|
Tela Choroidea
The tela choroidea (or tela chorioidea) is a region of meningeal pia mater that adheres to the underlying ependyma, and gives rise to the choroid plexus in each of the brain’s four ventricles. ''Tela'' is Latin for ''woven'' and is used to describe a web-like membrane or layer. The tela choroidea is a very thin part of the loose connective tissue of pia mater overlying and closely adhering to the ependyma. It has a rich blood supply. The ependyma and vascular pia mater – the tela choroidea, form regions of minute projections known as a choroid plexus that projects into each ventricle. The choroid plexus produces most of the cerebrospinal fluid of the central nervous system that circulates through the ventricles of the brain, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space. The tela choroidea in the ventricles forms from different parts of the roof plate in the development of the embryo. Structure In the lateral ventricles the tela choroidea–a double-layere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microanatomy The chor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fornix Of Brain
The fornix (from lat, fornix, lit=arch) is a C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that acts as the major output tract of the hippocampus. The fornix also carries some afferent fibers to the hippocampus from structures in the diencephalon and basal forebrain. The fornix is part of the limbic system. While its exact function and importance in the physiology of the brain are still not entirely clear, it has been demonstrated in humans that surgical transection—the cutting of the fornix along its body—can cause memory loss. There is some debate over what type of memory is affected by this damage, but it has been found to most closely correlate with recall memory rather than recognition memory. This means that damage to the fornix can cause difficulty in recalling long-term information such as details of past events, but it has little effect on the ability to recognize objects or familiar situations. Structure The fibers begin in the hippocampus on each side of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Cerebral Veins
The internal cerebral veins (deep cerebral veins) drain the deep parts of the hemisphere and are two in number; each internal cerebral vein is formed near the interventricular foramina by the union of the superior thalamostriate vein and the superior choroid vein. They run backward parallel with one another, between the layers of the tela chorioidea of the third ventricle, and beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum, where they unite to form a short trunk, the great cerebral vein of Galen; just before their union each receives the corresponding basal vein The basal vein is a vein in the brain. It is formed at the anterior perforated substance by the union of * (a) a ''small anterior cerebral vein'' which accompanies the anterior cerebral artery and supplies the medial surface of the frontal lobe b .... References External links Diagram at radnet.ucla.edu* http://neuroangio.org/venous-brain-anatomy/deep-venous-system/ Veins of the head and neck {{circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is the largest branch of the vertebral artery. It is one of the three main arteries that supply blood to the cerebellum, a part of the brain. Blockage of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery can result in a type of stroke called lateral medullary syndrome. Course It winds backward around the upper part of the medulla oblongata, passing between the origins of the vagus nerve and the accessory nerve, over the inferior cerebellar peduncle to the undersurface of the cerebellum, where it divides into two branches. The medial branch continues backward to the notch between the two hemispheres of the cerebellum; while the lateral supplies the under surface of the cerebellum, as far as its lateral border, where it anastomoses with the anterior inferior cerebellar and the superior cerebellar branches of the basilar artery. Branches from this artery supply the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle. Clinical significance A disrupted blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ependymal Cell
The ependyma is the thin neuroepithelial ( simple columnar ciliated epithelium) lining of the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. The ependyma is one of the four types of neuroglia in the central nervous system (CNS). It is involved in the production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and is shown to serve as a reservoir for neuroregeneration. Structure The ependyma is made up of ependymal cells called ependymocytes, a type of glial cell. These cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, which become filled with cerebrospinal fluid. These are nervous tissue cells with simple columnar shape, much like that of some mucosal epithelial cells. Early monociliated ependymal cells are differentiated to multiciliated ependymal cells for their function in circulating cerebrospinal fluid. The basal membranes of these cells are characterized by tentacle-like extensions that attach to astrocytes. The apical side is cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle, a thick rope-like strand situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle and the roots of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with the cerebellum, and comprises the juxtarestiform body and restiform body. Important fibers running through the inferior cerebellar peduncle include the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and axons from the inferior olivary nucleus, among others. Function The inferior cerebellar peduncle carries many types of input and output fibers that are mainly concerned with integrating proprioceptive sensory input with motor vestibular functions such as balance and posture maintenance. It consists of the following fiber tracts entering cerebellum: * Posterior spinocerebellar tract: unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower part of trunk and lower limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to Motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in Fine motor skill, fine movement, Equilibrioception, equilibrium, Human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. Anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
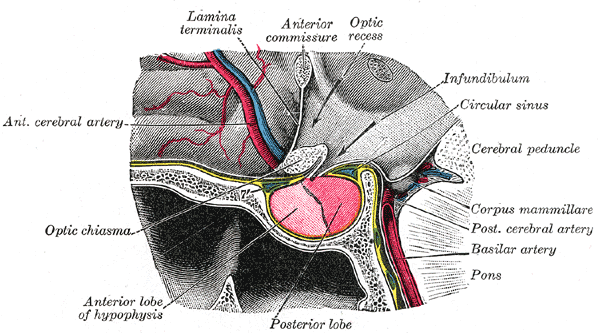
Third Ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ventricles, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Running through the third ventricle is the interthalamic adhesion, which contains thalamic neurons and fibers that may connect the two thalami. Structure The third ventricle is a narrow, laterally flattened, vaguely rectangular region, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, and lined by ependyma. It is connected at the superior anterior corner to the lateral ventricles, by the interventricular foramina, and becomes the cerebral aqueduct (''aqueduct of Sylvius'') at the posterior caudal corner. Since the interventricular foramina are on the lateral edge, the corner of the third ventricle itself forms a bulb, known as the ''anterior recess'' (it is also known as the ''bulb of the ventricl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Ventricles
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively. Each lateral ventricle resembles a C-shaped cavity that begins at an inferior horn in the temporal lobe, travels through a body in the parietal lobe and frontal lobe, and ultimately terminates at the interventricular foramina where each lateral ventricle connects to the single, central third ventricle. Along the path, a posterior horn extends backward into the occipital lobe, and an anterior horn extends farther into the frontal lobe. Structure Each lateral ventricle takes the form of an elongated curve, with an additional anterior-facing continuation emerging inferiorly from a point near the posterior end of the curve; the junction is known as the ''trigone of the lateral ventricle''. The centre of the superior curve is referred to as the ''body'', while the three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |