|
Ubiquitin
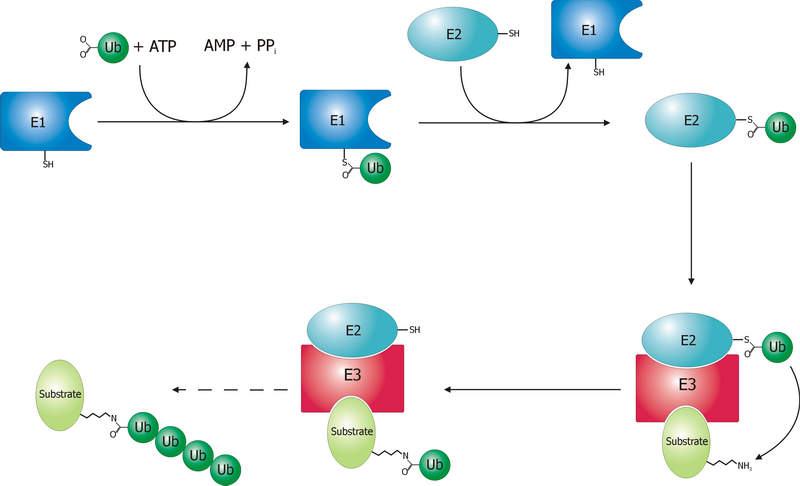
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the 26S proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
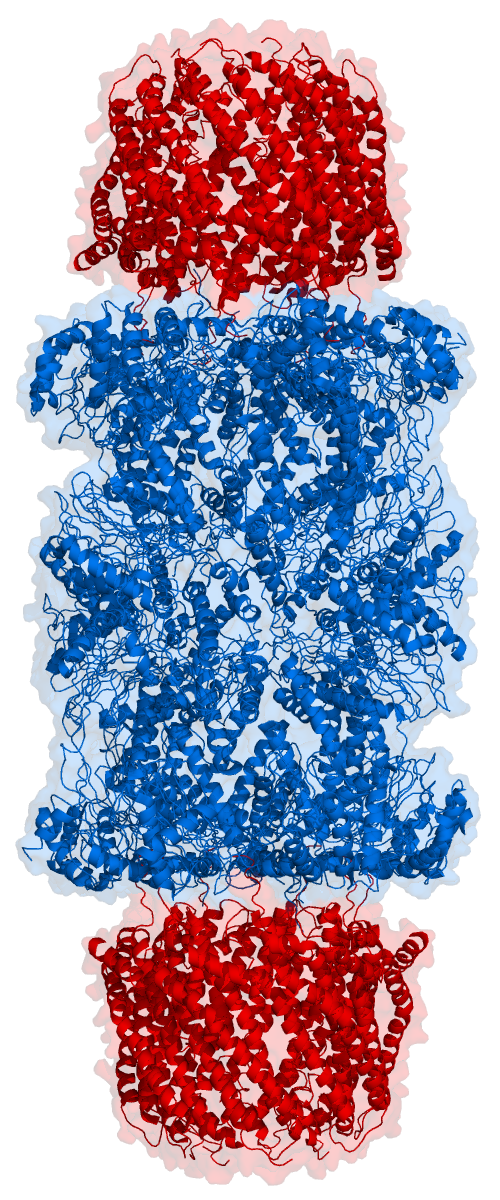
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, proteasomes are located both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation pathway is essential for many cellular processes, including the cell cycle, the regulation of gene expression, and responses to oxidative stress. The importance of proteolytic degradation inside cells and the role of ubiquitin in proteolytic pathways was acknowledged in the award of the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose. The core 20S proteasome (blue in the adjacent figure) is a cylindrical, compartmental protein complex of four stacked rings forming a central pore. Each ring is composed of seven individual proteins. The inner two rings a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another protein (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin C
Polyubiquitin-C is a protein encoded by the ''UBC'' gene in humans. Polyubiquitin-C is one of the sources of ubiquitin, along with UBB, UBA52, and RPS27A. ''UBC'' gene is one of the two stress-regulated polyubiquitin genes (''UBB'' and ''UBC'') in mammals. It plays a key role in maintaining cellular ubiquitin levels under stress conditions. Defects of ''UBC'' gene could lead to mid-gestation embryonic lethality. Structure Gene ''UBC'' gene is located at chromosome 12q24.3, consisting of 2 exons An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence i .... The promoter (genetics), promoter of the ''UBC'' gene contains putative heat shock elements (HSEs), which mediates UBC induction upon stress. ''UBC'' gene differs from ''UBB'' gene in the number of Ub coding units they contain. Nine t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin-activating Enzyme
Ubiquitin-activating enzymes, also known as E1 enzymes, catalyze the first step in the ubiquitination reaction, which (among other things) can target a protein for degradation via a proteasome. This covalent bond of ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like proteins to targeted proteins is a major mechanism for regulating protein function in eukaryotic organisms. Many processes such as cell division, immune responses and embryonic development are also regulated by post-translational modification by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Ubiquitination (ubiquitylation) Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) starts the ubiquitination process (Figure 1). The E1 enzyme, along with ATP, binds to the ubiquitin protein. The E1 enzyme then passes the ubiquitin protein to a second protein, called ubiquitin carrier or conjugation protein (E2). The E2 protein complexes with a ubiquitin protein ligase (E3). This ubiquitin protein ligase recognizes which protein needs to be tagged and catalyzes the transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin B
Ubiquitin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UBB'' gene. Function Ubiquitin is one of the most conserved proteins known in eukaryotic organisms. Ubiquitin is required for Adenosine triphosphate, ATP-dependent, non-lysosome, lysosomal intracellular protein degradation of abnormal proteins and normal proteins with a rapid turnover. Ubiquitin is covalently bound to proteins to be degraded, and presumably labels these proteins for degradation. Ubiquitin also binds to histone H2A in actively transcribed regions but does not cause histone H2A degradation, suggesting that ubiquitin is also involved in regulation of gene expression. This gene consists of three direct repeats of the ubiquitin coding sequence with no spacer sequence. Consequently, the protein is expressed as a polyubiquitin precursor with a final amino acid after the last repeat. Aberrant form of this protein (UBB+1) has been noticed in patients with Alzheimer's disease, Down syndrome, other tauopathy, tauop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopeptide Bond
An isopeptide bond is a type of amide bond formed between a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amino group of another. An isopeptide bond is the linkage between the side chain amino or carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-carboxyl, α-amino group, or the side chain of another amino acid. In a typical peptide bond, also known as eupeptide bond, the amide bond always forms between the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of the second amino acid. Isopeptide bonds are rarer than regular peptide bonds. Isopeptide bonds lead to branching in the primary sequence of a protein. Proteins formed from normal peptide bonds typically have a linear primary sequence. Amide bonds, and thus isopeptide bonds, are stabilized by resonance (electron delocalization) between the carbonyl oxygen, the carbonyl carbon, and the nitrogen atom. The bond strength of an isopeptide bond is similar to that of a peptide due to the similar bonding type. The bond strength of a pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzyme
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, also known as E2 enzymes and more rarely as ''ubiquitin-carrier enzymes'', perform the second step in the ubiquitination reaction that targets a protein for degradation via the proteasome. The ubiquitination process covalently attaches ubiquitin, a short protein of 76 amino acids, to a lysine residue on the target protein. Once a protein has been tagged with one ubiquitin molecule, additional rounds of ubiquitination form a polyubiquitin chain that is recognized by the proteasome's 19S regulatory particle, triggering the adenosine triphosphate, ATP-dependent denaturation (biochemistry), unfolding of the target protein that allows passage into the proteasome's 20S core particle, where proteases degrade the target into short peptide fragments for recycling by the cell (biology), cell. Relationships A ubiquitin-activating enzyme, or E1, first activates the ubiquitin by covalently attaching the molecule to its active site cysteine residue. The activated u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin A-52 Residue Ribosomal Protein Fusion Product 1
60S ribosomal protein L40 (RPL40) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''UBA52'' gene. Function Ubiquitin is a highly conserved nuclear and cytoplasmic protein that has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome. It is also involved in the maintenance of chromatin structure, the regulation of gene expression, and the stress response. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin moiety fused to an unrelated protein. This gene encodes a fusion protein consisting of ubiquitin at the N-terminus and ribosomal protein L40 at the C-terminus The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comp ..., a C-terminal extension protein (CEP). Multiple processed pseudogenes derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPS27A
40S ribosomal protein S27a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RPS27A'' gene. Ubiquitin, a highly conserved protein that has a major role in targeting cellular proteins for degradation by the 26S proteosome, is synthesized as a precursor protein consisting of either polyubiquitin chains or a single ubiquitin fused to an unrelated protein. This gene encodes a fusion protein consisting of ubiquitin at the N terminus and ribosomal protein S27a at the C terminus. When expressed in yeast, the protein is post-translationally processed, generating free ubiquitin monomer and ribosomal protein S27a. Ribosomal protein S27a is a component of the 40S subunit of the ribosome and belongs to the S27AE family of ribosomal proteins. It contains C4-type zinc finger domains and is located in the cytoplasm. Pseudogenes derived from this gene are present in the genome. As with ribosomal protein S27a, ribosomal protein L40 is also synthesized as a fusion protein with ubiquitin; similarly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Degradation
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases. Proteolysis can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein–protein Interaction
Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) are physical contacts of high specificity established between two or more protein molecules as a result of biochemical events steered by interactions that include electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and the hydrophobic effect. Many are physical contacts with molecular associations between chains that occur in a cell or in a living organism in a specific biomolecular context. Proteins rarely act alone as their functions tend to be regulated. Many molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from numerous protein components organized by their PPIs. These physiological interactions make up the so-called Interactome, interactomics of the organism, while aberrant PPIs are the basis of multiple aggregation-related diseases, such as Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, Creutzfeldt–Jakob and Alzheimer's diseases. PPIs have been studied with Methods to investigate protein–protein interactions, many methods and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |