|
University Of Manchester Institute Of Science And Technology
The University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) was a university based in the centre of the city of Manchester in England. It specialised in technical and scientific subjects and was a major centre for Research university, research. On 1 October 2004, it amalgamated with the Victoria University of Manchester (commonly called the University of Manchester) to produce a new entity called the University of Manchester. UMIST gained its royal charter in 1956 and became a fully autonomous university in 1994. Previously its degrees were awarded by the Victoria University of Manchester. The UMIST motto was ''Scientia et Labore'' (By Knowledge and Work). Manchester Mechanics' Institute (1824–1882) The foundation of UMIST can be traced to 1824 during the Industrial Revolution when a group of Manchester businessmen and industrialists met in a public house, the Bridgewater Arms, to establish the ''Mechanics' Institute in Manchester'', where artisans could lear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full achievement (heraldry), heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest (heraldry), crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Roll of arms, Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a nobility, noble family, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George William Wood
George William Wood (21 July 1781 – 3 October 1843) was an English businessman, Member of Parliament and leading member of civil society in Manchester. Life George William Wood was born in Leeds, the son of William Wood, a Unitarian minister who was Joseph Priestley's successor at the Mill Hill Chapel, amateur botanist and campaigner against the Test Acts. His mother was Louisa Ann ''née'' Oates, the daughter of a wealthy Leeds family.Wykes (2004) Wood moved to Manchester around 1801 and was elected to membership of the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society on 24.4.1807. He became a prominent businessman there. But, as a memorial in the Upper Brook Street Chapel cited, "having early in life engaged in commercial pursuits ... he quitted the pursuits of wealth for the nobler objects of public usefulness." He was member of parliament for Lancashire South from 1832 to 1835, and for Kendal from 1837 until his death. He was a prime mover in the establishment of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Heywood
Oliver Heywood (9 September 1825 – 1892) was an England, English banker and philanthropist. Born in Irlam O'Th' Height, Lancashire, the son of Benjamin Heywood, and educated at Eton College, Heywood joined the family business, Heywood's Bank in the 1840s. Heywood sponsored many philanthropic causes, including Manchester Mechanics' Institute, Chetham's Hospital, Manchester Grammar School and Owens College. He was selected as High Sheriff of Lancashire for 1888. He married Eleanor Barton, daughter of Richard Watson Barton, on 7 September 1847; they had no children. Life On 9 September 1825, Oliver Heywood was born in Irlams O' Th' Height near Manchester, England to the prominent English banker and well known philanthropist Sir Benjamin Heywood and his wife Sophia Ann Robinson. Located in St. Ann's Square, the Heywood bank was one of the more recognisable bank names in Manchester but had suffered some tarnishing of its image from the 1700s. Heywood was educated in Liverpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Heywood
Sir Benjamin Heywood, 1st Baronet (12 December 1793 – 11 August 1865) was an English banker and philanthropist. Early life Benjamin Heywood was born on 12 December 1793 in St Ann's Square, Manchester. He was the grandson of Thomas Percival, the son of Nathaniel Heywood and Ann Percival, the brother to Thomas Heywood and James Heywood, and the nephew to Samuel Heywood. He lived at "Claremont" to the north west of the city centre in Irlams o' th' Height.McConnell (2004) He graduated from the University of Glasgow. Career Heywood entered his father's bank becoming a partner in 1814 and sole proprietor in 1828. He was an enthusiast for workers' education and was a founder of the Manchester Mechanics' Institute, serving as its president from 1825 until 1840. Heywood briefly served as Member of Parliament for Lancashire from 1831 until 1832, receiving his baronetcy in recognition of his work in support of the 1832 Reform Bill. He was also active in the Manchester Statistical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
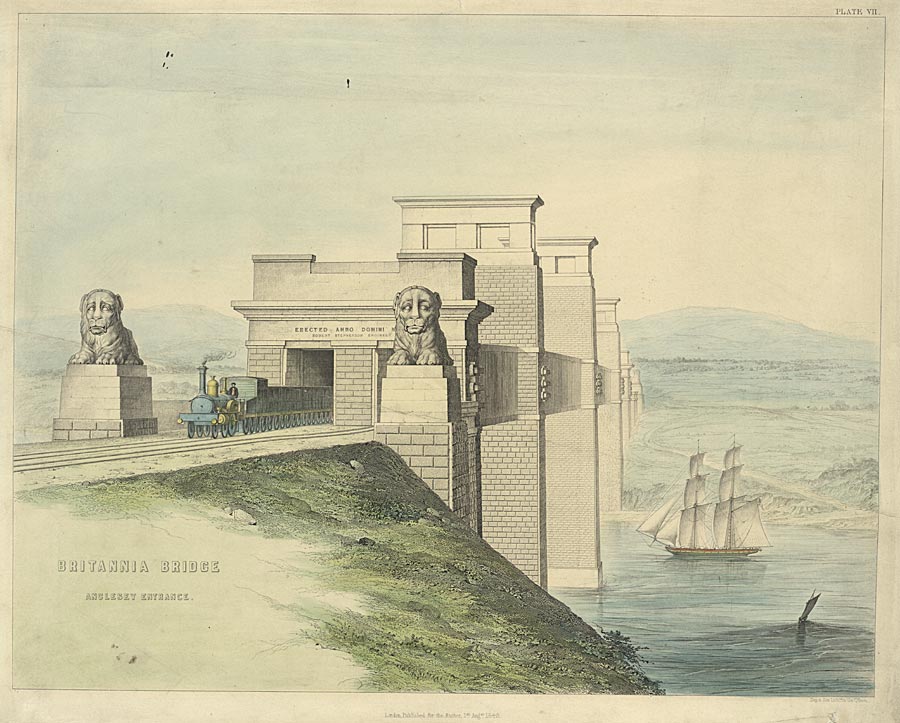
Britannia Bridge
Britannia Bridge () is a bridge in Wales that crosses the Menai Strait between the Isle of Anglesey and city of Bangor, Gwynedd, Bangor. It was originally designed and built by the noted railway engineer Robert Stephenson as a tubular bridge of wrought iron rectangular box-section spans for carrying rail traffic. Its importance was to form a critical link of the Chester and Holyhead Railway's route, enabling trains to directly travel between London and the port of Holyhead, thus facilitating a sea link to Dublin, Ireland. Decades before the building of the Britannia Bridge, the Menai Suspension Bridge had been completed, but this structure carried a road rather than track; there was no rail connection to Anglesey before its construction. After many years of deliberation and proposals, on 30 June 1845, a Act of Parliament#Bills, Parliamentary Bill covering the construction of the Britannia Bridge received royal assent. At the British Admiralty, Admiralty's insistence, the bridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a large wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with numerous blades or buckets attached to the outer rim forming the drive mechanism. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century, although they are no longer in common use today. Water wheels are used for milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth. Some water wheels are fed by water from a mill pond, which is formed when a flowing stream is dammed. A channel for the water flowing to or from a water wheel is called a mill race. The race bringing water from the mill pond to the water wheel is a headrace; the one carrying water after it has left the wheel is commonly referred to as a tailrace. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fairbairn
Sir William Fairbairn, 1st Baronet of Ardwick (19 February 1789 – 18 August 1874) was a Scotland, Scottish civil engineer, structural engineer and shipbuilder. In 1854 he succeeded George Stephenson and Robert Stephenson to become the third president of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Early career Born in Kelso, Scotland, Kelso to a local farmer, Fairbairn showed an early mechanical aptitude and served as an apprentice millwright in Newcastle upon Tyne where he befriended the young George Stephenson. He moved to Manchester in 1813 to work for Adam Parkinson and Thomas Hewes. In 1817, he launched his mill-machinery business with James Lillie as William Fairbairn & Sons, Fairbairn and Lillie Engine Makers. Structural studies Fairbairn was a lifelong learner and joined the Institution of Civil Engineers in 1830. In the 1820s and 30s, he and Eaton Hodgkinson conducted a search for an optimal cross section (geometry), cross section for iron beam (structure), beams. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry's Law
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is directly proportional at equilibrium to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century. In simple words, it states that the partial pressure of a gas in the vapour phase is directly proportional to the mole fraction of a gas in solution. An example where Henry's law is at play is the depth-dependent dissolution of oxygen and nitrogen in the blood of underwater divers that changes during decompression, going to decompression sickness. An everyday example is carbonated soft drinks, which contain dissolved carbon dioxide. Before opening, the gas above the drink in its container is almost pure carbon dioxide, at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. After the bottle is opened, this gas escapes, moving the partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry (chemist)
William Henry (12 December 17742 September 1836) was an English chemist. He was the son of Thomas Henry and was born in Manchester England. He developed what is known today as Henry's Law. Life William Henry was apprenticed to Thomas Percival and later worked with John Ferriar & John Huit at the Manchesters Infirmary. He began to study medicine at University of Edinburgh in 1795, taking his medical in 1807, but ill-health interrupted his practice as a physician, and he devoted his time mainly to chemical research, especially with regard to gases. One of his best-known papers (published in ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'', 1803) describes experiments on the quantity of gases absorbed by water at different temperatures and under different pressures. His results are known today as Henry's law. His other papers deal with gas-analysis, fire-damp, illuminating gas, the composition of hydrochloric acid and of ammonia, urinary and other morbid concretions, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Bellhouse
David Bellhouse (February 8, 1764 – 1840) was an English builder who did much to shape Victorian-era Manchester, both physically and socially. Biography Born in Leeds, Bellhouse received no formal education. An autodidact, he taught himself to read and write and the elements of arithmetic and technical drawing. In 1786, he moved to Manchester where he married Mary Wainwright and took up employment as a joiner with the building firm of Thomas Sharp. Sharp died in 1803 and his family had little appetite for the business so it was acquired by Bellhouse. During the Industrial Revolution there was a mass movement of workers towards Manchester to take up employment in the cotton spinning and textile industry. This created a demand for cheap housing and Bellhouse and his partners were among several tradesmen builders who made their fortunes in property speculation. From the early nineteenth century, Bellhouse expanded into the construction of complete factories and into work as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Roberts (engineer)
Richard Roberts (22 April 1789 – 11 March 1864) was a Welsh patternmaker and engineer whose development of high-precision machine tools contributed to the birth of production engineering and mass production. Early life Roberts was born at Llanymynech, Powys, on the border between England and Wales. He was the son of William Roberts, a shoemaker who also kept the New Bridge tollgate. Roberts was educated by the parish priest and early found employment with a boatman on the Ellesmere Canal and later at the local limestone quarries. He received some instruction in drawing from Robert Baugh, a road surveyor, who was working under Thomas Telford. Roberts then found employment as a patternmaker at Bradley Iron works, Staffordshire and, probably in 1813, moved to a supervisory position in the pattern shop of the Horseley Ironworks, Tipton. He had gained skills in turning, wheel-wrighting and the repair of millwork. He was drawn for the militia and to avoid this made for Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Ewart
Peter Ewart (14 May 1767 – 15 September 1842) was a British engineer who was influential in developing the technologies of turbines and theories of thermodynamics. Biography He was son of the Church of Scotland minister of Troqueer near Dumfries, and was one of eleven children. His brother Joseph Ewart became British ambassador to Prussia; John, a doctor, became Chief Inspector of East India Company hospitals in India; and William, father of William Ewart, was business partner of Sir John Gladstone, father of William Ewart Gladstone, whose godfather he was and whom he was named after. Following graduation from the University of Edinburgh, he was apprenticed to millwright John Rennie. His work with water wheels led him to work with Matthew Boulton and James Watt for whom by 1790 he was agent in Manchester. At the same time as acting as agent he was also trading on his own account as a millwright, enabling him to provide the complementary shafts, gears and other necessiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |