|
Unified Theory Of Acceptance And Use Of Technology
The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) is a technology acceptance model formulated by Venkatesh and others in "User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view" in the organisational context. The UTAUT aims to explain user intentions to use an information system and subsequent usage behavior. The theory holds that there are four key constructs: 1) performance expectancy, 2) effort expectancy, 3) social influence, and 4) facilitating conditions. The first three are direct determinants of usage intention and behavior, and the fourth is a direct determinant of user behavior. Gender, age, experience, and voluntariness of use are posited to moderate the impact of the four key constructs on usage intention and behavior. The theory was developed through a review and consolidation of the constructs of eight models that earlier research had employed to explain information systems usage behaviour (theory of reasoned action, technology acceptance mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Acceptance Model
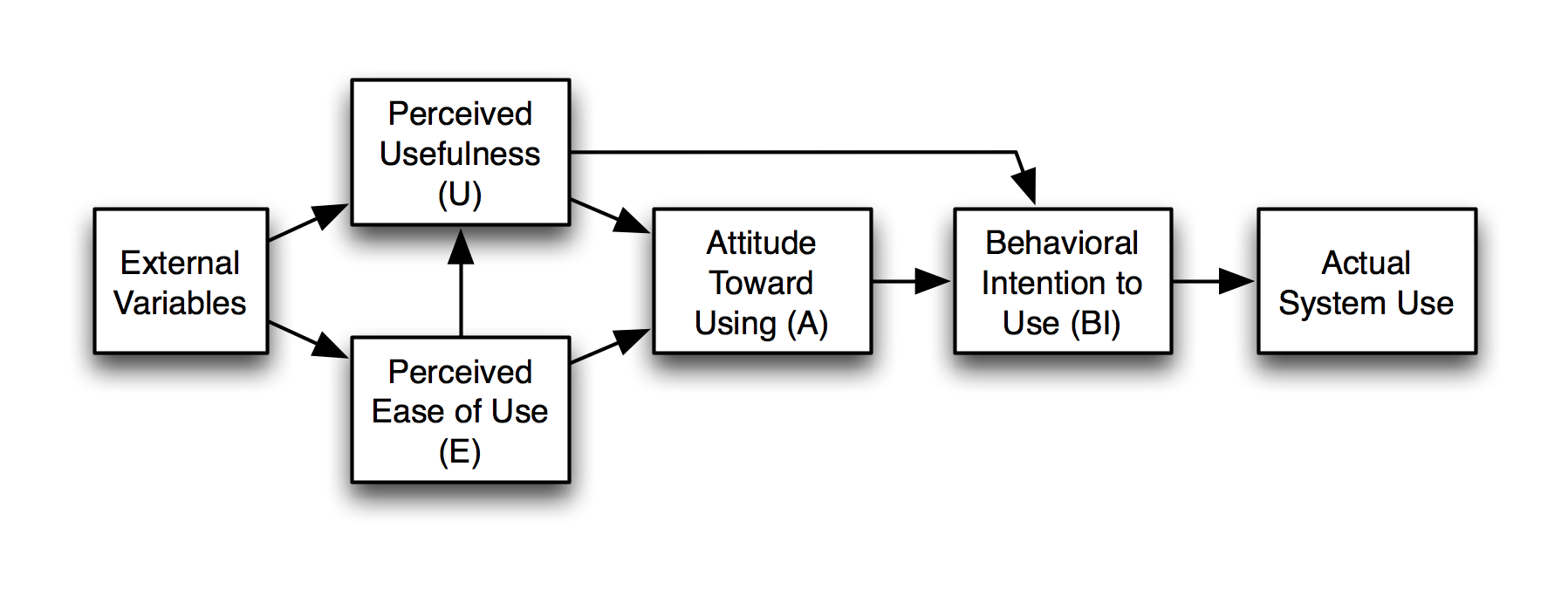
The technology acceptance model (TAM) is an information systems theory that models how users come to accept and use a technology. The ''actual system use'' is the end-point where people use the technology. ''Behavioral intention'' is a factor that leads people to use the technology. The behavioral intention (BI) is influenced by the ''attitude'' (A) which is the general impression of the technology. The model suggests that when users are presented with a new technology, a number of factors influence their decision about how and when they will use it, notably: *''Perceived usefulness'' (PU) – This was defined by Fred Davis as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would enhance their job performance". It means whether or not someone perceives that technology to be useful for what they want to do. *''Perceived ease-of-use'' (PEOU) – Davis defined this as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would be free from effo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Learning
Mobile may refer to: Places * Mobile, Alabama, a U.S. port city * Mobile County, Alabama * Mobile, Arizona, a small town near Phoenix, U.S. * Mobile, Newfoundland and Labrador Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Mobile (band), a Canadian rock band * Mobiles (band), a 1980s British band Other uses in music * ''Mobile'' (album), a 1999 album by Brazilian Paulinho Moska * "Mobile" (song), a 2003 song by Avril Lavigne from ''Let Go'' * "Mobile", a song by Gentle Giant from the album '' Free Hand'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Mobile (sculpture), a kinetic sculpture constructed to take advantage of the principle of equilibrium * ''Mobile'' (TV series), a British ITV drama * "Mobile", a short story by J. G. Ballard, later renamed " Venus Smiles" * Mobile, a feature of the game ''GunBound'' * '' Mobile Magazine'', a publication on portable electronics Military and law enforcement * '' Garde Mobile'', historic French military unit * M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted ''R''2 or ''r''2 and pronounced "R squared", is the proportion of the variation in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable(s). It is a statistic used in the context of statistical models whose main purpose is either the prediction of future outcomes or the testing of hypotheses, on the basis of other related information. It provides a measure of how well observed outcomes are replicated by the model, based on the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model. There are several definitions of ''R''2 that are only sometimes equivalent. In simple linear regression (which includes an intercept), ''r''2 is simply the square of the sample ''correlation coefficient'' (''r''), between the observed outcomes and the observed predictor values. If additional regressors are included, ''R''2 is the square of the '' coefficient of multiple correlation''. In both such cases, the coeffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Acceptance Model
The technology acceptance model (TAM) is an information systems theory that models how users come to accept and use a technology. The ''actual system use'' is the end-point where people use the technology. ''Behavioral intention'' is a factor that leads people to use the technology. The behavioral intention (BI) is influenced by the ''attitude'' (A) which is the general impression of the technology. The model suggests that when users are presented with a new technology, a number of factors influence their decision about how and when they will use it, notably: *''Perceived usefulness'' (PU) – This was defined by Fred Davis as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would enhance their job performance". It means whether or not someone perceives that technology to be useful for what they want to do. *''Perceived ease-of-use'' (PEOU) – Davis defined this as "the degree to which a person believes that using a particular system would be free from effo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsimonious
In philosophy, Occam's razor (also spelled Ockham's razor or Ocham's razor; ) is the problem-solving principle that recommends searching for explanations constructed with the smallest possible set of elements. It is also known as the principle of parsimony or the law of parsimony (). Attributed to William of Ockham, a 14th-century English philosopher and theologian, it is frequently cited as , which translates as "Entities must not be multiplied beyond necessity", although Occam never used these exact words. Popularly, the principle is sometimes paraphrased as "of two competing theories, the simpler explanation of an entity is to be preferred." This philosophical razor advocates that when presented with competing hypothesis, hypotheses about the same prediction and both hypotheses have equal explanatory power, one should prefer the hypothesis that requires the fewest assumptions, and that this is not meant to be a way of choosing between hypotheses that make different predictions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Variables
A variable is considered dependent if it depends on (or is hypothesized to depend on) an independent variable. Dependent variables are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical function), on the values of other variables. Independent variables, on the other hand, are not seen as depending on any other variable in the scope of the experiment in question. Rather, they are controlled by the experimenter. In pure mathematics In mathematics, a function is a rule for taking an input (in the simplest case, a number or set of numbers)Carlson, Robert. A concrete introduction to real analysis. CRC Press, 2006. p.183 and providing an output (which may also be a number). A symbol that stands for an arbitrary input is called an independent variable, while a symbol that stands for an arbitrary output is called a dependent variable. The most common symbol for the input is , and the most common symbol for the output is ; the function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura in 1977. Self-efficacy affects every area of human endeavor. By determining the beliefs a person holds regarding their power to affect situations, self-efficacy strongly influences both the power a person actually has to face challenges competently and the choices a person is most likely to make. These effects are particularly apparent, and compelling, with regard to investment behaviors such as in health, education, and agriculture. A strong sense of self-efficacy promotes human accomplishment and personal well-being. A person with high self-efficacy views challenges as things that are supposed to be mastered rather than threats to avoid. These people are able to recover from failure faster and are more likely to attribute failure to a lack of effort. They approach threatening situatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Internet
The mobile web comprises mobile browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile or other wireless network. History and development Traditionally, the World Wide Web has been accessed via fixed-line services on laptops and desktop computers. However, the web is now more accessible by portable and wireless devices. Early 2010 ITU (International Telecommunication Union) report said that with current growth rates, web access by people on the go via laptops and smart mobile devices was likely to exceed web access from desktop computers within the following five years. In January 2014, mobile internet use exceeded desktop use in the United States. The shift to mobile Web access has accelerated since 2007 with the rise of larger multitouch smartphones, and since 2010 with the rise of multitouch tablet computers. Both platforms provide better Internet access, screens, and mobile browsers, or applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other than their sex assigned at birth. Most cultures use a gender binary, in which gender is divided into two categories, and people are considered part of one or the other;Kevin L. Nadal, ''The Sage Encyclopedia of Psychology and Gender'' (2017, ), p. 401: "Most cultures currently construct their societies based on the understanding of gender binary—the two gender categorizations (male and female). Such societies divide their population based on biological sex assigned to individuals at birth to begin the process of gender socialization." those who are outside these groups may fall under the umbrella term '' non-binary''. Some societies have ''third genders'' (and ''fourth genders'', etc.) such as the hijras of South Asia and two-spirit per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networks
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities along with a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine dynamics of networks. For instance, social network analysis has been used in studying the spread of misinformation on social media platforms or analyzing the influence of key figures in social networks. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant Messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involving simple text message exchanges, modern IM applications and services (also called "social messengers", "messaging apps", "chat apps" or "chat clients") tend to also feature the exchange of multimedia, emojis, file transfer, VoIP (voice calling), and video chat capabilities. Instant messaging systems facilitate connections between specified known users (often using a contact list also known as a "buddy list" or "friend list") or in chat rooms, and can be standalone apps or integrated into a wider social media platform, or in a website where it can, for instance, be used for conversational commerce. Originally the term "instant messaging" was distinguished from " text messaging" by being run on a computer network instead of a cellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its Urbanization by country, highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined Free area of the Republic of China, territories under ROC control consist of list of islands of Taiwan, 168 islands in total covering . The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei (the capital), New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries. Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |