|
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors on other cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, a family of transmembrane proteins that are cytokines, chemical messengers of the immune system. Excessive production of TNF plays a critical role in several inflammatory diseases, and TNF-blocking drugs are often employed to treat these diseases. TNF is produced primarily by macrophages but is also produced in several other cell types, such as T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and mast cells. It is produced rapidly in response to pathogens, cytokines, and environmental stressors. TNF is initially produced as a type II transmembrane protein (tmTNF), which is then cleaved by TNF alpha converting enzyme (TACE) into a soluble form (sTNF) and secreted from the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy biological tissue, tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use humoral immunity, molecules and cell-mediated immunity, cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against bacteriophage, viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
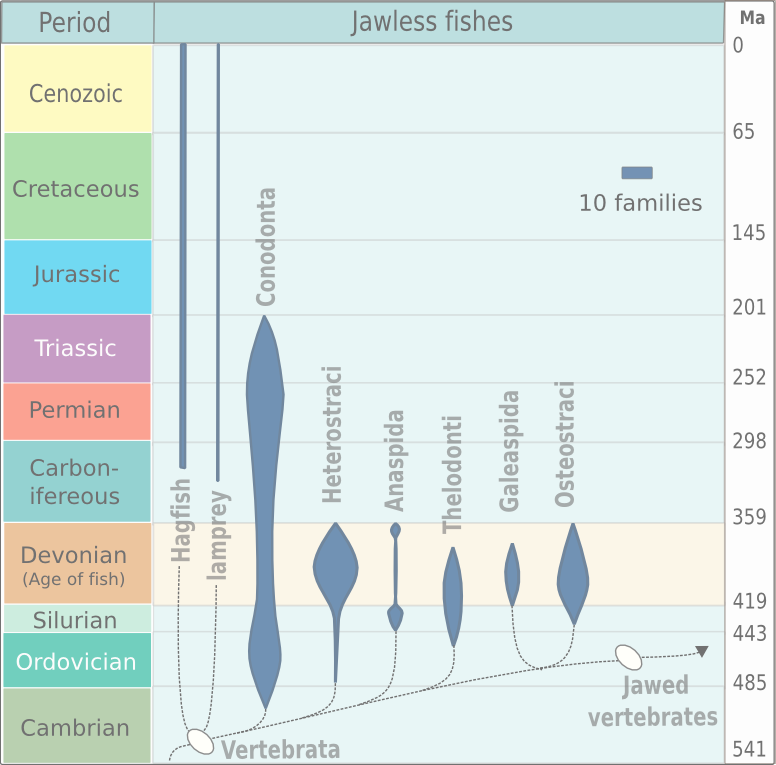
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphotoxin Beta
Lymphotoxin-beta (LT-beta) formerly known as tumor necrosis factor C (TNF-C) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LTB'' gene. Function Lymphotoxin beta is a type II membrane protein of the TNF family. It anchors lymphotoxin-alpha to the cell surface through heterotrimer formation. The predominant form on the lymphocyte surface is the lymphotoxin-alpha 1/beta 2 complex (e.g. 1 molecule alpha/2 molecules beta) and this complex is the primary ligand for the lymphotoxin-beta receptor. The minor complex is lymphotoxin-alpha 2/beta 1. LTB is an inducer of the inflammatory response system and involved in normal development of lymphoid tissue. Lymphotoxin-beta isoform b is unable to complex with lymphotoxin-alpha suggesting a function for lymphotoxin-beta which is independent of lymphotoxin-alpha. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Pro-tumorigenic function of membrane LT is clearly established: mice with overexpression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as Endothelium, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. Due to their size, cytokines cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm and therefore typically exert their functions by interacting with specific cytokine receptor, cytokine receptors on the target cell surface. Cytokines are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral immunity, humoral and cell-mediated immunity, cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and responsiveness of particular cell populations. Some cytokines enhance or inhibit the action of other cytokines in complex way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphotoxin Alpha
Lymphotoxin-alpha (LT-α) formerly known as tumor necrosis factor-beta (TNF-β) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LTA'' gene. Belonging to the hematopoietic cell line, LT-α exhibits anti-proliferative activity and causes the cellular destruction of tumor cell lines. As a cytotoxic protein, LT-α performs a variety of important roles in immune regulation depending on the form that it is secreted as. Unlike other members of the TNF superfamily, LT-α is only found as a soluble homotrimer, when found at the cell surface it is found only as a heterotrimer with LTβ. LT-α has a significant impact on the maintenance of the immune system including the development of secondary lymphoid organs. Absence of LT-α leads to the disruption of gastrointestinal development, prevents Peyer's patch development, and results in a disorganized spleen. As a signaling molecule, LT-α is involved in the regulation of cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. LT- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNF Inhibitor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors on other cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, a family of transmembrane proteins that are cytokines, chemical messengers of the immune system. Excessive production of TNF plays a critical role in several inflammatory diseases, and TNF-blocking drugs are often employed to treat these diseases. TNF is produced primarily by macrophages but is also produced in several other cell types, such as T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and mast cells. It is produced rapidly in response to pathogens, cytokines, and environmental stressors. TNF is initially produced as a type II transmembrane protein (tmTNF), which is then cleaved by TNF alpha converting enzyme (TACE) into a soluble form (sTNF) and secreted from the cell. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural architecture. Lipopolysaccharides are large molecules consisting of three parts: an outer core polysaccharide termed the O-antigen, an inner core oligosaccharide and Lipid A (from which toxicity is largely derived), all covalently linked. In current terminology, the term endotoxin is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins (in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by '' Bacillus thuringiensis''. Lipopolysaccharides can have substantial impacts on human health, primarily through interactions with the immune system. LPS is a potent activator of the immune sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Coley
William Bradley Coley (January 12, 1862 – April 16, 1936) was an American bone surgeon and cancer researcher best known for his early contributions to the study of cancer immunotherapy, specifically causing infection as a way to fight cancer, a practice used as far back as 1550 BC. Coley is recognized as the ''Father of Cancer Immunotherapy'' for his contributions to the science. Early life and career Education William Coley was born on January 12, 1862, in Saugatuck, a neighborhood of Westport, Connecticut. His parents were Horace Bradley Coley and Clarina B. Wakeman. He received his bachelor's degree in Classics from Yale University and his medical degree from Harvard Medical School in 1888. After his schooling, Coley began working at New York Hospital, now Weill Cornell Medical Center, as a surgical intern. Early sarcoma patients In 1890, Coley began his first year of private practice at New York Hospital and met Elizabeth (Bessie) Dashiell, a 17-year-old patient who would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Fibrosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced with scar tissue ( fibrosis) and regenerative nodules as a result of chronic liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue and nodules of regenerating hepatocytes can replace the parenchyma, causing increased resistance to blood flow in the liver's capillaries—the hepatic sinusoids—and consequently portal hypertension, as well as impairment in other aspects of liver function. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Stages include compensated cirrhosis and decompensated cirrhosis. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |