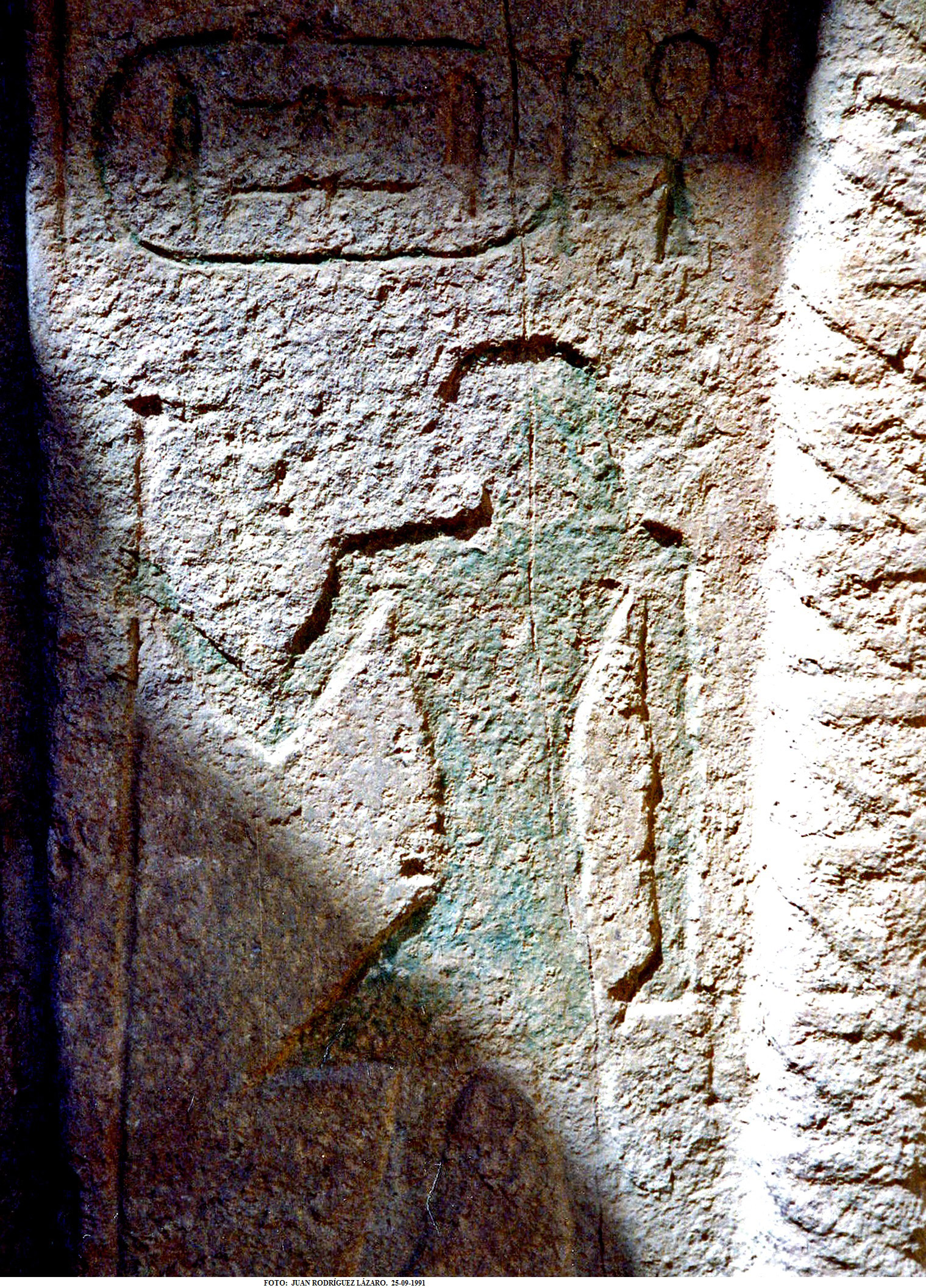
Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary texts, dating to the late Old Kingdom. They are the earliest known corpus of ancient Egyptian religious texts. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved onto the subterranean walls and sarcophagi of pyramids at Saqqara from the end of the Fifth Dynasty, and throughout the Sixth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, and into the Eighth Dynasty of the First Intermediate Period. The oldest of the texts have been dated to c. 2400–2300 BCE. Unlike the later Coffin Texts and Book of the Dead, the Pyramid Texts were reserved only for the pharaoh and were not illustrated. The use and occurrence of Pyramid Texts changed between the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms of Ancient Egypt. During the Old Kingdom (2686 BCE – 2181 BCE), Pyramid Texts could be found in the pyramids of kings as well as three queens, named Wedjebten, Neith, and Iput. During the Middle Kingdom (2055 BCE – 1650 BCE), Pyramid Texts were not writt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djedkare Isesi
Djedkare Isesi (known in Greek as Tancheres) was a pharaoh, the eighth and penultimate ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt in the late 25th century to mid- 24th century BC, during the Old Kingdom. Djedkare succeeded Menkauhor Kaiu and was in turn succeeded by Unas. His relationship to both of these pharaohs remain uncertain, although it is often conjectured that Unas was Djedkare's son, owing to the smooth transition between the two. Djedkare likely enjoyed a reign of more than 40 years, which heralded a new period in the history of the Old Kingdom. Breaking with a tradition followed by his predecessors since the time of Userkaf, Djedkare did not build a temple to the sun god Ra, possibly reflecting the rise of Osiris in the Egyptian pantheon. More significantly, Djedkare effected comprehensive reforms of the Egyptian state administration, the first undertaken since the inception of the system of ranking titles. He also reorganised the funerary cults of his forebears buri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Sixth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty VI), along with the Third, Fourth and Fifth Dynasty, constitutes the Old Kingdom of Dynastic Egypt. Pharaohs Known pharaohs of the Sixth Dynasty are listed in the table below. Manetho accords the dynasty 203 regnal years from Teti to Nitocris, while the Turin Canon assigns 181 regnal years, but with three additional kings concluding with Aba – discounting the reigns of the added Eighth Dynasty kings, this is reduced to 155 regnal years. This estimate varies between both scholar and source. History The Sixth Dynasty is considered by many authorities as the last dynasty of the Old Kingdom, although ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'' includes Dynasties VII and VIII as part of the Old Kingdom. Manetho writes that these kings ruled from Memphis, since their pyramids were built at Saqqara, very close one to another. By the Fifth Dynasty, the religious institution had established itself as the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebet (queen)
Nebet was an Egyptian Queen, the wife of King Unas. She lived during the time of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is held the mother of the Crown Prince Unas-ankh, though this fact is disputed. In addition to Unas Anch, Nebet may also be the mother of Khentkaues, Neferut, and Nefertkaues. Tomb Nebet was buried in a double mastaba with another queen, Khenut, next to the Pyramid of Unas in Saqqara. The mastaba was excavated by Peter Munro. Titles Nebet's titles are: "Great One of the ''hetes-sceptre''" (''wrt-hetes''), "She who sees Horus and Seth" (''mȝȝt-ḥrw-stẖ''), "Great of Praises" (''wrt-ḥzwt''), "King's Wife, his beloved" (''ḥmt-nsw mryt.f''), "Consort and Beloved of the Two Ladies In Ancient Egyptian texts, the "Two Ladies" ( egy, nbtj, sometimes anglicized ''Nebty'') was a religious epithet for the goddesses Wadjet and Nekhbet, two deities who were patrons of the ancient Egyptians and worshiped by all after the unificati ..." (''smȝyt-mry-nbty''), "Attendant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Fifth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty V) is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and VI under the group title the Old Kingdom. The Fifth Dynasty pharaohs reigned for approximately 150 years, from the early 25th century BC until the mid 24th century BC. Chronology The Fifth Dynasty of Egypt is a group of nine kings ruling Egypt for approximately 150 years in the 25th and 24th centuries BC. The relative succession of kings is not entirely secured as there are contradictions between historical sources and archaeological evidence regarding the reign of the shadowy Shepseskare. Rulers Known rulers in the Fifth Dynasty are listed below. Manetho assigns 248 years of rule to the Fifth Dynasty; however, the pharaohs of this dynasty more probably ruled for approximately 150 years. This estimate varies by both scholar and source. The Horus names and most names of the queens are taken from Dodson and Hilton. Manetho writes that the Dynasty V kings ruled from Eleph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khenut
Khenut was the Queen of Egypt, the wife of King Unas. She lived during the time of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She was a suspected mother of Queen Iput. Burial Khenut was buried in a double mastaba with another queen named Nebet next to the Pyramid of Unas in Saqqara. The mastaba was excavated by Peter Munro. The pyramid of the Queen mother Sesheshet lies near the pyramid which belong to Khenut. Titles Khenut’s titles are: "Great One of the ''hetes-sceptre''" (''wrt-hetes''), "She who sees Horus and Set" (''mȝȝt-ḥrw-stẖ''), "Great of Praises" (''wrt-ḥzwt''), "King’s Wife, his beloved" (''ḥmt-nisw mryt.f''), "Companion of Horus, his beloved" (''smrt-ḥrw-mryt.f''), "Consort and Beloved of the Two Ladies" (''smȝyt-mry-nbty''), and "Companion of Horus" (''tist-ḥrw''). Khenut may have been mentioned in the mortuary temple of Unas. Her tomb, unlike that of Queen Nebet, has suffered extensive damage.Wolfram Grajetzki, ''Ancient Egyptian Queens: A Hieroglyphic Dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iput
Iput I was a Queen of Egypt, a daughter of King Unas, the last king of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She married Teti, the first Pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Their son was Pepi I Meryre.Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2004. She possibly ruled as regent for her son Pepi I. Life Iput was a daughter of the Fifth Dynasty King Unas. Her mother was Nebet or Khenut. She married King Teti, who was the first king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Their son was King Pepi I. Iput is depicted with her son Pepi on a decree-stela from Koptos. The skeletal remains found at her pyramid show she died as a middle-aged woman. Iput had another son, Nebkauhor. She had several daughters: Seshseshet Waatetkhethor, Seshseshet Idut, Seshseshet Nubkhetnebty and Seshseshet Sathor. Titles of Iput I Iput I held several titlesGrajetzki, Ancient Egyptian Queens: A Hieroglyphic Dictionary, Golden House Publications, London, 2005, becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teti
Teti, less commonly known as Othoes, sometimes also Tata, Atat, or Athath in outdated sources, was the first king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. He was buried at Saqqara. The exact length of his reign has been destroyed on the Turin King List but is believed to have been about 12 years. Biography Teti had several wives: * Iput, the daughter of Unas, the last king of the Fifth dynasty. Iput was the mother of Pepi I. *Khuit, who may have been the mother of Userkare (according to Jonosi and Callender)Miroslav Verner, The Pyramids,1994 *Khentkaus IV *Neith Teti is known to have had several children. He was the father of at least three sons and probably ten daughters. Of the sons, two are well attested, a third one is likely: * Pepi I * Tetiankhkem * Nebkauhor, with the name of Idu, "king’s eldest son of his body", buried in the mastaba of Vizier Akhethetep/Hemi, buried in a fallen Vizier’s tomb, within the funerary complex of his maternal grandfather According to N. Kanawati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hare (hieroglyph)
The ancient Egyptian Hare hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. E34 (𓃹) is a portrayal of the desert hare or Cape hare, ''Lepus capensis'' of Egypt, within the Gardiner signs for mammals. The ancients used the name of ''sekhat'' for the hare. It is an Egyptian language biliteral with the value ''wn'', (or ''un''), often used in a hieroglyph composition block with the horizontal ''n''. E34:N35:N35 or E34:N35 The biliteral expresses the sound "oon", or "oonen",; it is also an ideogram for the verb "to be", or "to exist",Schumann-Antelme, and Rossini, 1998, p. 232-233, p. 232. (i.e. "is", "are", "was", etc.). The famous Pharaoh Unas, (for his Pyramid texts), is named using the hare hieroglyph. It also appears in the name of Wenamun, a (possibly fictional) priest who appears in a famous history of c. 1000 BCE. } Image:Thutmose III and Hatshepsut.jpg, Relief Image:Edfu51.JPG, Detail of ''Hare and water-ripple'' quadrat (hieroglyph block) (also shows Stool-or-mat (hier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unut
Unut, alt. Wenut or Wenet, is a Prehistory, prehistoric Egyptian snake goddess. Originally, she had the form of a snake and was called "The swift one". She came from the fifteenth Upper Egypt, Egyptian province, the Hare nome (called Wenet in Egyptian), and was worshipped with Thoth at its capital Hermopolis (in Egyptian: ''Wenu''). Later she was depicted with a woman's body and a hare's head.Erik Hornung, ''Conceptions of God in Ancient Egypt: The One and the Many'', Cornell University Press 1996, , p. 82 She was taken into the cult of Horus and later of Ra. Her name can be represented with five different Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyphs, but she rarely appears in literature and inscriptions. Her name was taken into the highest royal position just once in the long Egyptian history. Her male companion is Wenenu, who was sometimes regarded as a form of Osiris or Ra.Richard H. Wilkinson, Richard Wilkinson: ''The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt''. London, Thames and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_032007_27_det.jpg)



_-_046_(cropped).jpg)

