|
Trichophyton Rubrum
''Trichophyton rubrum'' is a dermatophytic fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is an exclusively clonal, anthropophilic saprotroph that colonizes the upper layers of dead skin, and is the most common cause of athlete's foot, fungal infection of nail, jock itch, and ringworm worldwide. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' was first described by in 1845 and is currently considered to be a complex of species that comprises multiple, geographically patterned morphotypes, several of which have been formally described as distinct taxa, including ''T. raubitschekii'', ''T. gourvilii'', ''T. megninii'' and ''T. soudanense''. Growth and morphology Typical isolates of ''T. rubrum'' are white and cottony on the surface. The colony underside is usually red, although some isolates appear more yellowish and others more brownish. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' grows slowly in culture with sparse production of teardrop or peg-shaped microconidia laterally on fertile hyphae. Macroconidia, when present, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
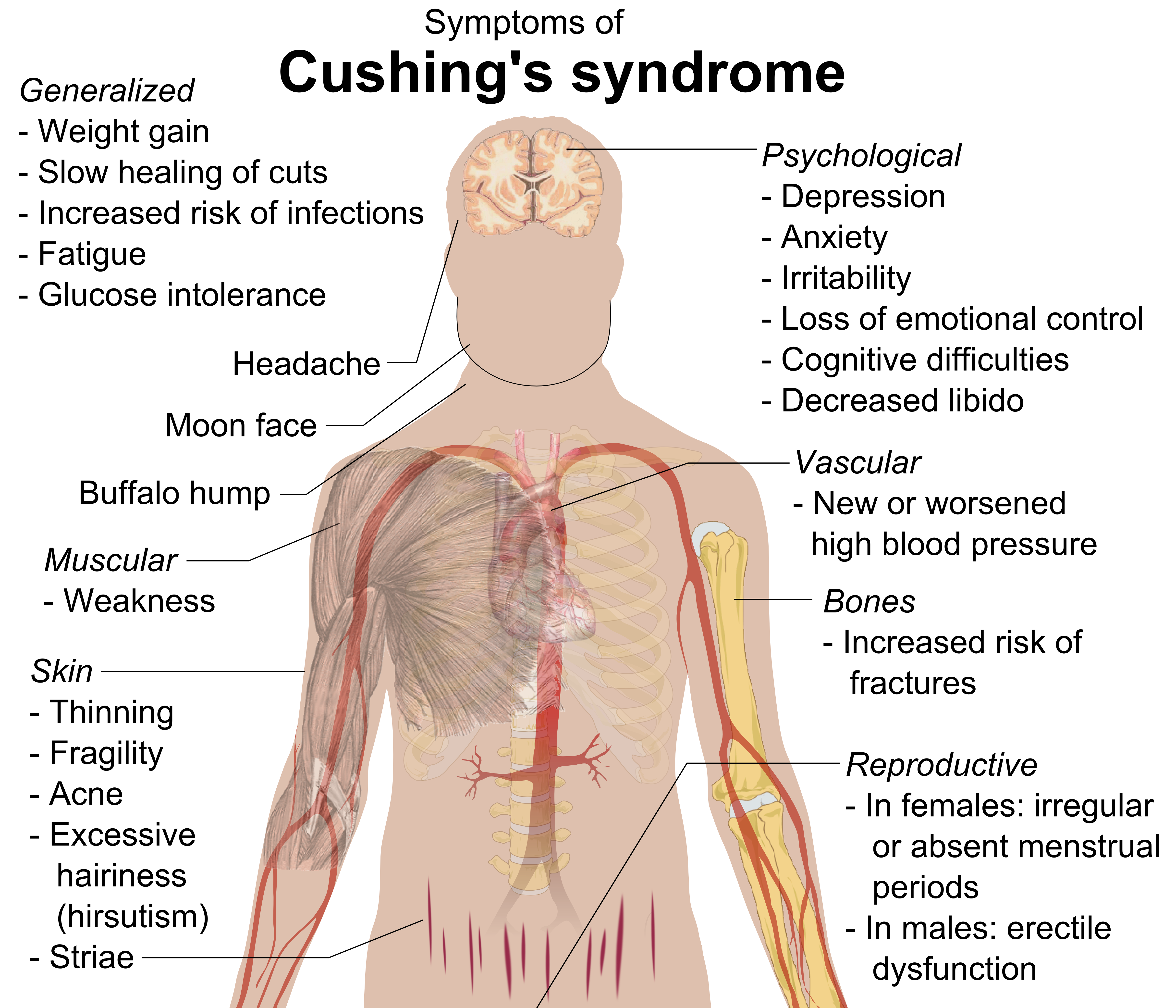
Cushing Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ectopic due to their placement outside the pituitary, may also cause Cushing's. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments. Definition In pathology, a granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages. In medical practice, doctors occasionally use the term ''granuloma'' in its more literal meaning: "a small nodule". Since a small nodule can represent any tissue from a harmless nevus to a malignant tumor, this use of the term is not very specific. Examples of this use of the term ''granuloma'' are the lesions known as vocal cord granuloma (known as contact granuloma), pyogenic granuloma, and intubation granuloma, all of which are examples of granulation tissue, not granulomas. "Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma" is a lesion characteriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head. Although acne can often involve superficial infection and inflammation of some hair follicles, the condition of those follicles is usually not called folliculitis, as that term is usually reserved for the separate set of disease entities comprising infected and inflamed hair follicles with causes other than acne. Signs and symptoms * Rash (reddened skin area) * Itching skin * Pimples or pustules located around a hair or follicle; may be confused with chicken pox ** May crust over ** Typically occur on neck, armpit, or groin ** May present as genital lesions * Spreading from leg to arm to body through improper treatment with antibiotics File:Sebaceaous Hyperplasia Chronic folliculits Right Mid Chest.jpg, Chronic folliculitis surround ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoscytalidium Dimidiatum
''Neoscytalidium dimidiatum'' was first described in 1933 as ''Hendersonula toruloidea'' from diseased orchard trees in Egypt. Decades later, it was determined to be a causative agent of human dermatomycosis-like infections and foot infections predominantly in the tropical areas; however the fungus is considered to be widespread. A newer name, ''Scytalidium dimidiatum'', was applied to synanamorph of ''Nattrassia mangiferae'', otherwise known as ''Neofusicoccum mangiferae''. Substantial confusion has arisen in the literature on this fungus resulting from the use of multiple different names including: ''Torula dimidiata'', ''Scytalidium dimidiatum'', ''Fusicoccum dimidiatum'', and ''Hendersonula toruloidea''. History and taxonomy In 1933, British mycologist Dr. Rolland Marshall Nattrass described an arthroconidial asexual fungus that he named ''H. toruloidea'' that was responsible for causing die-back disease of plum, apricot and apple trees in Egypt. At the time, he recognized tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urease
Ureases (), functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous bacteria, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates, as well as in soils, as a soil enzyme. They are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high molecular weight. These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia: : (NH2)2CO + H2O CO2 + 2NH3 The hydrolysis of urea occurs in two stages. In the first stage, ammonia and carbamic acid are produced. The carbamate spontaneously and rapidly hydrolyzes to ammonia and carbonic acid. Urease activity increases the pH of its environment as ammonia is produced, which is basic. History Its activity was first identified in 1876 by Frédéric Alphonse Musculus as a soluble ferment. In 1926, James B. Sumner, showed that urease is a protein by examining its crystallized form. Sumner's work was the first demonstration that a protein can function as an enzyme and led eventually to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC. Histidine was first isolated by Albrecht Kossel and Sven Gustaf Hedin in 1896. It is also a precursor to histamine, a vital inflammatory agent in immune responses. The acyl radical is histidyl. Properties of the imidazole side chain The conjugate acid (protonated form) of the imidazole side chain in histidine has a p''K''a of approximately 6.0. Thus, below a pH of 6, the imidazole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxotrophy
Auxotrophy ( grc, αὐξάνω "to increase"; ''τροφή'' "nourishment") is the inability of an organism to synthesize a particular organic compound required for its growth (as defined by IUPAC). An auxotroph is an organism that displays this characteristic; ''auxotrophic'' is the corresponding adjective. Auxotrophy is the opposite of prototrophy, which is characterized by the ability to synthesize all the compounds needed for growth. Prototrophic cells (also referred to as the 'wild type') are self sufficient producers of all required metabolites (e.g. amino acids, lipids, cofactors), while auxotrophs require to be on medium with the metabolite that they cannot produce. For example saying a cell is methionine auxotrophic means that it would need to be on a medium containing methionine or else it would not be able to replicate. In this example this is because it is unable to produce its own methionine (methionine auxotroph). However, a prototroph or a methionine prototrophic ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Unguium
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the ''Trichophyton'', ''Microsporum'', or ''Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Pedis
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the ''Trichophyton'', ''Microsporum'', or ''Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Capitis
Tinea capitis (also known as "herpes tonsurans", "ringworm of the hair", "ringworm of the scalp", "scalp ringworm", and "tinea tonsurans") is a cutaneous fungal infection (dermatophytosis) of the scalp. The disease is primarily caused by dermatophytes in the genera ''Trichophyton'' and '' Microsporum'' that invade the hair shaft. The clinical presentation is typically single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a 'black dot' pattern (often with broken-off hairs), that may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching. Uncommon in adults, tinea capitis is predominantly seen in pre-pubertal children, more often boys than girls. At least eight species of dermatophytes are associated with tinea capitis. Cases of ''Trichophyton'' infection predominate from Central America to the United States and in parts of Western Europe. Infections from ''Microsporum'' species are mainly in South America, Southern and Central Europe, Africa and the Middle East. The dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |