|
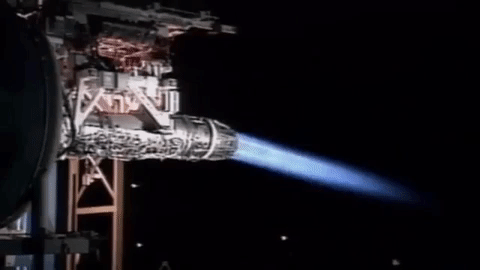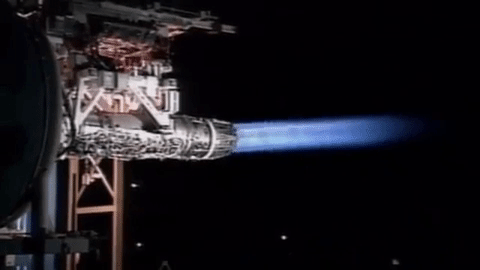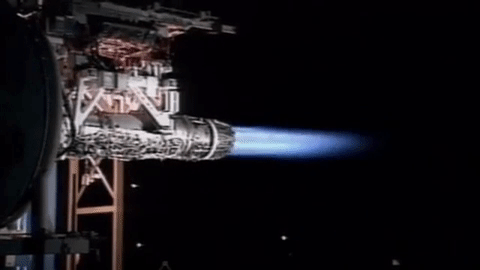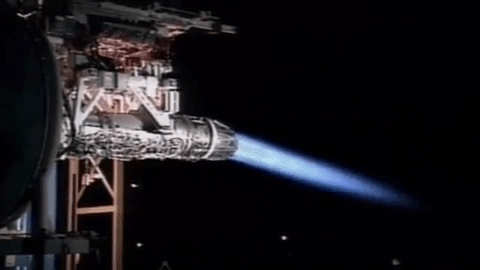
Type 07 VL-ASROC
The is a Japanese ship-launched anti-submarine missile. Description In fiscal year 1991, the Japanese began developing an extended-range version of the RUR-5 ASROC to exploit the greater direct-path range of the new low-frequency OQS-XX and OQS-2x sonar systems. Following the end of the Cold War, this new anti-submarine missile yielded a complete improvement over prior systems, including not only simple range extension but also an improvement in responsiveness. The missile is fired from Mark 41 vertical launching systems and is capable of reaching supersonic speeds. It is controlled by an inertial guidance system and uses thrust vectoring. Its maximum range is said to be over . Operators ; :- :- :- See also * List of missiles by country#Japan * RUM-139 VL-ASROC * SMART ''SMart'' was a British CBBC television programme based on art, which began in 1994 and ended in 2009. The programme was recorded at BBC Television Centre in London. Previously it had been recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-submarine Missile
An anti-submarine missile is a standoff missile, standoff anti-submarine weapon, often a specialized variant of anti-ship missile. Anti-submarine missiles usually include a jet engine, jet or rocket engine, rocket engine and a warhead aimed directly at a submarine. In these missiles, a torpedo or a depth charge is used as a warhead. The anti-submarine missile can be either a cruise missile or a ballistic missile. History Depth charges were the earliest weapons designed for use by ships against submerged submarines. These explosives were initially dropped as the ship moved over the presumed location of a submarine. Before World War II, shipboard sonar was unable to maintain contact with a submarine at close range. Various mortar (weapon), mortar-type projectors, including hedgehog (weapon), Hedgehog and squid (weapon), Squid, were devised during World War II to allow a ship to maintain sonar contact while lobbing explosive charges toward the submarine. During the Cold War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term ''Cold war (term), cold war'' is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in regional conflicts known as proxy wars. In addition to the struggle for ideological and economic influence and an arms race in both conventional and Nuclear arms race, nuclear weapons, the Cold War was expressed through technological rivalries such as the Space Race, espionage, propaganda campaigns, Economic sanctions, embargoes, and sports diplomacy. After the end of World War II in 1945, during which the US and USSR had been allies, the USSR installed satellite state, satellite governments in its occupied territories in Eastern Europe and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMART (missile)
SMART (supersonic missile assisted release of torpedo) is a canister-based, long-range supersonic anti-submarine missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the Indian Navy. Description SMART is a canisterised hybrid system, made up of a long-range missile carrier that can travel at supersonic speed and a lightweight torpedo as payload, for anti-submarine warfare (ASW) role. The objective behind the project was to develop a quick-reaction system that can launch torpedoes from standoff distance. The missile has a range of 643 km (400 mi) carrying a light weight torpedo of range 20 km (12.5 mi) with 50 kg high explosive warhead. SMART uses two-way data link connected to airborne or ship based submarine detection and identification systems. SMART can be launched from a surface ship or a truck-based coastal battery. The missile delivery system was developed jointly by Defence Research Development Laboratory (DRDL) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RUM-139 VL-ASROC
The RUM-139 Vertical-Launch Anti-Submarine Rocket (VL-ASROC or VLA) is an anti-submarine missile in the ASROC family, currently built by Lockheed Martin for the U.S. Navy. History Design and development of the missile began in 1983 when Goodyear Aerospace was contracted by the U.S. Navy to develop a ship-launched anti-submarine missile compatible with the new Mark 41 vertical launching system (VLS). The development of the VLS ASROC underwent many delays, and it was not deployed on any ships until 1993. During this development, Goodyear Aerospace was bought by Loral Corporation in 1986, and this defense division was in turn purchased by Lockheed Martin in 1995. The first VLS ASROC missile was an RUR-5 ASROC with an upgraded solid-fuel booster section and a digital guidance system. It carries a lightweight Mark 46 homing torpedo that is dropped from the rocket at a precalculated point on its trajectory, and then parachuted into the sea. The vertical launch missile first beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missiles By Country
This list of missiles by country displays the names of missiles in order of the country where they originate (were developed), with the countries listed alphabetically and annotated with their continent (and defence alliance, if applicable). In cases where multiple nations have developed or produced a missile, it is listed under each significantly participating nation. Within the lists of each country, missiles are ordered by designation and/or calling name (the latter being especially relevant for Russian/Soviet missiles). In some cases multiple listings are used, in order to provide cross-references for easier navigation. This is a list of missiles developed by a particular country; a list of military rockets. Anti-tank missiles are listed elsewhere. For an alphabetical list by missile name, see the list of missiles. Argentina * ''Alacrán'' (a short-range exploratory development based on the Condor I program) * AS-25K anti-ship missile (AShM), air-to-surface missile ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Vectoring
Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to Aircraft flight control system, control the Spacecraft attitude control, attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle. In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic Flight control surfaces, control surfaces are ineffective, so thrust vectoring is the primary means of Flight dynamics (fixed-wing aircraft), attitude control. Exhaust vanes and Gimbaled thrust, gimbaled engines were used in the 1930s by Robert H. Goddard, Robert Goddard. For aircraft, the method was originally envisaged to provide upward vertical thrust as a means to give aircraft vertical (VTOL) or short (STOL) takeoff and landing ability. Subsequently, it was realized that using vectored thrust in combat situations enabled aircraft to perform various maneuvers not available to conventional-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic Speed
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach number, Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2. Sounds are traveling vibrations in the form of pressure waves in an elastic medium. Objects move at supersonic speed when the objects move faster than the speed at which sound propagates through the medium. In gases, sound travels longitudinally at different speeds, mostly depending on the molecular mass and temperature of the gas, and pressure has little effect. Since air temperature and composition varies significantly with altitude, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |