|
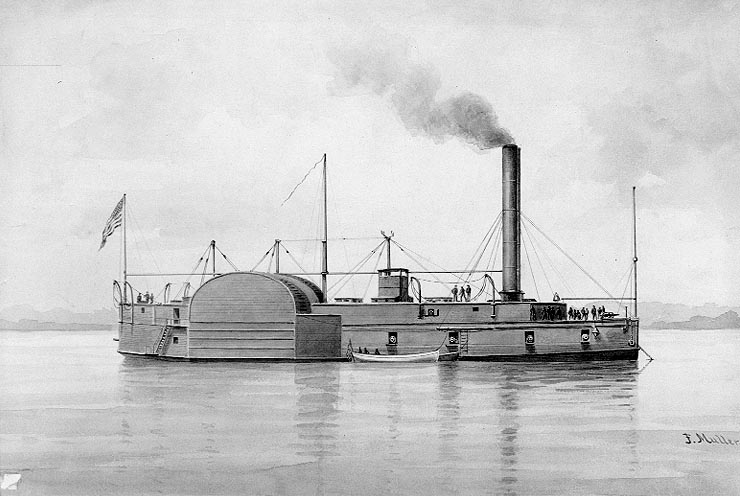
Timberclad Warship
A timberclad warship is a kind of mid 19th century river gunboat. They were based upon a similar design as ironclad warships but had timber in place of iron to act as ablative armour. See also *Cottonclad warship *Battle of Fort Henry The Battle of Fort Henry was fought on February 6, 1862, in Stewart County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. It was the first important victory for the Union and Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant in the Western Theater. On February 4 and ... * USS ''Conestoga'' (1861) * USS ''Essex'' (1856) * USS ''Lexington'' (1861) * USS ''Tyler'' (1857) References Further reading * External linksCivil War Warship Types Ship types {{AmericanCivilWar-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad Warship
An ironclad is a steam-propelled warship protected by iron or steel armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859 - narrowly pre-empting the British Royal Navy. They were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when ironclads operated against wooden ships and, in a historic confrontation, against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and coastal defense ships. Rapid development of warship design in the late 19th century transformed the ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablative Armour
Ablative armor is armor which prevents damage through the process of ablation, the removal of material from the surface of an object by vaporization, chipping, or other erosive processes. In contemporary spacecraft, ablative plating is most frequently seen as an ablative heat shield for a vehicle that must enter atmosphere from orbit, such as on nuclear warheads, or space vehicles like the Mars Pathfinder probe. A large amount of developmental usage was on the early 1960s rocket powered X-15 crewed aircraft traveling at hypersonic speeds in excess of Mach 6.5 (roughly 5,000 mph). The idea is also commonly encountered in science fiction. In recent years, the concept has had widespread usage in robot combat as a method of reducing impact energy transfer to vital components. Ablative armor is distinct from the concept of reactive armor which is actually in common use in modern armored vehicles. Uses in fiction ''Star Trek'' Ablative hull armor appears frequently in the ''St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cottonclad Warship
Cottonclads were a classification of steam-powered warships where a wooden ship was protected from enemy fire by bales of cotton lining its sides. Cottonclads were prevalent during the American Civil War, particularly in the Confederate States Navy for riverine and coastal service such as in the battles of Memphis, Galveston, and Sabine Pass. Confederate tactics generally had cottonclads, which were outgunned by Union warships, steam at full speed towards enemy vessels, relying on the cotton to absorb fire. Once they were within firing range, they would open fire, and, if possible, ram or board the enemy. Conversion Around 1863, Confederate Commander John B. Magruder realized that Texas did not possess the funding and resources—such as iron mills—to produce impressive and potent vessels such as the ironclad CSS Virginia, thus inspiring the development of a new type of warship, later classified as a cottonclad warship. Cottonclads were various kinds of steamboats transformed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fort Henry
The Battle of Fort Henry was fought on February 6, 1862, in Stewart County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. It was the first important victory for the Union and Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant in the Western Theater. On February 4 and 5, Grant landed two divisions just north of Fort Henry on the Tennessee River. (The troops serving under Grant were the nucleus of the Union's successful Army of the Tennessee, although that name was not yet in use.) Grant's plan was to advance upon the fort on February 6 while it was being simultaneously attacked by Union gunboats commanded by Flag Officer Andrew Hull Foote. A combination of accurate and effective naval gunfire, heavy rain, and the poor siting of the fort, nearly inundated by rising river waters, caused its commander, Brig. Gen. Lloyd Tilghman, to surrender to Foote before the Union Army arrived. The surrender of Fort Henry opened the Tennessee River to Union traffic south of the Alabama border. In the days following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Conestoga (1861)
USS ''Conestoga'' was originally a civilian side-wheel towboat built at Brownsville, Pennsylvania, in 1859. She was acquired by the U.S. Army in June 1861 and converted to a 572-ton " timberclad" river gunboat for use by the Western Gunboat Flotilla, with officers provided by the navy. Civil War service ''Conestoga'''s first combat action took place in September 1861 when she engaged CSS ''Jackson'' near Lucas Bend, Kentucky. Other skirmishes punctuated the routine of river patrol service into 1862. In February, she participated in an expedition up the Tennessee River that led to the capture of Forts Henry and Donelson. Later in the month, she saw action at Columbus, Kentucky, a Confederate strongpoint on the Mississippi River. During the rest of her service, ''Conestoga'' continued to operate along the rivers. She took part in the bombardment of Saint Charles, Arkansas, in June 1862 and was formally transferred to the navy in October of that year. In April and July 1863, she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Essex (1856)
USS ''Essex'' was a 1000-ton ironclad river gunboat of the United States Army and later United States Navy during the American Civil War. It was named for Essex County, Massachusetts. USS ''Essex'' was originally constructed in 1856 at New Albany, Indiana as a steam-powered ferry named ''New Era''. Service in Tennessee In September 1861 ''New Era'' was purchased by the United States Army for use in its Western Gunboat Flotilla and was modified into a 355-ton timberclad gunboat. In November 1861 USS ''New Era'' took part in an expedition up the Cumberland River. Shortly thereafter she was renamed USS ''Essex'' and received an upgrade to iron armor and various other alterations. On 11 January 1862, USS ''Essex'' engaged Confederate States Navy gunboats near Lucas Bend, Missouri. On 6 February 1862, she took part in the attack on Fort Henry, Tennessee and was badly damaged by Confederate gunfire. Battling the CSS ''Arkansas'' Commanding officer William D. Porter upgraded his sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Lexington (1861)
The third USS ''Lexington'' was a timberclad gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. Purchase and conversion ''Lexington'' was built as a sidewheel steamer at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, in 1861 and was purchased by the War Department and converted into a gunboat at Cincinnati, Ohio, under the direction of Commander John Rodgers. The gunboat, operated by the navy, joined the army's Western Flotilla at Cairo, Illinois, 12 August 1861. On 22 August, she seized steamer ''W. B. Terry'' at Paducah, Kentucky, and on 4 September, with , she engaged Confederate gunboat ''Jackson'' and southern shore batteries at Hickman and Columbus, Kentucky. On 6 September, the two gunboats spearheaded General Ulysses S. Grant's drive to seize strategic Paducah and Smithland, Kentucky, at the mouths of the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers. In his first use of strength afloat, Grant countered a Confederate move into the state, helping preserve Kentucky for the Union and fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Tyler (1857)
USS ''Tyler'' was originally a merchant ship named ''A. O. Tyler'', a commercial side-wheel steamboat with twin stacks and covered paddles positioned aft. Constructed in Cincinnati, Ohio in 1857, it was acquired by the United States Navy, 5 June 1861 for service in the American Civil War and converted into the gunboat USS ''Tyler'' on 5 June 1861. She was commissioned in September 1861. She was protected with thick wooden bulwarks. Before military acquisition Just four days after Mississippi's secession, on the evening of 13 January 1861, the steamboat was fired upon by cannon used by militia defending Vicksburg. On the Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers ''Tyler'' served in the Western Flotilla from June 1861 to 1 October 1862, fighting for the Mississippi River. Soon after being commissioned, ''Tyler'' participated in the attack on the Confederate forces in Hickman and Columbus in Kentucky, doing battle with the CSS ''Jackson''. In November 1861, ''Tyler'' escorted troops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |