|
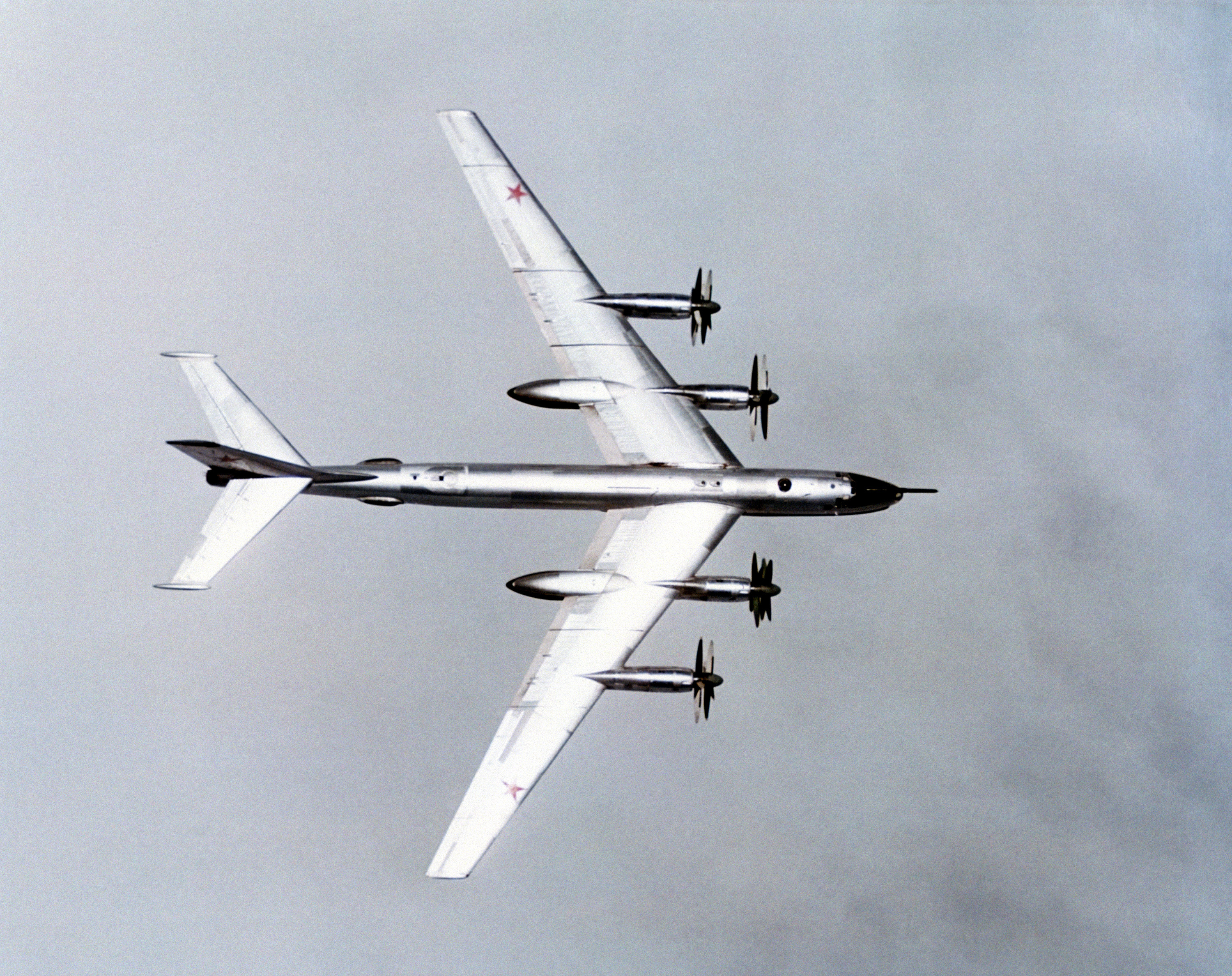
Tu-95
The Tupolev Tu-95 (; NATO reporting name: "Bear") is a large, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the Long-Range Aviation of the Soviet Air Forces in 1956 and was first used in combat in 2015. It is expected to serve the Russian Aerospace Forces until at least 2040. A development of the bomber for maritime patrol is designated the Tu-142, while a passenger airliner derivative was called the Tu-114. The aircraft has four Kuznetsov NK-12 engines with contra-rotating propellers. It is the only turboprop-powered strategic bomber still in operational use today. The Tu-95 is one of the loudest military aircraft, particularly because the tips of the propeller blades move faster than the speed of sound. Its distinctive swept-back wings are set at an angle of 35°. The Tu-95 is the only propeller-driven aircraft with swept wings built in large numbers. Design and development The design bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tu-95 Wingspan
The Tupolev Tu-95 (; NATO reporting name: "Bear") is a large, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the Long-Range Aviation of the Soviet Air Forces in 1956 and was first used in combat in 2015. It is expected to serve the Russian Aerospace Forces until at least 2040. A development of the bomber for maritime patrol is designated the Tu-142, while a passenger airliner derivative was called the Tu-114. The aircraft has four Kuznetsov NK-12 engines with contra-rotating propellers. It is the only turboprop-powered strategic bomber still in operational use today. The Tu-95 is one of the loudest military aircraft, particularly because the tips of the propeller blades move faster than the speed of sound. Its distinctive swept-back wings are set at an angle of 35°. The Tu-95 is the only propeller-driven aircraft with swept wings built in large numbers. Design and development The design bureau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-95LAL
The Tupolev Tu-95LAL experimental aircraft () which flew from 1961 to 1965 was a modified Tupolev Tu-95 Soviet bomber aircraft, analogous to the United States' earlier Convair NB-36H. It was intended to see whether a nuclear reactor could be used to power an aircraft, primarily testing airborne operation of a reactor and shielding for components and crew. The reactor did not actually power the aircraft. Design and development During the Cold War the USSR had an experimental nuclear aircraft program. Without the need to refuel, a nuclear-powered aircraft would have greatly extended range compared to conventional designs. On 12 August 1955 the Council of Ministers of the USSR issued a directive ordering bomber-related design bureaus to join forces in researching nuclear aircraft. The design bureaus of Andrei Tupolev and Vladimir Myasishchev became the chief design teams, while N. D. Kuznetsov and A. M. Lyulka were assigned to develop the engines. They chose to focus on the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-142
The Tupolev Tu-142 (142; NATO reporting name: Bear F/J) is a Soviet/Russian maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) aircraft derived from the Tu-95 turboprop strategic bomber. A specialised communications variant designated ''Tu-142MR'' was tasked with long-range communications duties with Soviet ballistic missile submarines. The Tu-142 was designed by the Tupolev design bureau, and manufactured by the Kuibyshev Aviation and Taganrog Machinery Plants from 1968 to 1994. Formerly operated by the Soviet Navy and Ukrainian Air Force, the Tu-142 currently serves with the Russian Navy. Developed in response to the American Polaris programme, the Tu-142 grew out of the need for a viable Soviet ASW platform. It succeeded the failed Tu-95PLO project, Tupolev's first attempt at modifying the Tu-95 for maritime use. The Tu-142 differed from the Tu-95 in having a stretched fuselage to accommodate specialised equipment for its ASW and surveillance roles, a reinforced und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
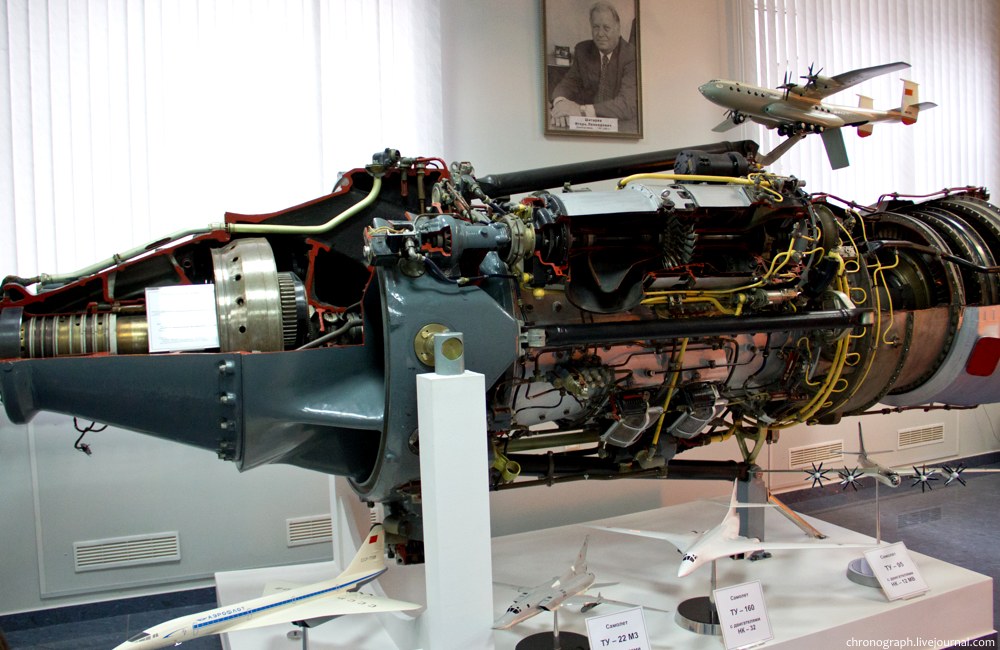
Kuznetsov NK-12
The Kuznetsov NK-12 is a Soviet turboprop engine of the 1950s, designed by the Kuznetsov design bureau. The NK-12 drives two large four-bladed contra-rotating propellers, diameter (NK-12MA), and diameter (NK-12MV). It is the most powerful turboprop engine to enter service. Design and development The design that eventually became the NK-12 turboprop was developed after World War II by a team of Soviet scientists and imprisoned German engineers under Ferdinand Brandner, who had worked for Junkers previously; the design bureau was headed by chief engineer Nikolai D. Kuznetsov. Thus, the NK-12 design evolved from late-war German turboprop studies. This started with the postwar development of the wartime Jumo 022 turboprop design that was designed to develop , weighing . The effort continued with a , weighing , completed by 1947. Evolution to the TV-12 engine required extensive use of new Soviet-developed alloys and was completed in 1951. The NK-12 is the most powerful turbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-114
The Tupolev Tu-114 Rossiya (; NATO reporting name Cleat) is a retired large turboprop-powered long-range airliner designed by the Tupolev design bureau and built in the Soviet Union from May 1955. The aircraft was the largest and fastest passenger plane at that time and also had the longest range, at 10,900 km (6,800 mi). It has held the official title of fastest propeller-driven aircraft since 1960."FAI official database" ''''. Retrieved: 5 September 2007. Due to its |
Contra-rotating Propellers
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers (CRP) coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single engine piston powered or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Although contra-rotating propellers are also known as '' counter-rotating propellers'', the term is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions. Operation When airspeed is low, the mass of the air flowing through the propeller disk (thrust) causes a significant amount of tangential or rotational air flow to be created by the spinning blades. The energy of this tangential air flow is wasted in a single-propeller design, and causes handling problems at low speed as the air strikes the vertical stabilizer, causing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Tupolev
Andrei Nikolayevich Tupolev (; – 23 December 1972) was a Russian and later Soviet aeronautical engineer known for his pioneering aircraft designs as the director of the Tupolev Design Bureau. Tupolev was an early pioneer of aeronautics in Russia and served as a protégé of Nikolay Zhukovsky (scientist), Nikolay Zhukovsky. Tupolev designed or oversaw the design of more than 100 types of civilian and military aircraft in the Soviet Union over 50 years, some of which set 78 world records. Tupolev produced many notable designs such as the Tupolev Tu-2, Tu-2, Tupolev Tu-16, Tu-16, Tupolev Tu-95, Tu-95, and Tupolev Tu-104, Tu-104, and the reverse engineered Tu-4. Tupolev was highly honoured in the Soviet Union and awarded various titles and honours including the Hero of Socialist Labor three times, Order of Lenin eight times, Order of the Red Banner of Labour two times, made an academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1953, and a Colonel-General of the Soviet Air Forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range Penetrator (aircraft), penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombing, tactical bombers, Penetrator (aircraft), penetrators, fighter-bombers, and attack aircraft, which are used in air interdiction operations to attack enemy combatants and military equipment, strategic bombers are designed to fly into enemy territory to destroy strategic targets (e.g., infrastructure, logistics, Military base, military installations, factories, etc.). In addition to strategic bombing, strategic bombers can be used for tactical bombing, tactical missions. There are currently only three countries that operate strategic bombers: the United States, Russia and China. The modern strategic bomber role appeared after Strategic bombing during World War II, strategic bombing was widely employed, and Atomic bombing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev
Tupolev ( rus, Туполев, , ˈtupəlʲɪf), officially United Aircraft Company Tupolev - Public Joint Stock Company, is a Russian aerospace and Arms industry, defence company headquartered in Basmanny District, Moscow. UAC Tupolev is successor to the Soviet Tupolev Design Bureau (OKB-156, Soviet Union military aircraft designation systems#Soviet system after December 9.2C 1940, design office prefix ''Tu'') founded in 1922 by aerospace pioneer and engineer Andrei Tupolev, who led the company for 50 years until his death in 1972. Tupolev designed over 100 models of civilian and military aircraft and produced more than 18,000 aircraft for Russia, the Soviet Union and the Eastern Bloc since its founding, and celebrated its 100th anniversary on 22 October 2022. Tupolev is involved in numerous aerospace and defence sectors including development, manufacturing, and overhaul for both civil and military aerospace products such as aircraft and weapons systems, and also missile and nava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-95 At Victory Day Parade 2008
Tupolev ( rus, Туполев, , ˈtupəlʲɪf), officially United Aircraft Company Tupolev - Public Joint Stock Company, is a Russian aerospace and defence company headquartered in Basmanny District, Moscow. UAC Tupolev is successor to the Soviet Tupolev Design Bureau ( OKB-156, design office prefix ''Tu'') founded in 1922 by aerospace pioneer and engineer Andrei Tupolev, who led the company for 50 years until his death in 1972. Tupolev designed over 100 models of civilian and military aircraft and produced more than 18,000 aircraft for Russia, the Soviet Union and the Eastern Bloc since its founding, and celebrated its 100th anniversary on 22 October 2022. Tupolev is involved in numerous aerospace and defence sectors including development, manufacturing, and overhaul for both civil and military aerospace products such as aircraft and weapons systems, and also missile and naval aviation technologies. In 2006, Tupolev became a division of the United Aircraft Corporation in a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Air Force
The Ukrainian Air Force (, PS ZSU) is the air force of Ukraine and one of the eight Military branch, branches of the Armed Forces of Ukraine (ZSU). Its current form was created in 2004 by merging the Ukrainian Air Defence Forces into the Air Force. When the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991, many aircraft were left in Ukrainian territory. After Ukrainian independence in 1991, the air force suffered from chronic under-investment, leading to the bulk of its inventory becoming mothballed or otherwise inoperable. However its domestic defense industry Ukroboronprom and its Antonov subsidiary are able to maintain its older aircraft. The Ukrainian Air Force participated in the War in Donbas (2014–2022), war in Donbas. Following the 2014 ceasefire, the air force was suspended from carrying out missions in the areas of Donbas. Since February 2022, the Air Force has been engaged in constant combat operations in the face of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The air force flies General Dynam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-116
The Tupolev Tu-116 () is a turboprop-powered long-range airliner designed by the Tupolev design bureau and built in the USSR. Development The Tu-116, like the Tu-114, was based on the Tu-95 strategic bomber. Both airliners were developed in parallel with the Tu-116 taking priority due to the numerous visits of General Secretary Nikita Khrushchev to both Western and Eastern countries during the so-called Khrushchev Thaw The Khrushchev Thaw (, or simply ''ottepel'')William Taubman, Khrushchev: The Man and His Era, London: Free Press, 2004 is the period from the mid-1950s to the mid-1960s when Political repression in the Soviet Union, repression and Censorship in .... The aircraft's mission was to transport the head of state together with his security detail and entourage. Concurrent development of the Tu-114 and Tu-116 was justified by Khrushchev's visit to the United States, at which time the Tu-114 might not have been ready. Initially, the airliner was to be developed very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |