|
True's Shrew Mole
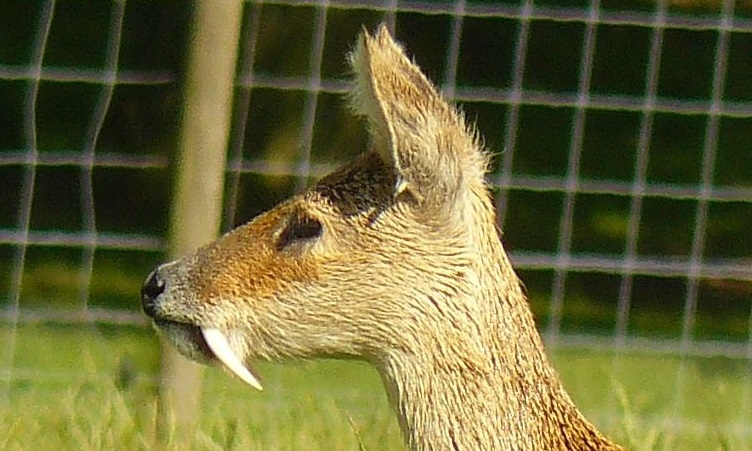
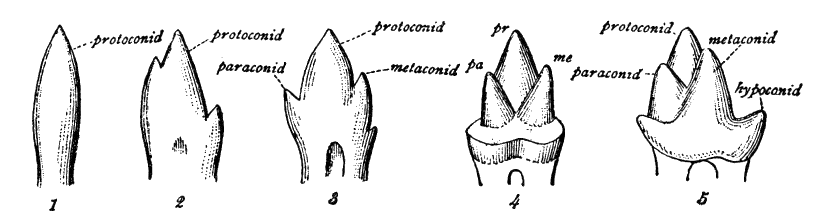
True's shrew mole (''Dymecodon pilirostris'') is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to Japan (Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu) and is a common species above 1000 meters in grassland, shrubland and forest. Sometimes this species is called the lesser Japanese shrew mole and another species, '' Urotrichus talpoides'', is called the "greater Japanese shrew mole". It is the only species in the genus ''Dymecodon''. It has sometimes been considered belonging to the genus '' Urotrichus''. Etymology The genus name is the compound of δύο () "two", μήκος () "size", and όδούς () "tooth", so "two size teeth", because of the alternation in size of the teeth in the lower jaw. Description ''D. pilirostris'' is a mole resembling the Japanese shrew mole, with a head-body length of about 6½ cm covered in thick, 5 mm long, darkbrown fur with a strong greenish metallic lustre, and a tail of about 3½ cm, covered with dark hair of about 7 mm. The pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick W
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Given name Nobility = Anhalt-Harzgerode = * Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) = Austria = * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans = Baden = * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden = Bohemia = * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia = Britain = * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain = Brandenburg/Prussia = * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urotrichus
''Urotrichus'' is a genus of talpid that contains a single living species, the Japanese shrew mole ''(Urotrichus talpoides)''. Two fossil species ('' Urotrichus dolichochir'' and '' Urotrichus giganeus'') are also known. ''Urotrichus talpoides'' is also known from the Late Pleistocene of Japan, while ''U. giganteus'' is known from the Miocene of Austria, ''U. dolichochir'' from the Miocene of Germany, Poland and Slovakia, and an unidentified species from the Miocene of Greece. The genus may be descended from the structurally-similar Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ... species '' Tenuibrachiatum storchi'', which shares features such as a slender humerus and a missing lower incisor. References Talpidae Mammal genera Mammal genera with one living speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Mammals Of Japan
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more flattened, however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called ''incisiform''. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two upper maxillary canines and the two lower mandibular canines. They are specially prominent in dogs (Canidae), hence the name. Details There are generally four canine teeth: two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Terminology Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed '' polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Shrew Mole
The Japanese shrew mole (''Urotrichus talpoides'') or is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to Japan and is found on Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, Awaji Island, Shodo Island, Oki Islands, Tsushima Island, Goto Islands, Mishima Island (Yamaguchi Prefecture), and Awashima Island (Niigata Prefecture), but is absent from Hokkaido, which is north of Blakiston's Line. It is one of three Urotrichini and it is the only extant species in the genus ''Urotrichus''. It is common between sea level and approximately 2,000 m. Sometimes this species is called the greater Japanese shrew mole and another species, True's shrew mole, is called the "lesser Japanese shrew mole". The species is an omnivore, but their diet is largely composed of invertebrates and plants, which is why they tend to inhabit soil that is nutrient-rich. Heinrich Bürger, assistant of Philipp Franz von Siebold, collected specimens of ''Urotrichus talpoides'' near Dejima between 1824 and 1826, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The United States National Museum
The Smithsonian Contributions and Studies Series is a collection of serial periodical publications produced by the Smithsonian Institution, detailing advances in various scientific and societal fields to which the Smithsonian Institution has made contributions. History The Smithsonian Institution began publishing consolidated compilations of quarto-sized papers in 1848, under the name ''Smithsonian Contributions to Knowledge''.History of Scholarly Publishing , ''''. In 1862 -sized papers called ''Smithsonian Miscellaneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |