|
Type 92 Machine Gun
The was developed for aerial use for the Imperial Japanese Navy in 1932. The Type 92 is a light machine gun and not to be confused with the similarly named Type 92 heavy machine gun. Description It was the standard hand-held machine gun in multi-place IJN aircraft during the most part of the Pacific War. It proved to be seriously inadequate. Aircraft produced in the later part of the conflict often were equipped with weapons such as Type 1 and Type 2 machine guns or Type 99 cannon. Essentially a copy of the shroudless post-World War I aircraft-mounted version of the British Lewis gun, the Type 92 was fed with a 97-round drum magazine and used on a flexible mount. It was chambered in a Japanese copy of the .303 British cartridge. The main external difference between the two models was the trigger guard, and cooling fins around the barrel and gas piston tube. Neither the post-World War I British aircraft Lewis nor the Japanese copy featured the distinctive thick barrel shroud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) are typically designed more for firing short bursts rather than continuous firepower, and are not considered true machine guns. As a class of military kinetic projectile weapon, machine guns are designed to be mainly used as infantry support weapons and generally used when attached to a bipod or tripod, a fixed mount or a heavy weapons platform for stability against recoils. Many machine guns also use belt feeding and open bolt operation, features not normally found on other infantry firearms. Machine guns can be further categorized as light machine guns, medium machine guns, heavy machine guns, general purpose machine guns and squad automatic weapons. Similar automatic firearms of caliber or more are classified as autocannons, rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyūshū Q1W
The Kyūshū Q1W ''Tokai'' (東海 "Eastern Sea") was a land-based anti-submarine patrol bomber aircraft developed for the Imperial Japanese Navy in World War II. The Allied reporting name was ''Lorna''. Although similar in appearance to the German Junkers Ju 88 medium bomber, the Q1W was a much smaller aircraft with significantly different design details. Design and development The Imperial Japanese Navy ordered development of the Kyūshū Q1W as the Navy Experimental 17-Shi Patrol Plane in September 1942, and the first test flight took place in September 1943. It entered service in January 1945. The Q1W carried two low-power engines, allowing for long periods of low-speed flight. In same period Kyūshū built the K11W1 Shiragiku, a bomber training plane (also used in Kamikaze strikes) and the Q3W1 Nankai (''South Sea''), a specialized antisubmarine version of the K11W. The latter was of all-wood construction and was destroyed during a landing accident on its first flig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Guns Of Japan
A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems. Renaissance natural philosophers identified six simple machines which were the elementary devices that put a load into motion, and calculated the ratio of output force to input force, known today as mechanical advantage. Modern machines are complex systems that consist of structural elements, mechanisms and control components a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Guns
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers VGO
The Vickers K machine gun, known as the Vickers Gas Operated (Vickers G.O.) or Gun, Machine, Vickers G.O. .303-inch in British service, was a rapid-firing machine gun developed and manufactured for use in aircraft by Vickers-Armstrongs. The high rate of fire was needed for the short period of time when the gunner would be able to fire at an attacking aircraft. The weapon was adopted for land use during World War II. Development The Vickers K was a development of the Vickers-Berthier (VB) light machine gun, adopted in 1932 by the Indian Army.Weeks, John, ''World War II Small Arms'', New York: Galahad Books (1979), , p. 88-89 The VB, like the Bren light machine gun, used a locking tilting breechblock. However, unlike the Bren, the VB locked its breech only at the last moment of forward travel and this enabled the development of the Vickers K also known as the "Vickers Gas Operated" (VGO) or "Vickers GO" . With lighter moving parts and the VB locking design, the Vickers K had an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
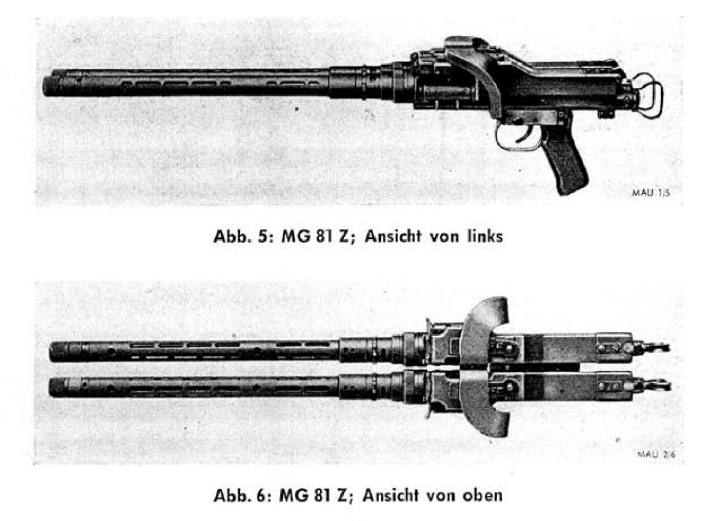
MG 81 Machine Gun
The MG 81 was a German belt fed 7.92×57mm Mauser machine gun which was used in flexible installations in World War II Luftwaffe aircraft, in which capacity it replaced the older drum magazine-fed MG 15. The MG 81 was developed by Mauser as a derivative of their successful MG 34 general-purpose machine gun. Development focus was to reduce production cost and time and to optimize the machine gun for use in aircraft. Developed in 1938/1939, it was in production from 1940 to 1945. A special twin-mount MG 81Z (the Z suffix stands for ''Zwilling'', meaning "twin") was introduced in 1942. It paired up two of the weapons on one mount to provide even more firepower with a maximum cyclic rate of fire of 3,200 rounds per minute without requiring much more space than a standard machine gun. Towards the end of the war many specimens were delivered to the army and equipped for use in ground battles with shoulder rest and bipod. Applications The MG 81Z was found in many unique installations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MG 15 Machine Gun
The MG 15 was a German 7.92 mm machine gun designed specifically as a hand-manipulated defensive gun for combat aircraft during the early 1930s. By 1941 it was replaced by other types and found new uses with ground troops. History The MG 15 was developed from the MG 30, which was designed by Rheinmetall using the locking system invented by Louis Stange in the mid to late 1920s. Though it shares the MG 15 designation with the earlier gun built by Bergmann, the MG 15nA (for ''neuer Art'', meaning new model having been modified from an earlier design) has nothing in common with the World War II gun except the model number. The World War I gun used a tipping lock system while the WWII aircraft gun uses a rotating bolt/lockring. The World War II MG 15 was used in nearly all Luftwaffe aircraft with a flexible-mount defensive position. It was a modular design with various attachments that could be quickly attached or removed. The bolt mechanism acted as a traditional open-bolt ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 89 Machine Gun
Type 89 refers to two unrelated Imperial Japanese Army aircraft machine guns. Its Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service, Imperial Japanese Navy counterparts are the Type 97 aircraft machine gun, Type 97 machine gun (fixed), and Type 92 machine gun, Type 92 machine gun (a Lewis gun copy). Type 89 fixed The first machine gun is a recoil-operated, licensed copy of the Vickers machine gun, Vickers Class E machine gun re-chambered to 7.7x58mmSR Type 89 cartridge, it is referred to as the "fixed type". It was used in synchronized applications in fighter cowls and in wing gun applications. It was Belt (firearm), belt-fed, using a steel link disintegrating belt. The fixed Type 89 was used in the Nakajima Ki-27, Nakajima Ki-43, Ki-43, early Nakajima Ki-44, Ki-44 fighters, the Mitsubishi Ki-30 and Mitsubishi Ki-51, Ki-51 light bombers, the Kawasaki Ki-32 light bomber and various others. Communist forces used some ex-Japanese Type 89s during the Korean War. Type 89 flexible type The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka K5Y
The was a two-seat unequal-span biplane trainer that served in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Due to its bright orange paint scheme (applied to all Japanese military trainers for visibility), it earned the nickname ''"aka-tombo"'', or " red dragonfly", after a type of insect common throughout Japan. A K5Y of the Kamikaze Special Attack Corps 3rd Ryuko Squadron was credited with sinking the destroyer USS ''Callaghan'' on July 28, 1945, the last US warship lost to kamikaze attack during the war. Design and development The aircraft was based on the Yokosuka Navy Type 91 Intermediate Trainer, but stability problems led to a redesign by Kawanishi in 1933. It entered service in 1934 as Navy Type 93 Intermediate Trainer K5Y1 with fixed tail-skid landing gear, and remained in use throughout the war. Floatplane types K5Y2 and K5Y3 were also produced. After the initial 60 examples by Kawanishi, production was continued by Watanabe (556 aircraft built), Mitsubishi ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka B4Y
The Yokosuka B4Y, (Navy Type 96 Carrier Attack Bomber), carrier-borne torpedo bomber was used by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service from 1936 to 1943. The B4Y replaced the Mitsubishi B2M2 and was the last biplane bomber used operationally by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The Allied reporting name was "Jean". Design and development In 1932, the Imperial Japanese Navy issued a requirement for a new carrier-borne attack aircraft. Aichi, Mitsubishi and Nakajima responded to this requirement and each built a prototype. None of these aircraft were deemed satisfactory, and the service thus issued in 1934 a new requirement, 9-''Shi'', for a more capable aircraft to replace the obsolescent Yokosuka B3Y. The B4Y was designed by Sanae Kawasaki at the First Naval Air Technical Arsenal at Yokosuka. Regarded only as an interim type, the Navy wanted a torpedo bomber offering performance comparable to the Mitsubishi A5M monoplane fighter. The result was a biplane with fixed landing ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakajima B6N
The Nakajima B6N ''Tenzan'' ( ja, 中島 B6N 天山, "Heavenly Mountain", World War II Allied names for Japanese aircraft, Allied reporting name: "Jill") was the Imperial Japanese Navy's standard Aircraft carrier, carrier-borne torpedo bomber during the final years of World War II and the successor to the Nakajima B5N, B5N "Kate". Due to its protracted development, a shortage of experienced pilots and the United States Navy's achievement of air superiority by the time of its introduction, the B6N was never able to fully demonstrate its combat potential. Design and development The B5N carrier torpedo-bomber's weaknesses had shown themselves early in the Second Sino-Japanese War and, as well as updating that aircraft, the Imperial Japanese Navy began seeking a faster longer-ranged replacement. In December 1939 it issued a specification to Nakajima for a Navy Experimental ''14-Shi'' Carrier Attack Aircraft capable of carrying the same external weapons load as the B5N. The new plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakajima B5N
The Nakajima B5N ( ja, 中島 B5N, Allied reporting name "Kate") was the standard carrier-based torpedo bomber of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) for much of World War II. Although the B5N was substantially faster and more capable than its Allied counterparts, the American Douglas TBD Devastator monoplane (the U.S. Navy's first all-metal, carrier-borne monoplane of any type with retracting gear), and the British Fairey Swordfish and Fairey Albacore torpedo biplanes, it was nearing obsolescence by 1941. Nevertheless, the B5N operated throughout the whole war, due to the delayed development of its successor, the B6N. In the early part of the Pacific War, when flown by well-trained IJN aircrews and as part of well-coordinated attacks, the B5N achieved particular successes at the battles of Pearl Harbor, Coral Sea, Midway, and Santa Cruz Islands. Design and development The B5N was designed by a team led by Katsuji Nakamura in response to a 1935 specification by the Navy for a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |